![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the 3 point princiople? |
single force applied at the area of deformity or angulation (force acting laterally is placed medially at knee to correct genu valgus) -2 additional counterforces, each half the value of the single force, act in the opposite diretion (e.g. 2 forces acting medially located on the lateral thigh and calf. |
|
|
Blucher opening of shoes: |
Has vamps (the flaps contain the lace stays) that open wide apart from the anterior margin of the shoe for ease of application |
|
|
Bal (Balmoral) opening of shoes: |
Has stitched down vamps |
|
|
what is a heel insert? |
reduces the pressure on the tender area with cutouts and sloping anteriorly |
|
|
what is a scaphoid pad? |
usually supports longitudinal arch used for pes planus |
|
|
what is a semirigid plastic insert? (UCBL) |
1. Encompasses heel and midfoot 2. applies medial or lateral force to calcaneus 3. used for subtalar (rearfoot) eversion or inversion abnormalities |
|
|
what is metatarsal pad? |
1. used for metatarsalgia 2. placed proximal to met heads/over met shafts 3. takes pressure off met heads |
|
|
what is metatarsal bar? |
1. flat strip of material 2. placed posterior to met heads 3. used for metatarsalgisaa |
|
|
Thomas heel wedge is what? |
aka medial heel wedge Extended anteriorly along the medial side to augment the effect of the medial wedge in supporting the medial longitudinal arch |
|
|
Thomas or medial heel wedge is used for what? |
Pronation
|
|
|
Lateral heel wedge does what? |
1. Provides support along the lateral side of the heel
|
|
|
Medial/lateral sole wedges do what? |
1. Alter metatarsal alignment |
|
|
|
1. Builds up the sole proximal to the metatarsal heads 3. shifts weight bearing load onto shafts 4. used for metatarsalgia and with weak PF
|
|
|
what does the plastic foot plate do? |
1. provides best control of the foot 2. shoe must close high on dorsum of foot 3. allows for ease of donning orthosis 4. allows changing shoes of the same heel height |
|
|
Metal stirrup is what? |
1. U-shaped attachment riveted to the sole of the shoe |
|
|
Free motion ankle joint allows for what? |
DF & PF while providing for medial and lateral stability |
|
|
Solid AFO allows what? |
No movement -to compensate for lack of PF in early stance, a hinged solid AFO may be utilized to provide slight sagittal motion |
|
|
Limited motion ankle control allows motion where? |
To be restricted in one or both directions
|
|
|
Bichannel adjustable ankle lock (BiCAAL) is what? |
Consists of a pair of joints with anterior and posterior channels that can have either springs to assist motion or pins to reduce motion |
|
|
Posterior stop limits what? |
PF |
|
|
Posterior stop is used to correct for what? |
Knee recurvatum in stance |
|
|
Anterior stop limits what? |
DF |
|
|
Anterior stop is used to prevent what? |
Knee buckling or excessive knee flexion during early stance |
|
|
Posterior leaf spring provides what? |
DF assistance from a plastic insert that lifts the foot during swing phase |
|
|
Spring assist (Klenzak joint) does what? |
-double upright metal AFO with single anterior channel for spring assist to aid DF -coil spring is compressed in stance and rebounds in swing -not appropriate if spasticity is a factor |
|
|
what can medial and lateral motion of the foot/ankle be controlled by? |
plastic AFO or leather correction straps (valgus/varus straps) |
|
|
Varus or Valgus T-straps? |
1. Medial strap buckles around lateral upright and corrects valgus -applies lateral force to restrain pronation -control subtalar joint or rear foot 2. lateral strap buckles around medial upright and corrects varus -exerts medial force to restrain supination of rear foot |
|
|
Molded plastic AFOs are what? |
-Have a single upright or shell that can: 1. limit mediolateral motion (e.g.,solid AFO) 2. assist with motion (e.g.,posterior leaf spring) or 3. control for motion in all planes (e.g.,spiral AFO) |
|
|
Molded plastic AFOs are contraindicated for patients with what? |
changing leg volume (e.g. dialysis or CHF) |
|
|
Conventional AFOs are what? |
Have one or two metal uprights that attach to the shoe and to a calf band (leather or plastic) that provides proximal stabilization on the leg |
|
|
Conventional AFOs provide for what? |
1. Maximal mediolateral support |
|
|
Floor reaction orthosis is what? |
Has an/anterior band that is part of a solid ankle AFO and imposes a posterior force near the knee, resisting knee flexion |
|
|
Patella tendon bearing brim is what? |
Resembles an below knee prosthetic socket that allows for weight distribution on the patellar shelf -brim is used with a plastic solid AFO or a metal limited motion ankle joint
|
|
|
Tone reducing orthoses are what? |
1. Plastic AFOs designed for children with spastic cerebral palsy and adults with spastic hemiplegia
|
|
|
What does a hinge joint on a KAFO provide? |
1. Mediolateral support 2. hyperextension control 3. while allowing flexion/extension of the knee |
|
|
Offset knee joint is what? |
A hinge placed posterior to the midline of the leg (weight-bearing line) |
|
|
Offset joint assists in what? |
1. Knee extension during mid-late stance |
