![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define fertile:
|
PRODUCE healthy sperm to fertilize an egg
|
|
|
Define potency:
|
Ability to ENGAGE in copulation
|
|
|
Testicular degeneration refers to...
|
a reduction in FUNCTIONALITY.
|
|
|
Causes of testicular degeneration (REDUCTION in sperm production):
|
Thermal (local & systemic infections → pyrexia)
Cryptorchidism (congenital lesion) |
|
|
How may pyrexia from local & systemic infections affect the testicles?
|
May result in CELL DEGENERATION → abnormal sperm morphology & function.
|
|
A condition characterized by the failure of one/both testis to descend to the scrotum & may be located in abdomen/inguinal canal
|
Cryptorchidism
|
|
|
Cryptorchid animals are prone to ___ & ___ of spermatic cord.
|
Testicular neoplasia/Torsion
|
|
|
An inherited testicular degeneration in BULLS
|
Testicular Hypoplasia
|
|
|
Estrogenic compounds/excessive endogenous estrogen production (neoplasia) may lead to
|
CHEMICAL testicular degeneration.
|
|
|
If sperm MORPHOLOGICALLY NORMAL but malfunctioning then it suggests it is a ___ issue.
Spem morphological abnormalities are often due to ___ or ___. |
Gene/Infection or heredity
|
|
|
Inflammation of the testes (___) is often due to ___ or ___.
|
Orchitis (acute/chronic)/Trauma or Infection (local/systemic)a
|
|
|
What BACTERIA have predilection sites at testes?
|
· Brucella
· Pseudomonas · Mycobacteria · Nocardia BMPN the testes |
|
|
What VIRUSES have predilection sites at testes?
|
· Canine Distemper Virus
· Equine Viral Arteritis · Equine Infectious Anemia |
|
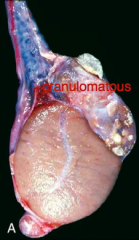
Sterility (problem with POTENCY) relates to...
|
· Tubular damage (inflammation)
· Bacterial toxins/cytokine production · ↑Temperature · Pressure atrophy/necrosis · Pus mixed with ejaculate Duct blockage (due to fibrosis) |
|
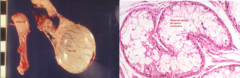
Foreign body inflammatory reaction to SPERM (foreign) which may have escaped the tubular structures OR inflammatory cells may have infiltrated due to damage.
|
Sperm Granuloma (seen in epididymis, seminal vesicles, prostate)
|
|
|
NEOPLASIA (may be bilateral) may be a ___ post-mortem finding, may cause ____ of the testicles, and may cause ___-induced abnormalities.
|
Incidental/Enlargement/Hormonal
|
|
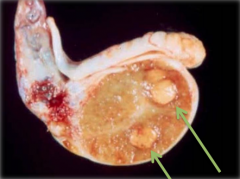
What is the most common NON-FUNCTIONAL testicular neoplasm in dogs (occasionally seen in the bull)?
|
Interstitial Cell Tumors (Leydig Cell Tumor): may be ***BILATERAL***
|
|
|
Leydig Cell Tumors (***usu. <1 cm*** & well-demarcated) are derived from ___ cells of the intersitium, are often ____ post-mortem findings, and malignancy is very ___.
|
Endocrine/ Incidental/Rare
|
|
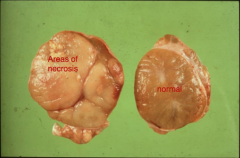
What other NON-FUNCTIONAL tumor is NEARLY AS COMMON as Interstitial Cell Tumors (Leydig Cell Tumor) and generally ENLARGES the testis?
|
Seminoma (Tumor of spermatogonia/ germ cells): usu. ***UNILATERAL***
|
|
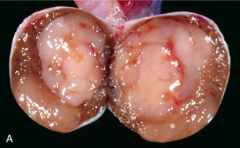
You find a mass that is ENLARGING the testicles, PALE, and ***SOFT***, what is your diagnosis?
