![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Critical Value |
An x-value that makes f'(x)=0 or f'(x) undefined. |
|
|
Extrema |
The max and min of a function. |
|
|
The First Derivative Test |
This test helps us identify if a critical point is a max or min. To use the test, first find the critical values; then graph them on a number line and test values in between the C.P by plugging them in to f' and observing the sign. When the derivative changes from + to - at a point that point is a max. When the derivative changes from - to + its a min. |
|
|
Interval of increase |
The part of a graph with positive slopes. Analytically this happens on interval where f'(x)>0 |
|
|
Interval of decrease |
The part of a graph with negative slopes. Analytically this happens on intervals where f'(x)<0 |
|
|
Inflection Point |
A point where the concavity of a function changes. Analytically, this happens at the x-values for which f''(x)=0. |
|
|
Concave Up |
The part of a graph where it is curved upwards. Analytically, this happens on intervals where f''(x)>0. |
|
|
Concave Down |
The part of a graph where it is curved downwards. Analytically, this happens on intervals where f''(x)<0. |
|
|
Second Derivative Test. |
This is a test using the second derivative to deterring whether a critical point is a max or a min. To use this test first find the critical values then test them in the second derivative:
If f'(a)=0 and f''(a) is positive then f(x) has a local min at x=a.
If f'(a)=0 and f''(a) is negative then f(x) has a local max at x=a.
If f'(a)=0 and f''(a)=0 or DNE then a is neither a min nor a max. |
|
|
Velocity Function |
First Derivative of the Position Function. |
|
|
Acceleration Function |
Second Derivative of the Position Function (and first derivative of velocity). |
|
|
Area of a Rectangle |
A=b*h |
|
|
Area of a Triangle |
A= 1/2 b * h
|
|
|
Area of a Circle |
A=pi * r^2 |
|
|
Circumference of a Circle |
C= 2 * pi * r |
|
|
Volume of a box |
V= b * h * w |
|
|
Volume of a Prism |
V= B * h ( B is the area of the base which can be different shapes) |
|
|
Volume of a cone/pyramid |
V= 1/3 * B * h |
|
|
Optimization |
The process of finding an ideal condition (i.e. maximizing or minimizing something). |
|
|
Locally Linear (at a point) |
A function is locally linear at a point if, when we zoom in on the function the curve starts to look like a straight line. (If the function is "locally linear" it is differentiable). |
|
|
Linearization |
A linear equation whose y-values can be used to approximate a function near a particular x-value. (essentially it is the equation of a tangent line). |
|
|
Newton's Method (say the formula and the idea!) |
IDEA: A process for estimating the root of a function using tangent lines and their x-intercepts.
FORMULA: new x = old x - f(old x)/ f'(old x) |
|
|
When does Newton's Method fail? |
1) When we choose an x-value with a slope of 0
2) When we start too far from the root we are trying to find. |
|
|
Differential (what is it?) |
A variable that represents a small change. |
|
|
What does dy equal? (differential formula) |
dy= f'(x) * dx |
|
|
What is the difference between absolute and relative change? How do you calculate them? |
Absolute Change= the difference in the numbers (subtract the outputs before and after)
Relative Change= the percent that changed (divide Absolute Change by the original output) |
|
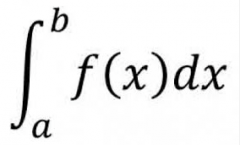
What is the the meaning of: |
The area under the f curve between a and b. |
|
|
What is "RAM"? How do you set it up? What determines its accuracy? |
RAM is the "Rectangular Approximation Method." It approximates the area under a curve by dividing that area in to a bunch of rectangles. To set it up you simply multiply the width (delta x) times the height (y-value) of each rectangle. The accuracy depends on how many rectangles you use (n)... more is better. |
|
|
What is "LRAM"? How does its set up differ from RRAM? How do you know if it is an over or underestimate? |
The "Left Hand Approximation Method" is a type of RAM where we use the y-values (heights) that correspond to the left edge of each rectangle.
LRAM is an underestimate when the function is increasing. LRAm is an overestimate when the function is decreasing.
|
|
|
What is "RRAM"? How does its set up differ from LRAM? How do you know if it is an over or underestimate? |
The "Right Hand Approximation Method" is a type of RAM where we use the y-values (heights) that correspond to the right edge of each rectangle.
