![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
117 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Someone who feels sad and then happy goes and buys a bunch of stuff what drug would you want to tx them with?
|
you would want to give an anti-psychotic (lithium, carbamazepine, & valproate)
|
|
|
What drug can you use for simple, complex partial seizures, bipolar disorder, & trigeminal neuralgia
|
carbamazepine
|
|
|
this drug treats tonic-clonic seizures, mood disroders, and if preggo can cause neural tube defects
|
valproate
|
|
|
someone has a tremor and they blame it on the voice in there head what can you give to treat this?
|
probabaly drug-induced Parkinson's caused by an anti-psychotic, give them an anti-muscarinis "park your mercedes- benz" benztropine
|
|
|
what kind of drug is paroxetine?
|
serotonin-reuptake inhibitor makes manic worse
|
|
|
Bupropian is what
|
dopamine and NE re-uptake inhibitor, used for depression and stopping smoking
|
|
|
PCA supplies which regions of the brain
|
comes off the basiliar at pontomesocephalic junction supplies the thalamus, tedial temporal lobe, splenium of corpus callousoum, para hipo gyrus, fusiform gyrus, & occiptal lobe
|
|
|
anterior chordate artery supplies
|
is last branch of internal carotid before trifurcation, post limb, gen of internal capsule, optic tract, lateral geniculate body, choroid plexus, uncux, hippocampas, & amygldala
|
|
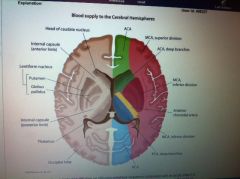
|
good pic to know
|
|
|
Strict diets to lose weight devoid of a vitamine is likely?
|
think vegan- B12 cobalamin, causes megaloblastic anemia..take years to see a problem bc tons in the hepatic storage
|
|
|
Most water soluble vitamins flush out the body
|
FAST except for cobalamin & folate
|
|
|
tibial hematomoa & painful gums in a 79 yo poor woman your thinking?
|
Vit C defieicieny, ascorbic acid- from fruits (poor homeless ppl wont have that) scurvy: hemorrhage, subperiosteal hematoma, bleed, gingivial swelling
also important to hydroxylase prolyl and lysyl--> precollagen |
|
|
Folic acid deficicney you would see
|
megaloblastic anemia & neural tube deficients
|
|
|
Zinc deficiency you would seee
|
growth retardatsion/infertility and acrodermatitis
|
|
|
2 mutatnt strains no problem, but together they make progeny that becomes virulent this describes
|
recombination (genetic) 2 viruses must exchange genes for their progeny to change that much
|
|
|
host cell co infected and they exchange whole genome, sudden change describes?
|
reassortment
|
|
|
Uptake of naked DNA in prok/euk describes?
|
transformation
|
|
|
inhibition one virus replication and release describes?
|
interference
|
|
|
describe how morphine works
|
activates mu opiod receptors, which is a G-protein linked so has many secondary messengers...K+ conductance increase the efflux so you hyperpolarize and terminate pain, close Ca2+
|
|
|
immigrant with fever, rash, face travels to body and lyphadenopathy behind the ears
|
thinking no vaccine for measle, mumps, rubella, rubella presents with a rash, face--> trunk/extremities...fast spread- no darkening, lymphadenopathy is rubella too which is caused by togavirus!
|
|
|
bean-shape bacteria appears in an army person how did he get this?
|
nasopharynx--> blod--> choroid plexus--> meninges transmit by respiratory droplets
|
|
|
polydraminiosis appears in pregnant lady what are the likely causes
|
Gi obsturction (duodenal, esophageal, intestinal atresia) or anencephaly
|
|
|
What is seen with a baby in the womb w renal agenesis?
|
severe oligohydromanisos ( too low) potter's syndrome
|
|
|
Normal thryoid gland exists in anterior neck lower in fron of the upper trachea & larynx...thyroid gland is an outpouch that descends- remaining forms the
|
thyroglossal duct
|
|
|
What happens if the thyroid fails to migrate?
|
you form thyroid in the tongue "linguial thyroid" or "thyroglossal duct"
|
|
|
What should surgeons be catious of when removing a thyroglossal cyst
|
it may be the only thyroid hormone a child so can cause severe hypothyroidism
|
|
|
Common signs of 3 mo old w hypothyroidism
|
dry skin, constipated, mass appears in throat, hard to swallow, Macroglossia,
|
|
|
foramen cecum t is a normal remenant of what
|
thyroglossal duct
|
|
|
Failure of GnRH to migrate from olfactory is
|
kallman's syndrome
|
|
|
tested fail to migrate to scrotum is
|
cryptorchidism
|
|
|
What does sensitivity measure?