|
Seminoma (RARELY metastatic)
|
|
|
Cryptorchidism is a PREDISPOSING FACTOR for what neoplasms?
|
Seminoma
Sertoli Cell Tumor |
|
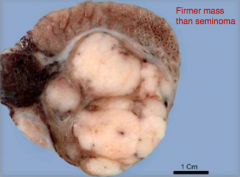
What FUNCTIONAL (produces estrogen) tumor is the LEAST COMMON and generally ENLARGES the testis?
|
Sertoli Cell Tumor: usu. ***UNILATERAL***
|
|
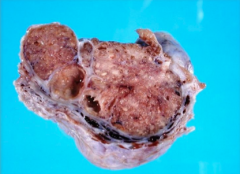
You find an ESTROGEN producing mass that is ENLARGING the testicles, WHITE, and ***FIRM***, what is your diagnosis?
|
Sertoli Cell Tumor
|
|
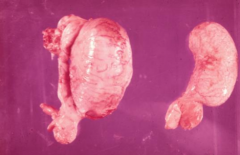
What are the effects related to the estrogen-producing Sertoli Cell Tumors?
|
· Atrophy of NON-NEOPLASTIC testicular tissue
· Mammary gland & teat enlargement · Reduced libido · Swelling of prepuce · Attractive to other male dogs · SYMMETRICAL ALOPECIA · Prostatic hyperplasia & metaplasia · BM suppression |
|
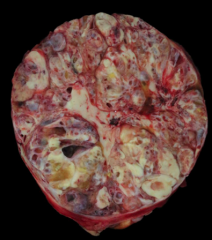
Rare tumor in young horses composed of multiple germ layers (connective tissue, bone, cartilage, m., n., glandular, hair & dental)
|
Teratoma
|
|
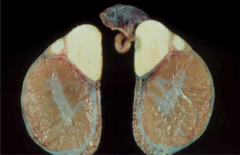
Term used to describe an OCCLUDED epididymis (due to inflammation/congenital) → SPERM ACCUMULATION.
|
SpermATOCOELE
|
|
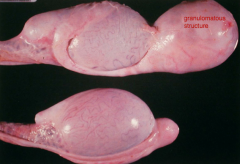
Epithelial damage of the epididymis leads to a...
|
Sperm Granuloma
|
|
|
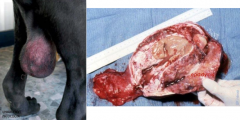
Most of the time fat becomes trapped BUT intestines may become trapped as well in the parietal peritoneum. What is the picture depicting?
|
Scrotal hernia
|
|
|
Hemorrhage in the TUNICA VAGINALIS:
|
HemATOCELE
|
|
|
Serous fluid in the TUNICA VAGINALIS:
|
HydroCELE
|
|
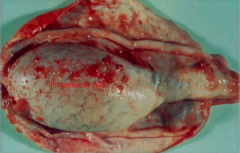
INFLAMMATION of the TUNICA arises from..
|
direct extensions from:
Orchitis Epididymitis Scrotal dermatitis PERITONITIS |
|
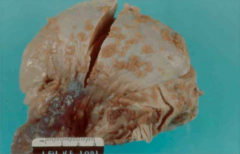
Tumors cells surrounding the peritoneal cavity
|
Mesothelioma
|
|
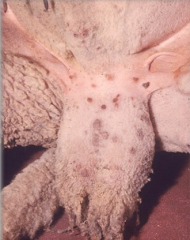
Multifocal red-brown papules on a rams scrotum.
|
Sheep pox
|
|
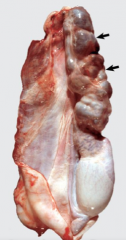
DILATION and TORTUOSITY of the veins of the pampiniform plexus and cremasteric veins
|
VaricoCELE
|
|
|
Common neoplasms on the scrotum on a dog
|
Mast Cell Tumor/Hemanioma
|
|
|
PROSTATIC ATROPHY (reduction in organ size, cell numbers, & acinar structures) often occurs as a ___ change & following ___.
