![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In order of activation, list ectcopic cardiac foci and their inherent rates.
|
Atria: 60-80
AV Jn: 40-60 Ventricles: 20-40 |
|
|
What is idioventricular rhythm?
|
Rhythm under control of His-Purkinje System
|
|
|
Triplets for determining rate.
|
300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50
|
|
|
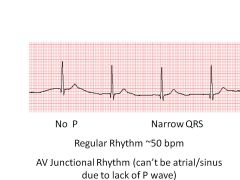
If p waves are absent, and heart rate is 60, what foci is setting the heart's pace?
|
No p waves = No SA node activity
60 is in range of atria Thus: AV Node conduction |
|
|
How do you determine slow rate?
|
Use 3-sec hashmarks on top of EKG:
Cycles per 6 sec (2 hashmarks) x 10 = HR |
|
|
Peak vs Sad Face on EKG
|
Peak = Depolarization (+)
Sad face = Repolarization (-) |
|
|
Draw an EKG and describe all phases.
When does systole begin and end? |
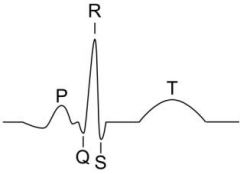
P wave: atrial depolarization and contraction; forcec blood through AV valves
QRS: ventricular depolarization and beginning of contraction T hump: Rapid phase of ventricular repolarization (K+ ions out) Systole begins at QRS and ends at end of T |
|
|
What defines an S wave?
|
Any downward wave with an upward wave in front of it
|
|
|
What interval changes with heart rate?
|
QT interval
|
|
|
What does a long QT interval singify?
How would you determine if it's long? |
If QT is long, then there is a rapid ventricular rhythm
QT is greater than 1/2 R to R |
|
|
1 big box vs 1 small box:
Time |
1 big box = 0.2 sec
1 little box = 0.04 sec |
|
|
Which leads are precordial? Which heart region does each monitor?
How does Q value (positive/negative) differ among the leads? |
V1-V6 are precordial
V1-2 Right chest leads (RV): mainly negative V3-V4: Interventricular Septum (R/L BB's); Isoelectric V5-V6: Left Chest Leads (LV): Mostly positive QRS |
|
|
What heart region is the origin of the mean QRS vector?
|
AV Node
|
|
|
What is normal axis range?
|
Between 0 and +90 degrees
|
|
|
Effect of hypertrophy on vector and mean QRS shifts.
|
Hypertrophy increases vector and mean QRS in its direction
|
|
|
Effect of infarction on vector and mean QRS shifts.
|
Infarction decreases vector and shifts mean QRS away from it.
|
|
|
Steps for determining axis deviation.
|
Find quadrant of mean QRS vector
Find limb lead with most isoelectric QRS Use reference angles |
|
|
Steps for determining axis rotation.
|
Look at precordial leads.
If isoelectric in V1/V2: RIGHTWARD ROTATION If isoelectric in V5/V6: LEFTWARD rotation |
|
|
Normal range for heart rate.
|
60-100: Normal
<60 = brady >100 = tachy |
|
|
How do you decide if rhythm is regular?
|
Measure distance between QRS complexes (should always have ventricular contraction). Should be constant.
|
|
|
QRS Complex:
Narrow vs Wide: What do they mean? What defines narrow/wide? |
Narrow QRS: Rhythm originates ABOVE ventricle:
so sinus or supraventricular rhythm: Sinus, Atrium, AV Junction QRS<0.12 sec Wide QRS: originates from ventricle QRS >0.12 sec Note: 0.12 = 3 tiny boxes |
|
|
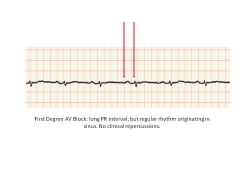
What is the significance of wide PR interval?
What's the cutoff for a wide interval? |
Wide PR interval = more than .20 seconds between beginning of P wave and beginning of QRS
0.2 seconds = 1 big box Signifies AV block (impaired conduction); taking too long for signal to get through AV junction |
|
|
|
|
|
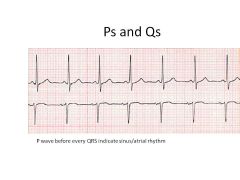
|
|
|
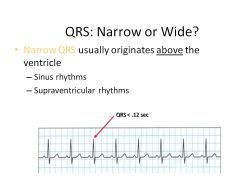
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
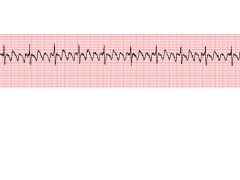
|
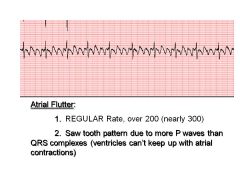
|
|
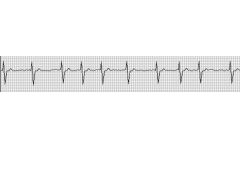
|

|
|
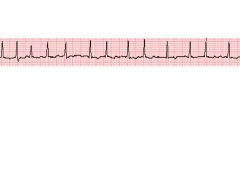
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
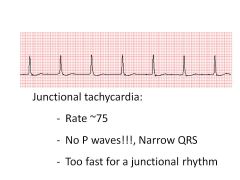
|
|
|
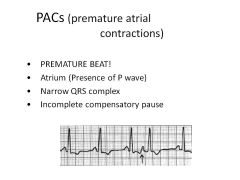
|
|
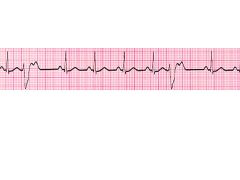
|
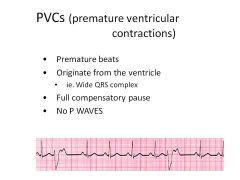
|
|

|
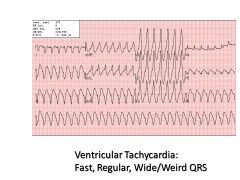
|
|

|
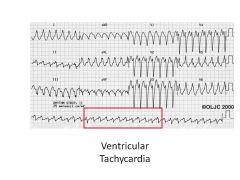
|
|
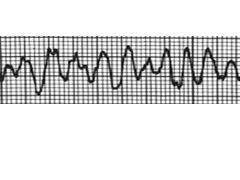
|
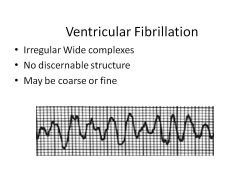
|
|
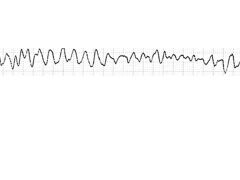
|
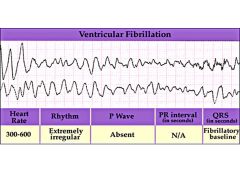
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
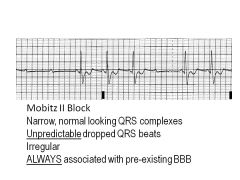
|
|
|
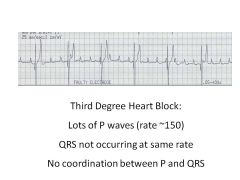
|
|