|
#True (+)/ patients w dz. (TP+FP)
ability of test to tell who has the disease good for illnesses that are severe or can be prevented w early tx |
|
|
What is sepcficity?
|
more expensive, and how much the test can detect a true negative, TN(TN+FP)
confirmatory test after a + test is seen |
|
|
3 ways to get Down Syndrome?
|
1. trisomy 21 -95% cases, meiototis nondisjunction failure of homologous chrom to seperate (always maternal)
2. unbalanced robertsonian translocation- 2-3% DS, 46 chromosome an extra chrom 3. mosaicism: patient has 2 cell lines one normal and one with DS |
|
|
genetic imprinting and partial deletion are example for which disease
|
prader-willi and angelman
|
|
|
uniparental disomy is what and give an example
|
2 copies from one parent and none from the other--> complete hyatidform mole
|
|
|
21 yo fasting w jaundice and an increased amount of unconjugated bilirubin is
|
gilber-syndrome
|
|
|
what happens with gilbert syndrome
|
you decrrease UDP glucornyl transferase or decr in bilirubin uptake, increasing inconjugated amount and usually onset w stress/fasting
|
|
|
What is AST:ALT in an alcholic w hepatitis
|
2:1
|
|
|
What is AST/ALT in a person w viral hepatitis
|
ALT>AST
|
|
|
What is suppression?
|
mature defense mechanisms, voluntarily withholding an idea or feeling from conscious awareness ( not thinking about boards till later)
|
|
|
What is repression?
|
involuntary withholding an idea or feeling from conscious awareness- rape forget about it until see it on tv
|
|
|
what is humor?
|
appreciating the amusement nature of anxiety making it light
|
|
|
Describe altruism
|
guilty feelings are alleviated with generosity towards others
|
|
|
What is isolation
|
describing a hard time w no emotion connection, seperate feelings from a horrible event
|
|
|
what is the only class of antibody that crosses the placenta?
|
IgG
|
|
|
some dopamine drugs block the interfindibular area what would this cause in a patient?
|
galactorrhea & lacrimation, heavy breasts, sexual dysfunction
|
|
|
which hormones use the JAK/STAT pathway
|
GH & prolactin!
|
|
|
mutation of germline RET effects?
|
adrenal medulla (pheochromoctyoma) parathyroid (3/4th pharyngeal pouch), & parafollicular cells derived from neural crest cells (4t/5th pouches)
|
|
|
MEN are unique because
|
all derived from neural crest cells, remember MEN 2A= parathyroid, pheochromocytoma, & medullary thyroid cancer (parafollicular C Cells)
MEN 2B= pheochromocytoma & oral mucosa & medullary thyroid cancer |
|
|
Decribe the role of histones in Huntington's Disease
|
hypermethylated histones bind to DNA and prevent transcription and production of neurotrophic factors
|
|
|
What ae histones?
|
small proteins complex with DNA make some genome unavailable for transcription
|
|
|
adrenal cortex develops from the
|
mesoderm
|
|
|
adrenal medulla develops from the
|
ectoderm (neural crest cells)
|
|
|
Whats the genetic inheritance for sickle cell anemia
|
autosomal recessive
|
|
|
erythrocytes get their energy with which 2 pathways
|
glycolysis and shunt (HMP)
HMP- makes NADPH to prevent damage & G6PD is the rate-limiting enzyme in this reaction |
|
|
How is hydrogen peroxide reduced in RBC?
|
with glutathione peroxidase and oxidizes with glutathion and regnerated which produces one NADPH
|
|
|
So which 2 mechanisms would present with problens in RBC?
