![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Embryonal Age vs Gestational Age
|
Embryonal age ends at 8 weeks, and translates to 10 weeks gestational age.
Gestational age is 40 weeks, but mother has only been pregnant for 38 weeks. Gestational age is weeks post-menstrual period. |
|
|
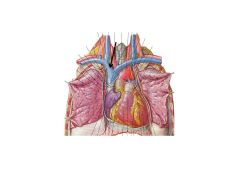
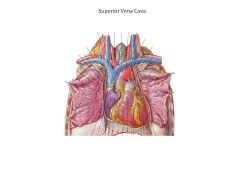
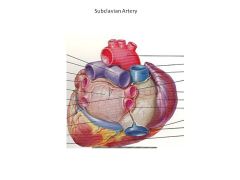
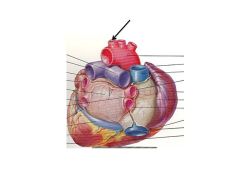
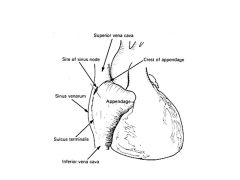
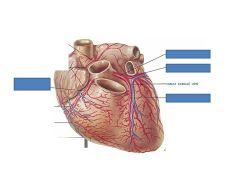
Superior VC returns blood from the _______.
|
Head and neck
|
|
|
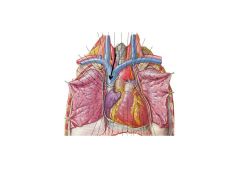
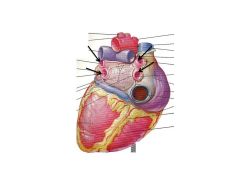
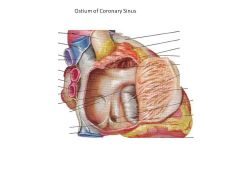
What is the crux of the heart?
|
Where all chambers of the heart meet
|
|
|
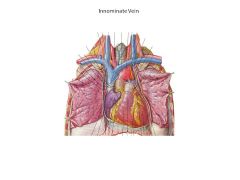
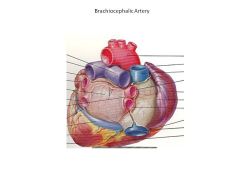
Innominate AKA?
|
Brachiocephalic
|
|
|
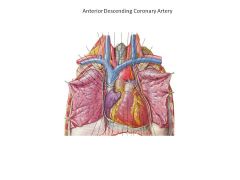
What vessel denotes the location of the the ventricular septum?
|
Anterior descending coronary artery
|
|
|
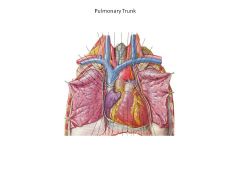
Pulmonary Trunk AKA
|
Pulmonary Artery
|
|
|
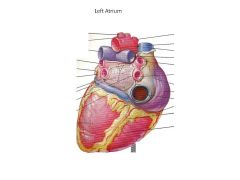
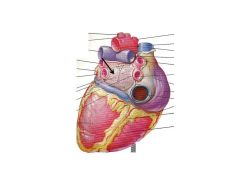
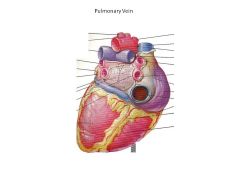
What vessels enter the left atrium?
|
Pulmonary Veins (4 of them)
|
|
|
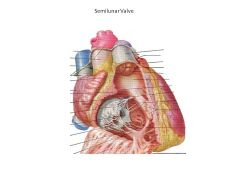
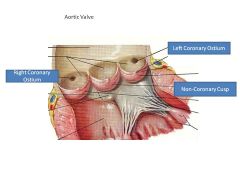
Which valves are semilunar?
|
Pulmonic (Artery) Valve, Aortic Valve
i.e., valves leaving ventricles |
|
|
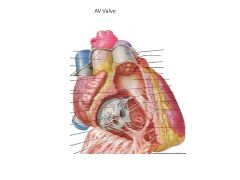
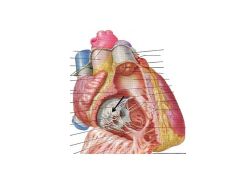
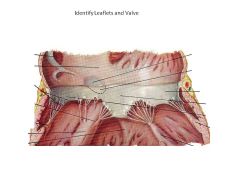
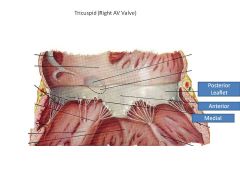
What is an AV valve?
|
Atrioventricular valve (separates atrium and ventricle), has chorda tendonae attached to papillary muscles
|
|
|
Which ventricle is thickest and why?
|
LV because has to overcome greatest resistance (pressure)
|
|
|
How does the texture of the two ventricles differ?
