![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define the following:
1. Chorion: 2. Allantois: 3. Amnion: 4. Amniotic plaques: |
1. Layer that contacts the mother (fused with allantois = chorioallantois/allantochorion)
2. Contains FETAL urine & other fluids arising from membrane. 3. Surrounds the fetus & holds amniotic fluid 4. Foci of squamous epithelium on INTERNAL surface of amnion. |
|
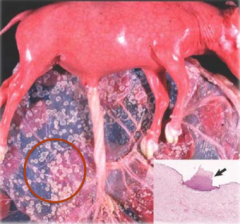
Identify the structures that are indicated by the red circle.
|
Amniotic plaques
|
|
|
Define the following:
1. Abortion: 2. Stillbirth: 3. Mummification: |
1. Expulsion of fetus PRIOR to time of EXPECTED VIABILITY
2. DEATH of fetus in the last part of gestation during the period where IT IS INDEPENDENTLY VIABLE 3. Fetus RETAINED indefinitely & becomes dehydrated |
|

What process occurred with this fetus?
Process: |
Process: Mummification (dehydration of fetus in utero)
|
|
|
Causes of mummification in...
1. Horses: 2. Cattle: 3. Dog: 4. Cat: 5. Sow: |
1. Twining
2. Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD virus) 3. Canine Herpesvirus 4. Uterine horn torsion 5. Parvoviral infection |
|
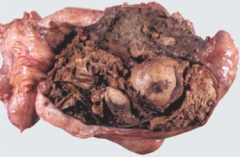
Name this lesion, what is it associated with, and what may be a consequence of it?
Name: Association: Sequela: |
Name: Maceration
Association: Dystocia/incomplete abortion infected by bacteria Sequela: Pyometra or maternal death (from peritonitis & toxemia) |
|
|
Placental insufficiency (important in the mare) may occur in cases of:
(5 causes) |

Twinning
Endometrial fibrosis Uterine body pregnancy Premature placental separation (short umbilical cord) Torsion of umbilical cord |
|
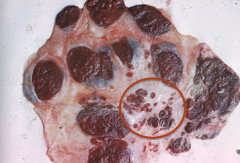
In this placenta, several big cotyledons are evident and these are normal. In addition, there are some smaller scattered areas where NEW cotyledonary type tissue has formed. Name this occurrence and why does it occur?
Name: Reason behind it: |
Name: Adventitial Placentation.
Reason behind it: COMPENSATION MECHANISM for inadequate development of placentomes. |
|
|
Define the following:
1. Hydramnios & association: 2. Hydrallantois & association: |
1. Excessive accumulation of fluid in the amniotic sac.
Associated with malformation of the fetus 2. Excessive accumulation of fluid in the allantoic sac. Associated with uterine disease → inadequate #'s of caruncles → adventitial placentation |
|
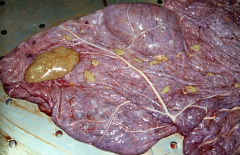
Identify the structures and their significance.
Structures: Significance: |
Structures: Hippomane
Significance: Incidental (proteinaceous soft calculi, aggregated mineral & organic allantoic concrements) |
|
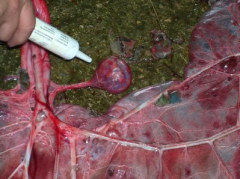
Identify the structure and its significance.
Structure: Significance: |
Structure: Yolk sac remnant
Significance: Incidental |
|
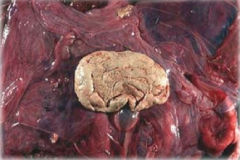
Identify the structure and its significance.
Structure: Significance: |
Structure: Hippomane
Significance: Incidental |
|
|
When do we submit aborted bovine fetuses for diagnostic evaluation?
|
・When abortion rate exceeds 3%
・When a # of animals abort over a short period of time |
|
|
Myocardial lesions on aborted calf, we are thinking:
|
Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD)
Neospora caninum Nutritional myopathy |
|
|
1. Dermatitis on aborted calf, we are thinking:
2. Focal necrosis in the liver/other tissues on aborted calf, we are thinking: |
1. Mycotic abortion
2. Herpesviral infection |
|
|
EARLY embryonic deaths & an important cause of infertility in cattle.
Gross placental lesions: intercotyledonary placentitis & necrosis of the cotyledons |
Campylobacter foetus ssp. venerealis
|
|
|
Causes embryonic deaths & can be found in preputial washes, vaginal mucus, & in cases of abortion, in STOMACH CONTENTS of the fetus
|
Tritrichomonas foetus
|
|
|
LATE term abortion more common (7-9 mths) & ***ZOONOTIC***
Gross placental lesions: intercotyledonary placentitis & necrosis of the cotyledons |
***Brucella abortus***
|
|
|
LATE term abortion more common (last trimester)
Gross lesions: AMNION is the most severely affected (amnionitis) |
Ureaplasma diversum
|
|
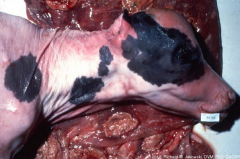
Dermatitis in the aborted fetus, what is our Dx?
Dx: |
Dx: Mycotic abortion
|
|
|
1. Viral etiology for arthrogryphosis (curly calf syndrome) in aborted calf.
2. Viral etiology for cerebellar hypoplasia in aborted calf |
1. Akabane virus
2. Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD) |
|
|
MOST COMMON cause of abortion in SHEEP
Gross placental lesions: intercotyledonary placentitis & multifocal necrotizing HEPATITIS in fetus |
Campylobacter foetus ssp. foetus
|
|
|
Cause of IN UTERO infection in SHEEP & GOATS → abortion, stillbirth, & birth of weak offspring & is ***ZOONOTIC*** .
Gross placental lesions: acute suppurative-chronic placentitis |
Chlamydophila abortus (Ovine enzootic abortion/Enzootic abortion of ewes)
(Infected early in gest → abort during SAME gest; Infected late in gest → abort during NEXT pregnancy) |
|
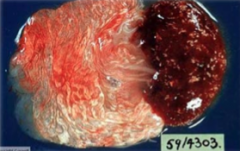
MAJOR ROLE in ovine abortion & source is usually infected CATS.
Gross placental lesions: cotyledons are bright-dark red with numerous small soft white nodules |
Toxoplasma gondii
|
|
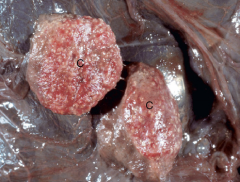
Infection of cotyledon resulted in abortion. What caused this abortion and "strawberry-like" lesions?
|
Toxoplasma gondii
|
|

