![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
opposite Rays |

|
|
|
|
angle
|
formed by two Rays that have a common endpoint endpoint
|
|
|
|
endpoing
|
the vertex of the angle
|
|
|
|
side
|
each Ray is a "side" of the angle
|
|
|
|
postulate 9
|
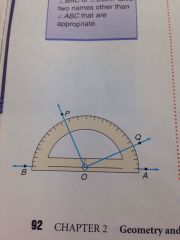
let O be a point on AB such that O is between A and B. All Rays can be drawn from O on one side of AB . These Rays can be paired with the real numbers from 0 to 180 so that
1. OA is paired with 0 and OB is paired with 180 2. If OP is paired with x and OQ is paired with y, then the number paired with <POQ is |x-y| this number is called the measure or the degree measure of <POQ |
|
|
|
complementary angles
|
two angles whose measures have a sum of 90 degrees
|
|
|
|
supplementary angles
|
two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 degrees
|
|
|
|
interior and exterior
|

an angle with measure less than 180 degrees divides a plane into 3 sets of points; the angle itself, the points in the interior of the plane and the points in the exterior of the plane.
|
|
|
|
Postulate 10
|
if point B is in the interior of <AOC, then the m<AOB + m<BOC = m<AOC
|

|
|
|
Postulate 11
|
if two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary
|
|
|
|
congruent angles
|
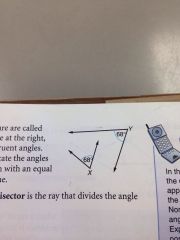
angles that are equal in measure
|
|
|
|
angle bisector
|
for any given angle, it is the Ray that divides the angle into 2 congruent angles
|
|
|
|
adjacent angles
|
two angles in the same plane that share a common side and common vertex, but have no interior points in common
|
|
|
|
linear pairs
|
two adjacent angles whose noncommon sides are opposite Rays
|
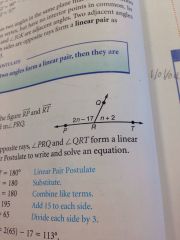
|
|
|
properties of equality
|

|
let a b and c be any real numbers
|
|
|
distributive property
|

use multiplication to distribute a to each term of the sum or difference within parentheses
|
|
|
|
properties of congruence
|

|
|
|
|
proof
|
a convincing argument that uses deductive reasoning. logically shows why a conjecture is true
|
|
|
|
two column proof
|
lists each statement on the left and then on the right, gives a reason for the statement
|
|
|
|
vertical angle theorem
|

vertical angles are congruent
|
|
|
|
paragraph proof
|
a proof written in senatnce a in a paragraph
|
|
|
|
congruent supplements theorem
|

if two angles are supplements of the same angle (or of the congruent angle) then the two angles are congruent
|
|
|
|
congruent complements theorem
|

if two angles are complements of the same angle (or of congruent) then the two angles are congruent
|
|
|
|
right angle theoren
|

all right angles are congruent
|
|
|
|
congruent supplementary right angle theorem
|
if two angles are congruent and supplementary, then each is a right angle |
|
|
|
deductive reasoning
|
the process of making logical conclusions from the given statements or facts |
|