|
Left ventricle has smooth upper septum
|
|
|
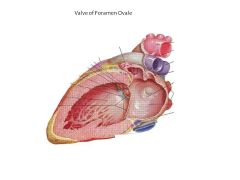
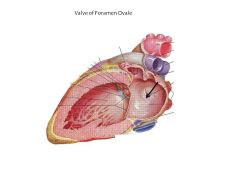
Valve of foramen ovale AKA?
|
Septum primum
|
|
|
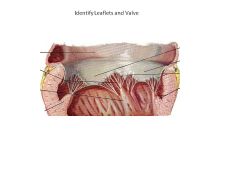
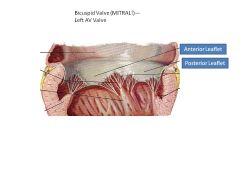
Which valve leaflet is septophobic? Why?
|
(Tricuspid valve septal leaflet is septophilic)
Mitral Valve Anterior Leaflet: Septophobic or will obstruct blood flow |
|
|
The ventricular septum has a large ______ portion and a small ________ portion.
|
Large muscular portion, small membranous portion
|
|
|
The aortic valve has fibrous continuity with which valve?
|
Mitral Valve
|
|
|
An adult heart weighs about _____ grams.
|
Female: 250-300g
Male: 300-350g (infant about 20 g) |
|
|
Cardiac myfibrils vs Skeletal myofibrils
|
Cardiac myofibrils contain nuclei within fibers and there are anastomoses between fibers
Skeletal myofibrils contaon nuclei at periphery of fibers and all fibers run parallel (no crosstalk) |
|
|
Specialized myocytes that are able to conduct electrical impulses are located in the ________.
|
Sinoatrial node
|
|
|
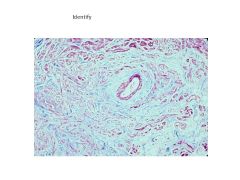
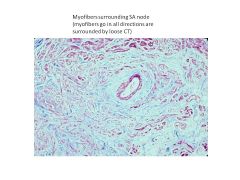
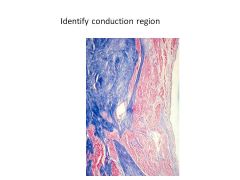
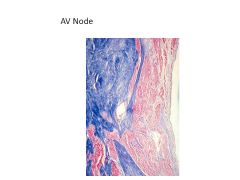
This node is located in the Triangle of Koch.
|
AV Node
|
|
|
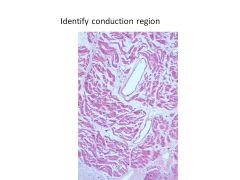
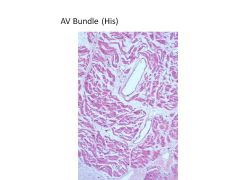
At what point does the AV node become the Bundle of His?
|
When node loses all contact with atrial myocardium
|
|
|
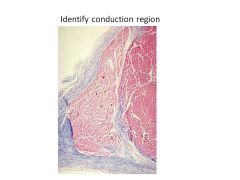
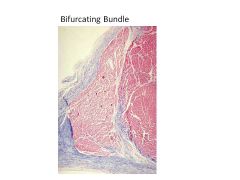
When does the His bundle bifurcate? What are the 2 branches?
|
Bifurcates as approaches membranous septum
Branches into Left and Right bundle branches |
|
|
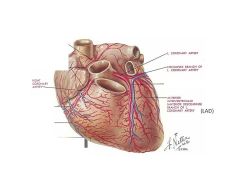
Which branches of the coronary arteries run in AV grooves?
|
Right Coronary Artery, Circumflex Artery
|
|
|
These arteries arise from the sinus of Vasalva.
|
R and L coronary aa
|
|
|
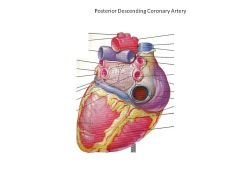
What coronary artery supplies the posterior aspect of the heart?
|
RCA
(although 15% of all people have a LCA dominant system) |
|
|
What coronary artery supplies the AV node?
|
RCA
|
|
|
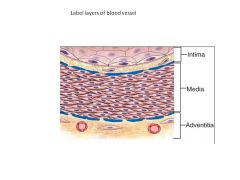
AV leaflets vs Semilunar Leaflets:
Core vs Atrial Lamina Presence of BVs The core of AV leaflets contain a lamina ______. |
AV:
Core: lamina fibrosa Atrial: lamina spongiosa (Also covered by thin layer of fibroelastic tissue and endocardium) Contains BVs, lymphatics, nerves, SM, striated muscle Semilunar: Core and Atrial aspects covered by fibroelastic tissue and endocardium No striated muscle, BVs, nerves, or lymphatics |
|
|
Which specific vessels are considered large elastic arteries?
|
Aorta and its large branches (innominates, subclavians, common carotids, iliacs)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

