![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ear consists of:
|
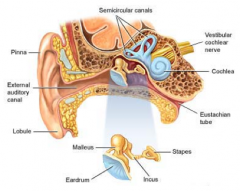
- External
- Middle - Internal |
|
|
External ear and internal ear is separated by the...
|
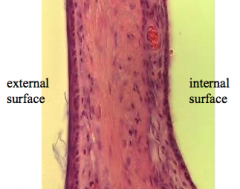
tympanic membrane
|
|
|
Tympanic membrane is derived from:
|
Ectoderm
Mesoderm Endoderm |
|
|
Middle ear consists of:
|
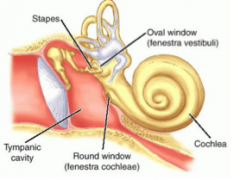
1. Ossicles ‑ malleus, incus, stapes
2. Muscles ‑ tensor tympani (CN V), stapedius (CN VII) 3. Oval window, round window |
|
|
Internal ear is composed of...
|
- two labyrinths
1. The bony labyrinth -series of spaces inside the petrous part of the temporal bone. 2. Membranous labyrinth (found within the bony labyrinth) |
|
|
Bony labyrinth is filled with ...
|
the perilymph (ExtraCellular Fluid)
|
|
|
The bony labyrinth is made up of:
|
1. Vestibule- Housing saccule and utricle
2. Semicircular canal- Housing semicircular ducts 3. Cochlea- Contains cochlear duct (scala media) |
|
|
and the membranous labyrinth is filled with ...
|
endolymph (IntraCellular Fluid)
|
|
|
The membranous labyrinth is also called...
|
= Cochlear duct
= Scala media |
|
|
Cochlea contains...
|
- cochlear duct (scala media)
- Makes two and one half turns around a bony core called modiolus |
|
|
The spiral ganglion lies in the ...
|
Modiolus
|
|
|
Extending laterally from the modiolus is a thin bony ridge called the...
|
osseus spiral lamina
|
|
|
The cochlear duct subdivides the perilymph filled cochlea into:
|
the superiorly located scala vestibuli
& the inferiorly placed scala tympani |
|
|
What are the two scalae ?
|
(tympani & vestibule)
-one long tube They communicate at the apex of the cochlea through an opening called helicotrema |
|
|
the Spiral organ of Corti consists mainly of:
|
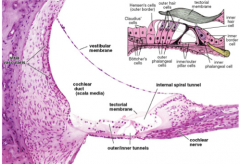
PHP
- phalangeal cells - Hair cells - pillar cells |
|
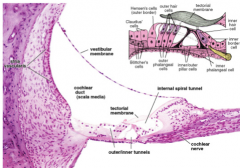
slide of cochlear duct
|
.
|
|
|
Features of the Cochlear Duct:
|
- Presence of stereocilia.
- Tips of these hair cells embedded in tectorial membrane. - Pillar cells occupies region between inner and outer hair cells thus, forming the inner tunnel. - contains spiral ganglion |
|
|
Cochlear duct fx:
|
This structure is important in sound transduction.
|
|
|
Cochlear duct (membranous labyrinth) contains...
|
spiral organ of Corti which lies on the basilar membrane
|
|
|
Histological features of the cochlear duct:
Vestibular membrane separates... |
the scala media from the scala vestibule.
|
|
|
Stria vascularis is responsible for
|
the ionic composition of the endolymph.
|
|
|
The organ of Corti (receptor for hearing) contains
|
neuroepithelial hair cells -rests on the basilar membrane.
|
|
|
Supporting cells and two types of hair cells can be distinguished as...
|
outer and inner hair cells
|
|
|
Sound comes from...
|
- OVAL WINDOW SETS UP SOUND WAVES WITHIN COCHLEA
- SOUND WAVES causes VIBRATION OF THE ORGAN OF CORTI |
|
|
Basillar membrane VS. Tectorial membrane
|
BASILLAR MEMBRANE IS MORE ELASTIC THAN THE TECTORIAL MEMBRANE
|
|
|
Vibration of the basillar membrane causes...
|
the hair cells to bend by a shearing force as they push against the tectorial membrane
--> which in turn causes firing of the cochlear nerve |
|
|
Internal ear consists of...
|
Saccule and Utricle
Semicircular ducts |
|
|
Saccule / Utricle are responsible for..
|
Linear acceleration
|
|
|
Saccule / Utricle consist of...
|
Macula, Neuroepithelial (hair) cells, and Otoliths
|
|
|
Semicircular ducts are important in...
|
Angular acceleration + motion
|
|
|
Semicircular ducts consist of...
|
Cristae ampullares
Neuroepithelial (hair) cells Cupula |