|
G6PD deficiency
glutathione (wouldn't make NADP& glutathione) increase amount of damage |
|
|
RMP at -70 mantained by
|
a lot of K+ conductance and some Na+ conductance
K= -80 mV Na= +60 mV |
|
|
Pt presents with reduced vision in the R eye, and exam shows R. hemanymous hemaniopa, with direct light on R pupil dilates, but indirect it constrict whats the likely area injured
|
optic tract
|
|
|
what is hemanymous hemaniopa
|
vertical loss of vision on same side in both eyes
|
|
|
if it was a lateral geniculate nucleus lesion what would you see
|
contralateral homonymous hemaniopa but pupil reflex would be intact
|
|
|
why does the marcus-gun pupil form with optic tract lesion
|
because this is a combination of nasal & temporal fibers going to the back and the nasal carries pretectal nucleus fibers to pupil
|
|
|
what would visual cortex lesion present with
|
contralateral homonymous hemaniopa w macula sparing but light reflex would be normal
|
|
|
pt w lesion under arm, seizures, and history of that mom had skin cancer what embryological derivative did the lesion develop from?
|
neural crest cells, melanoma is the 3rd common cancer to mestastize to the brain
|
|
|
name the order of common metastasis to the brain
|
lung, breast, melanoma
|
|
|
where do mealnocytes come from?
|
neural crest cells
|
|
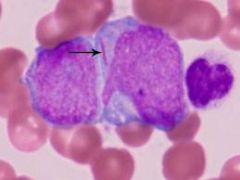
50 yo presents w this and recurrent gum bleeding what are you thinking?
|
Aeur rod, AML (M3 AML) accumulate myeloblasts in Bone marrow..stain with MPO..crystals aggregate= auer rods
|
|
|
Which chromosomes characterize acute promyelocytic leukemia
|
t (15;17) the translocation of the retinoic acid RAR on chrom 17 to chrom 15, RAR disruption blocks maturation of& promyelocyts accumulate...numerous primary granules incr DIC tx: trans-retinois acid
|
|
|
describe conversion disroder
|
sudden loss of sensory/motor from stress etc. common in females but no pathophysiology is present (all labs normal) pt can be indifferent to symptom
|
|
|
Describe what controls the symptoms of jetlag in the hypothalamus?
|
suprachiasmatic nucleus detect photosensitivie from the retina and controls pineal gland to release melatonin and cortisol during day time from ACTH
|
|
|
24 yo w headaches, visual changes and you see an intracranial calcified mass..remove it and see cystic space w brown rich cholesterol what other structure shares origin with this?
|
pituitary gland, its a craniopharyngioma derived from Rathke's pouch remnants
|
|
|
Benign tumor seen in children and adults MC supratentorial tumor
|
chraniopharyngioma
|
|
|
what embryo layer does the Rathke's pouch develop from
|
ectoderm invaginates and protrustion forms anterior pit
|
|
|
What does the posterior pituitary gland develop from?
|
neurhyphosis from the neuroectoderm
|
|
|
retrograde studies are more likely to have
|
recal biasis
|
|
|
Whats the problem w recall studies?
|
people who had adverse effects are more likely to recall the risk factors they were exposed to than people who didnt have adverse effects
|
|
|
4 yo w difficult walking and cells show radiation-induced genetic mutation whats the likely problem?
|
ataxia-relangiectasia defect in ATM gene codes for DNA repair enzymes, see cerebellar defects, spider angioma, & igA def...
|
|
|
an older pt comes in w visual disturbances you check and see yellow 1.5 mm diameter on the macula what kind of visual disturbances are they having?
|
central scotoma
|
|
|
what is central scotoma
|
any visual defect surrounded by relatively unimpaired field of vision
|
|
|
macular degeneration causes
|
central vision loss usually age related
|
|
|
3 mo old w recurrent vomiting & when seend he has pancreas in his duodenum what hapened?
|
ventral portion of pancreas ringed around the duodenum
|
|
|
how does pancreas development start off
|
dorsal bud is behind the stomach/duodenuma and ventral bud is in front, it then rotates behind and sits there
|
|
|
what does the ventral pancreatic bud develop into
|
uncinate process
|
|
|
someone with a gap in the long arm of the X arm will probably present with
|
macroorchidism (enalrged testes), long face w a large jaw, large everted ears, autism, mitral valve prolapse & MR
|
|
|
what is the mechanism of fragile X syndrome
|
repeast of CGG on the FMR1 gene, causes a skip in the long -arm of X when methylated
|
|
|
a study done testing colorectal cancer w + biopsy and those with - colorectal cancer by age & race is avoiding
|
confounding variables
|
|
|
taking out variable that could effect a study is eliminating
|
confounding variables
|
|
|
Does CO poisoning affect PaO2?