RRAM is an overestimate when the function is increasing. RRAm is an underestimate when the function is decreasing.
|
|
|
What is the Trapezoidal Approximation Method? How do you know if it is an over or under estimate? |
The Trapezoidal Approximation method allows us to estimate the area under a curve by dividing it up in to trapezoids.
It is an overestimate when the function is concave up and an underestimate when the function is concave down. |
|
|
What is the formula for the area of a trapezoid?
How does it relate/compare to the shortcut formula for the trapezoidal approximation method?
|
Area of a trapezoid: width * (height1 + height2)/2
Trapezoidal Approximation Method Shortcut: (only works if the widths are all the same!) width*(height1 + 2* height2 + 2* ... +height) |
|
|
In applied problems what does the area under the rate curve represent? |
The total change in the original function from the start to the end of that interval. |
|
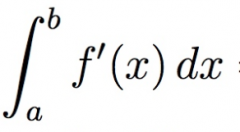
According to the first part of the FTC, what does the expression below equal?
|
f(b) - f(a) |
|
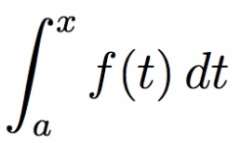
According to the second part of the FTC, what is the derivative of the function below:
|
f(x) |
|
|
What does " anti-derivative of f(x) " mean? |
A function whose derivative is f(x)... every function has a family anti-derivatives which differ only by a constant value ( + C). |
|
|
When Newton and Leibniz were inventing Calculus, how did they use the idea of RAM to come up with a precise way to calculate the area under a curve? |
They took the limit of RRAM as n approached infinity... thus they made their approximations infinitely close to the actual value of the area under the curve. |
|
|
What is the formula for the average value of a function? |
1/ (b-a ) * integral from a to b of f(x)dx. |
|
|
What are the two situations in which we consider the "area under the curve" to be negative? |
1) regions below the x-axis
2) when the limits of integration are reversed (i.e. if the upper limit is lower then the lower limit... i.e. going from right to left) |
|
|
What is the area under the sin curve from 0 to pi? |
2 units ^2 |
|
|
What is a differential equation? What are the two kinds of solutions to a differential equation? |
A differential equation is an equation with a term that represents a derivative. Its solution is a function for the original quantity.
GENERAL SOLUTION - represents a family of functions ( and includes + C) PARTICULAR SOLUTION - represents and exact function and requires more information so that we can solve for C. |
|
|
What is a slope field, when are they helpful? |
A slope field is a picture of how a function's shape depends on x and y. They are useful for getting a sense for what an anti-derivative might look like particularly in cases where we can't find one algebraically. |
|
|
What is the integration by parts formula? |
uv - int( v du) |
|
|
State the 3 pythagorean trig identities. |
sin^2 + cos^2 = 1 tan^2 = sin^2-1 cot^2 = csc^2-1 |
|
|
State the two situations when a definite integral will equal zero. |
1) when the upper and lower limits of integration are the same number
2) when the area above the x-axis equals the area under the x-axis. |
|
|
State the two power reducing identities.
(cos^2 = and sin^2 = ) |
cos^2(x) = (1+cos(2x))/2
sin^2(x) = (1-cos(2x))/2 |
|
|
If you are rotating an area around the the x-axis and using dx as your variable of integration, what method should you use?
|
Washers/Disks
|
|
|
If you are rotating an area around the the x-axis and using dy as your variable of integration, what method should you use?
|
Shells
|
|
|
If you are rotating an area around the the y-axis and using dx as your variable of integration, what method should you use?
|
Shells
|
|
|
If you are rotating an area around the the y-axis and using dy as your variable of integration, what method should you use?
|
Washers/Disks
|
|
|
What formula will help you calculate the length of a curve?
|
integral of SQRT ( 1 + (f'(x))^2)dx
|
|
|
If you are calculating the area between two curves and want to use horizontally oriented rectangles... what should your variable of integration be?
|
dx
|
|
|
If you are calculating the area between two curves and want to use vertically oriented rectangles... what should your variable of integration be?
|
dy
|