|
Senile/Castration
|
|
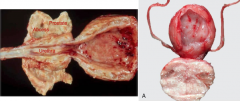
An EXTREMELY PAINFUL condition that causes dogs to feel like they have to defecate more BECAUSE PRESSING ON COLON.
|
Prostatic Inflammation
|
|
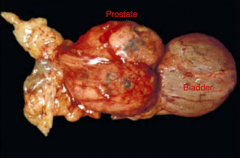
A common PAINLESS occurrence in INTACT males that causes them to feel like they have to defecate more BECAUSE PRESSING ON COLON.
|
Prostatic Hyperplasia (Proliferation of stroma with multiple cyst formation)
|
|
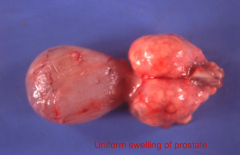
Prostatic hyperplasia is often due ___ imbalances and size of prostate can be reduced by ___.
|
Hormonal/Castrating
|
|
|
Prostatic metaplasia (columnar epithelial cells → squamous) is caused by the hormone ___ which is often from ___ OR ___ (iatrogenic).
|
Estrogen/Sertoli Cell Tumors/Estrogen administration
|
|
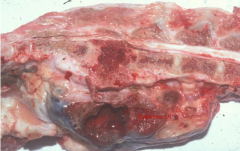
What neoplasm is RARE in dogs but metastasizes to SUBLUMBAR LN, lungs, liver, bone?
|
Adenocarcinoma originating from PROSTATE
|
|
|
What can EARLY castration or INTERSEX conditions cause?
|
Penile Hypoplasia
|
|
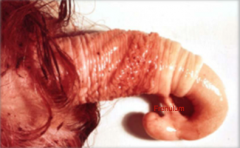
Developmental disorder often seen in BULLS where the ventral PENIS is connected to the PREPUCE causing penile deviation.
|
Persistent Frenulum
|
|

A congenital abnormality that causes failure of fusion of the urethra, prepuce, and scrotum resulting in a nonfunctional, caudoventrally deviated and exposed penis with a nonfused prepuce
|
Hypospadia
|
|
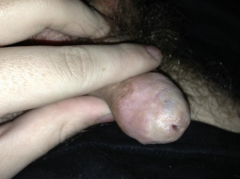
NARROWING of the preputial orifice preventing PROTRUSION of penis
|
Phimosis
|
|
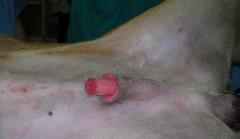
NARROWING of the preputial orifice preventing RETRACTION of already protruding penis
|
Paraphimosis
|
|
|
Inflammation of PREPUCE
|
Posthitis
|
|
|
Inflammation of GLANS PENIS
|
Balanitis (Ball of penis)
|
|
|
Inflammation of PREPUCE & GLANS PENIS
|
Balanoposthitis
|
|
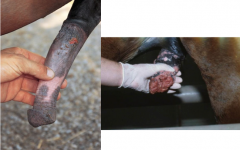
1. Viruses that cause BALANOPOSTHITIS:
2. Bacteria that cause BALANOPOSTHITIS: 3. Parasites that cause BALANOPOSTHITIS: |
1. Bovine Herpesvirus-1, Equine Herpesvirus-3 [L]
2. Corynebacteria in SHEEP/BOVINE 3. Trypanosoma equiperdum, Habronemiasis [R] |
|
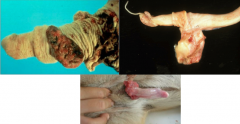
Neoplasm on penis of Ruminant:
Neoplasm on penis of Horse: Neoplasm on penis of Dogs: |
1. Fibropapilloma [Top L]
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma [Top R] 3. Transmissible Veneral Tumor [Bottom C] |