Results in early abortion, or the surviving lamb being undersized with an excessively hairy fleece.
|
Border disease (Hairy shaker disease)
|
|
|
The MOST COMMON cause of LATE term abortion in GOATS & is ***ZOONOTIC***.
Gross placental lesions: acute diffuse suppurative placentitis |
Coxiella burnetti
|
|
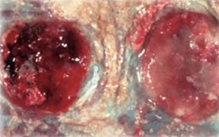
Multifocal-confluent areas of mineralization, exudate is copious, off-white & most obvious in the intercotyledonary region.
Dx: |
Coxiella burnetii (acute diffuse suppurative placentitis)
|
|
|
About 1/2 of abortions in horses can be determined by direct examination of the ____ & ____.
|
Placenta/Umbilical cord
|
|
|
1. Umbilical cords in mares should be between ___ cm long.
2. Longer cords result in ___ 3. Cords less than ___ cm may result in ___. |
1. 36-83 cm
2. Strangulation 3. Placental insufficiency (premature separation) |
|
|
Mare Reproductive Loss Syndrome (MRLS) & Late-term abortions are often caused by the ___.
|
Eastern Tent Caterpillar
|
|
|
Causes LATE-term (last 3 months) abortion in mares with prominent △'s in the fetus:
・Fibrin cast in trachea ・Interstitial pneumonia (die in first few days) ・Focal necrosis of liver ・Lymphoid follicles in spleen |
Equine Herpesvirus-1
|
|
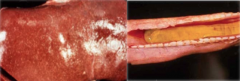
Necropsy of an aborted foal presents the following:
Focal necrosis of liver Fibrin cast in trachea Dx: |
Equine Herpesvirus-1
|
|
|
Abortion in pigs at 2-3 month of pregnancy (EARLY)
High incidence of STILLBORN/weak piglets at term |
Brucella suis
|
|
|
Stillbirths, Mummification, Embryonic death, Infertility complex (SMEDI)-type problems in pigs is mainly caused by ___.
|
Porcine parvovirus
|
|
|
Pregnancy failure in dogs/cats worry about ___ because zoonotic.
|
Brucella canis (abort after 30d)
|

