![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
For each anatomic region of the heart, provide its associated coronary artery.
|
Inferior: Right Coronary
AnteroSEPTAL: LAD AnteroAPICAL: LAD (distal) AnteroLATERAL: Circumflex Posterior: Right Coronary |
|
|
What effect does cardiac tamponade have on Pressure Volume loops?
|
Decreases preload
|
|
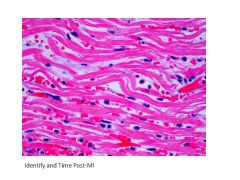
|
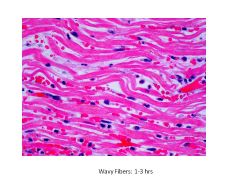
|
|
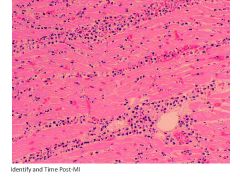
|
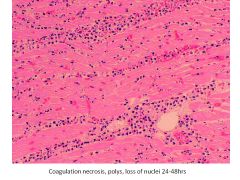
|
|
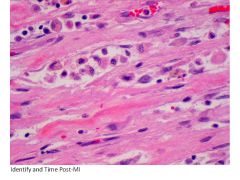
|
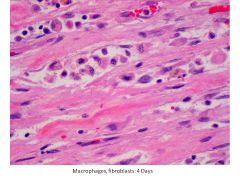
|
|
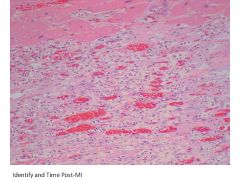
|
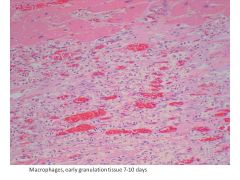
|
|
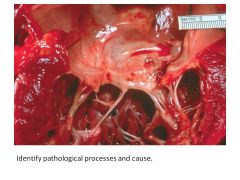
|
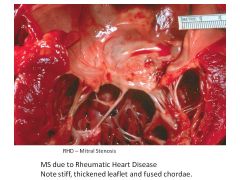
|
|
|
What is the effect of increased/decreased preloads and afterloads on pressure-volume loops?
How could each be effect accomplished? |
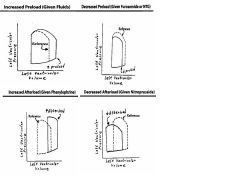
|
|
|
What is the effect of increased/decreased contractility on pressure-volume loops?
How could each be accomplished? |
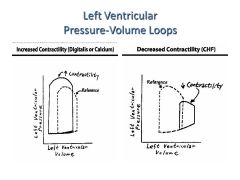
|
|
|
3 days after tooth abscess, patient presents with shaking chills and fever.
No JVD or bruits Normal Upstrokes Harsh systolic murmur at left sternal border and apex with no diastolic murmur or rub No gallop No edema What is the most likely valvular abnormality? |
ACUTE mitral regurgitation (acute because it's only been a few days)
|
|
|
Describe the events of the JVD pressure curve.
|
A: atrial contraction (end systole at peak)
X: Atrial relaxation and passive filling (rapid) due to low pressure V: Inc in pressure to increased venous return (tricupid closes) Y: Tricuspid opens, emptying of atria |
|
|
What is the effect of ACE-inhibitors on preload and afterload?
|
ACE-inhibitors decreases both of because PREVENTS vasoconstriction and fluid retention
|
|
|
Patient presents with acute mitral regurgitation and BP falls to 80/60. Pulse is at 130/min.
Should his heart rate be decreased? |
NO
|
|
|
What is the molecular effect of inhibition of Na/K-ATPase in cardiac myocytes?
What cardiac cycle phases are affected? |
Causes build up of sodium in cell and a decrease in sodium gradient
Thus Na/Ca pump can no longer work as effectively (reduced gradient) Less Ca pumped out and lengthens phases 4 and 0 hence, dec'd heart rate |
|
|
What metabolic imbalance is most likely to predispose to digoxin toxicity?
|
Hypokalemia:
Digoxin competes with K+ ions for same binding site on Na/K ATPase |
|
|
Digitalis mimics actions of which ANS branch?
|
Parasympathetic
|
|
|
Through what mechanism would prolongation of the AP of working ventricular myocytes facilitate arrhythmias?
|
Triggered activity due to early afterdepolarization:
|
|
|
Compare early and delayed afterdepolarizations.
|
Delayed afterdepol is due to digitalis and begins in phase 4 after full relaxation
Early afterdepol occur in phase 2/3 before relaxation is compelte |
|
|
Flecainide should never be used to ______________.
|
Treat a fib in someone with structural heart disease, e.g., prior MI.
|
|
|
Cardiomegaly is a general term for ________.
|
Dilation or hypertrophy of the heart
|
|
|
Rheumatic Fever is due to _______ and affects ______ and ______ valves.
|
Strep infection (sore throat), Scarlet fever
Affects Mitral and Aortic Valves |
|
|
Pressure overload is likely to result in ________ hypertrophy.
Example of pressure overload. |
Concentric LVH
P overload could be chronic, poorly cont'd HTN |
|
|
Volume overload is likely to result in _______ hypertrophy.
Example of volume overload. |
Eccentric hypetrophy of both ventricles.
V overload could be MR/AR |
|
|
When an atherosclerotic plaque ruptures, thrombosis is likely to occur when blood is exposed to thrombogenic substances in the _____.
|
Lipid Core
|
|
|
When a plaque ruptures, it refers to the rupture of the ______.
|
Fibrous Cap
|
|
|
After an aortic dissection, how long until cardiac tamponade?
|
4-7 days
|
|
|
What type of murmur would a patient with LVH have?
|
Late-peaking SYSTOLIC EJECTION MURMUR with delayed carotid upstrokes.
|
|
|
How would a JVD pressure curve appear with tamponade?
|
Blunted Y Descent
|
|
|
How would JVD pressure curve appear with restrictive pericarditis?
|
Rapid y-descent
|
|
|
What is pulsus paradoxus and what cardiac condition is it associated with?
|
Pulsus Paradoxus = Increase in SBP by 10mmHg upon inspiration
Associated with CARDIAC TAMPONADE |