|
|
Offset knee joint is contraindicated with what? |
Knee flexion contracture |
|
|
Drop ring lock is what & does what? |
1. The most common knee control
|
|
|
Pawl lock with bail release is what? |
1. A spring-loaded posterior projection (lever or ring) that allows the patient to unlock the knee by pulling up or hooking the pawl on the back of a chair and pushing it up |
|
|
how is sagittal stability achieved in KAFO? |
-bands or straps that provide posteriorly directed force that complements the anteriorly directed forces from the back of the shoe & thigh band -Anterior bands can be pretibial or suprapatellar as well and may interfere with sitting |
|
|
how is frontal plane stability achieved in KAFO? |
with plastic calf shells or straps to correct genu valgum or varum |
|
|
Craig-Scott KAFOs is what? |
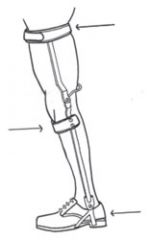
1. Commonly used for individuals with paraplegia (T9-T12 lesions) |
|
|
Oregon Orthotic System KAFOs is what? |
Uses rigid plastic AFOs or KAFOs to restrict motion in the transverse, frontal, and sagittal planes
|
|
|
what is a reciprocating gait orthosis (RGO) |
1. specialized THKAFO 2. Uses solid-molded AFOs with knee locks, plastic thigh shells, a hip joint with pelvic band & metal cables connecting both hips |
|
|
what is the procedure to ambulate with a THKAFO? |
1. shift weight to the R leg 2. tuck the pelvis by extending the upper thorax 3. press on the crutches 4. allow left leg to swing through |
|
|
Reciprocating gait orthosis (RGO) THKAFOs are used for patients with what? |
T9-12 level of spinal cord lesion or spina bifida lesion |
|
|
ParaWalker is what? |
1. very sturdy hip joints that limit hip flexion and resist hip abduction and adduction as the wearer shifts weight from side to side during ambulation |
|
|
ParaWalker is used for patients with what? |
Lower thoracic spinal cord lesions |
|
|
Lenox Hill Knee orthoses (KO) does what? |
Mediolateral |
|
|
Pro-Am Knee orthoses (KO) does what? |
Anteroposterior Rotatory |
|
|
|
Mediolateral |
|
|
Palumbo KO? |
Patellar |
|
|
what is a swedish knee cage |
controls excessive hyperext of knee |
|
|
function of knee wraps and soft supports. |
e.g. neoprene sleeves -supports knee -assists in stabilizing the patella -temp use for soft tissue injuries |
|
|
Patellar knee support is used for what? |
Postoperative rehabilitation |
|
|
what is the patellar knee support? |
neoprene sleeve with patellar cutout and rubber buttress that is horseshoe-shaped to aid patella in proper gliding |
|
|
Hip orthoses (HO) is usually used for what? |
Legg-Calve-Perth disease (avascular necrosis of he hip) in which the patient's affected hip is held in ABD & IR for proper centralization of the femoral head in the acetabulum (e.g. Toronto hip orthosis or Scottish Rite orthosis) |
|
|
what is a standing frame used for? |
aka swivel walker -permit wearer to stand without crutch support, freeing hands for activities -can move by rotating the upper torso to shift weight and rock the frame from side to side |
|
|
Parapodium is what? |
1. Differs from the standing frame because of the joints that permit the wearer to sit
|
|
|
Corset provides what? |
1. Abdominal compression & increases intra-abdominal pressures |
|
|
Thoracolumbosacral flexion-extension-control-orthosis (TLS FE) is what? |
aka Taylor Brace -Includes components of LS FEL (lumbosacral Flexion extension lateral control orthosis) with addition of axillary shoulder straps to limit upper trunk flexion |
|
|
Plastic thoracolumbosacral jacket does what? |
1. Provides maximum support and control of all motions |
|
|
Jewett (TLSO) does what? |
Limits flexion, but encourages hyperextension (lordosis) |
|
|
Philadelphia collar provides what? |
A more rigid form of support than soft cervical collar & less cervical motion because it's made of plastic |
|
|
Four-poster orthosis is what? |
-Have two plates (occipital & thoracic) with 2 anterior & 2 posterior posts to stabilize the head |
|
|
Halo orthosis is what? |
Attaches to the skull by screws with 4 uprights that attach to a thoracic jacket |
|
|
Minerva orthosis is what? |
Provides for maximal control of cervical motion using a forehead band instead of screws |
|
|
what are scoliosis orthoses used for? |
preventing lateral curve from increasing |
|
|
Milwaukee orthosis is what? |
A cervical, thoracic, lumbosacral orthosis (CTLSO) used to control scoliosis used for Scoliotic curves of 40° or less |
|
|
Boston orthosis (TLSO) is what? |
Low-profile, molded plastic orthosis for scoliosis |
|
|
Boston orthosis (TLSO) is used when? |
-curves of 40 degrees or less |
|
|
what is a resting splint (cock-up splint)? |
1. An anterior or palmar splint that positions the wrist and hand in a functional position |
|
|
when is a resting splint indicated? |
1. RA |
|
|
Dorsal wrist splint does what |
1. Frees the palm for feeling/grasping by the use of grips that curve around & over the 2nd & 5th metacarpal heads |
|
|
when is a wrist-driven tenodesis orthosis (flexor hinge orthosis) used? |
assist pt in using wrist extensors to approximate thumb and forefingers in absence of active finger flexion -patients with quadriplegia (usually C6) |

