![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What controls the process of DNA replication? |
Enzymes |
|
|
What are enzymes ? |
A class of proteins that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions |
|
|
What enzyme is in control of the unwinding and separating of the two strands of DNA? |
Helicase |
|
|
How does helicase unwind the DNA? |
Travels along the DNA backbone catalysing reactions that break the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs |
|
|
How do the free nucleotides bond with the newly exposed bases ? |
DNA polymerase catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds |
|
|
What causes a mutation? |
Replication error in newly stranded DNAs |
|
|
What is meant by the term genetic code? |
DNA codes for a sequence of amino acids |
|
|
What is the leading strand also known as? |
5’ |
|
|
What is the lagging strand also known as ? |
3’ |
|
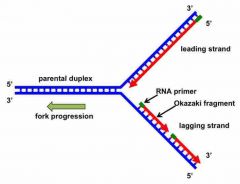
How does DNA polymerase work? |
-only travels in the 3’ to the 5’ direction -only leading strand can Be continuously replicated -and the lagging strand has to be replicated in the opposite direction in SHORT SECTIONS called Okazaki fragments |
|
|
What is meant by the term Okazaki fragments? |
It’s when the lagging strand of the DNA has to be replicated in the opposite direction in short sections |
|
|
What is meant by the term triplet code? |
The code in the base sequence |
|
|
What is meant by the term codon? |
A sequence 3 bases. (Each codon codes for an amino acid) |
|
|
What is a gene? |
A section of DNA that contains the complete sequence of bases (codons) to code for an entire protein |
|
|
What is meant by the term degenerate code? |
More codons than amino acids therefore many amino acids can be coded for by more than one codon |