|
No, only decrease oxygen binding on hemoglobin and unloading of O2 to tissues
|
|
|
Does CO cause any methemoglobin?
|
No that is when fe2+ gets reduced to Fe3+ which is the unusable form for O2, usually occurs bc of drugs
|
|
|
how does congenital torticollis present?
|
baby with possible mass on the neck & unable to turn their head one way, cries when turned a certain way and prefers the other
|
|
|
How does congenital torticollis usually happen?
|
2-4 weeks it's seem either due to malposition of the head in utero/birth canal causes SCM injury or birth trauma
|
|
|
What does maternal hypertension cause
|
asymmetrical growth, a normal head with reduced abdominal circumference
|
|
|
an upper respiratory infection of the maternal such as rubella could cause what in an infant?
|
usually not a problem but w rubella can cause mental retardation & congenital heart defects
|
|
|
influenza A combined with animal virus oxthomyovirus causes what to occur
|
genetic reassortment
|
|
|
What is needed in a virus to have genetic reassortment occur?
|
segmented genomes
|
|
|
VII cranial nerve controls what w hearing?
|
innervates the stapedius muscle which causes oscillation in the stapes making it more sensitive to sound ( if problem people have trouble hearing normal sounds)
|
|
|
Gram + motiliy tumbling rod seen in someone who is an organ transplant pt and w fever, headache, and vomiting...CSF shows pleocytosis & normal level of glucose
|
listeria meningitis
|
|
|
Can women with Turner Syndrome XO become pregnant?
|
5% do without medical assistance but 95% do by in vitro fertilization, and donor oocytes & estrogen/progesterone to maintain their lining
|
|
|
genetically fm born to a 23yo mom shows male ambigous genitalia and the mom experiences facial hair growth and a deepening of voice, what is the baby missing ?
|
aromatase
|
|
|
What does aromatase do?
|
converts androsterndione--> estrone & tesosterone --> estradiol
|
|
|
why does the mom with the baby aromtase def get facial hair growth and a deep voice?
|
extra androgens in the placenta
|
|
|
what does someone with a 5 alpha deficiency present with?
|
male with decr synthesis of DHT and feminized internal genitalia
|
|
|
What is the lecithin/ sphingomyeling ratio used to indicate?
|
fetal lung maturity
>1.9= mature |
|
|
How do we measure lecithin / sphingomyelin?
|
mothers amniocentosis bc pulmonary secretions come from fetus, and after 32/33 weeks the lecithin should be much greater
|
|
|
What hormones most control the release of lecithin/sphingomyelin?
|
glucocorticoids
|
|
|
2 siblings with the same mitochondrial disease from their mother have varied expression, how come?
|
mitochondria are randomly distributed to the kids, some get normal, damaged, or mixed...this is called heteroplasmy!
|
|
|
a male with a small phallus, hypospadia, and nomral HTN/electrolytes is deficient in?
|
5 alpha hydroxylase
|
|
|
failure to fuse the maxillary prominence with the medial nasal results in
|
cleft lip
|
|
|
a mother comes in at 16-18 weeks for her triple test and you find low alpha-feto protein, she also drinks & smokes what is this associated with?
|
trisomy 21
|
|
|
What is a high alpha-feto protein associated with for a child?
|
omphalocele, gastroschisis, neural tube defects (also see high acetycholinesterease), & multiple gestation
|
|
|
what is 2 standard deviations cover?
|
95%
|
|
|
Ventral pancreatic buds form from what, and make what?
|
come from the liver diverticulum and form the head of pancreas, main duct, & uncinate process
|
|
|
What does the dorsal bud make?>
|
everything else in the pancreas- body, tail, isthmuc, acessory pancreatic duct, rest of main
|
|
|
What happens in pancreatic divisum
|
The 2 ventral and dorsal fail to fuse so you have 2 drainage systems, santori from dorsal= minor papilla will drain most of the pancreas, the ventral wirsung open major papilla inferior/posterior head & unicinate drianage
|
|
|
A drug allowing people to survive longer with CLL with do what to incidence & prevalence?
|
incidence will be same, prevalence will incr (more people staying alive w the disease)
|
|
|
Alzheimer's disease early onset related to what genes:
|
APP (21), presenilin-1 (14), & presenilin-2 (1)
|
|
|
Alzheimer's late onset due to what genes
|
ApoE4(19)
|

