![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why is an abdominal resection done |
Cancer of the rectum |
|
|
What is another name for this |
Miles resection |
|
|
What position is done in |
Lithotomy |
|
|
How is done |
APRs involves removal of the anus, the rectum and part of the sigmoid colon along with the associated (regional) lymph nodes, through incisions made in the abdomen and perineum. The end of the remaining sigmoid colon is brought out permanently as an opening, called a colostomy, on the surface of the abdomen. |
|
|
What does the surgical team need to do in order to close the abdomem |
He needs to change gown and gloves and use separate set of instruments |
|
|
What is a imperforate anus repair and why is it done |
It's when the baby is born without we create an anus Physiotherapy is used to develop and control sphincters |
|
|
What is a tracheoesophageal fistula repair and when is it done |
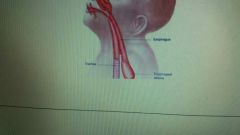
Baby is born with a communication between the trachea and esophagus and as a result food can enter into the trachea from the esophagus what we have to do to stop this is we have to block and cut out the fistula |
|
|
What is micro-tubal reanatomosis |
Simple plastic it means patients have Fallopian tubes litigated sometimes in the past for Family Planning and now the patient wants to get pregnant and that's the only possibility if her Fallopian tubes are open again for the passage of egg from the ovary to meet the sperm |
|
|
Why do we need a microscope? |
It's a very delicate procedure where we are performing reanastamosis of tubes |
|
|
What is done after the reanastamosis is performed? |
We inject methylene blue dye into the tube through the vagina and the uterus if the tubes are now patent open the methylene blue should flow from the uterine and uterine end of the fallopian tube is now called Cornu to the fimbria over the ovaries and there must be spillage of dye over ovaries to confirm patency of tubes |
|
|
What is a vulvectomy |
Valva= all external female reproductive and genital Parts clitorious distal urethra labia minora labia majora Bartholin glands... if there is cancer of these areas we have to cut out all the areas and replace them with skin grafting which is called a stent |
|
|
What is a stent |
Bolster dressing is used on skin grafts which is suture to the skin |
|
|
Why do we use a stent |
We want to have an even distribution of skin grafts over the moon to get blood uniformly in order to survive |
|
|
Wha is Wertheim procedure and why is it done |
Aka pelvic exenteration is done because of ovarian cancer... radical operation performed for cervical cancer, involving removal of the entire uterus, the connective tissue and lymph nodes close to it, Fallopian tubes, ovaries, and the upper part of the vagina. |
|
|
if it involves the pelvic organs the uterus and Fallopian tubes the old ways and the urinary bladder then a hysterectomy with bilateral salpingectomy and bilateral oophorectomy with cystectomy is done and we spare the rectum ...what is this then called |
Anterior exenteration |
|
|
What is the reconstructive surgery for this called |
Ileio conduit which we take part of the ileum and create a pouch of.it by closing its one end and bring the other end out throigh.an abdominal opening by creating a stoma- we also we implanted the uterus there to collect urine into this pouch which is collected in the Urostomy bag |
|
|
What is the rectum is involved. |
We have to take it out alomg with the other structures |
|
|
Now what is the procedure that has to be done |
Now we have to do a colostomy too besides ileal conduit and now procedure is called total pelvic exenteration |
|
|
What if the bladder isnt involved |
If the bladder is not involved in the rectum with the rest of the structures then we spare the bladder and do all posterior exentration |
|
|
Virectomy and why is it done |
Vitreous humor is a gel-like present in the posterior cavity of the eye it maintains the shape of the eye if vitreous humor is lost the eyeball can collapse the vitreous humor is transparent and if there is bleeding in it it is because of any reason then image cannot be transferred to the right now and it would be blurred - so we cut out the defective part of the vitreous humor and substitute it with healon or viscoat or a gas to prevent the collapse of the eyeball |
|
|
What is used to cut out the defective part of the vitreous humor? |
Oculotome |
|
|
What irrigation is used for the eye procedures |
BSS- Balanced salt solution |
|
|
What needle is needed |
Spatula or side cutting suture needle |
|
|
What sponge is used |
Weck or spear sponges |
|
|
What anesthesia is used |
Retrobulbar anesthesia given at the back of the eye ball |
|
|
What is used to dialate the pupil |
Mydriatic drops /atropine drops to dilate the pupil |
|
|
What is a laryngectomy and why is it done |
Because of cancer of the larynx we have to remove that part as a result the patient has to breathe through a permanent tracheostomy |
|
|
What must we cut in order to reach the larynx |
We have to cut through the strap muscles of the neck |
|
|
What is a radical neck dissection |
Because of cancer of any structure within the neck other structures of the neck can also be involved and we have to do the debulking procedure meaning we have to cut out the big tumor to ease the patient and all other structures of the neck which could possibly be removed along with the lymph nodes |
|
|
What is a stapedctomy |
3 small bones in middle ear.called ossicles from lateral to medial side or from eardrums Ward's oval window of inner ear malleus incus stapes which are connected by ligaments please let humans get hard and feet of the Staples can get stuck in the oval window normally feet of the state you should move in and out of the old windows cause vibration in the paralympic winter a year to receive child but when the feet of the state please get stuff sound cannot be conducted we call it conductive deafness - so we have to remove the feet Stapes and replace them with a prosthesis so hardening of these ossicles is called osteosclerosis meaning ear and sclerosis means hardening |
|
|
What is craniosyntosis |
Is a premature closure of fusion of the skull sutures cranial joints on on one side of the skull and the side of the skull does not grow further the other side of the skull keeps growing and now there is no balance between the two sides of the skull which causes deformity |
|
|
What is done |
We have to cut open the Fusion 2 and an expansion or growth of the cranial bones this is called cranial facial reconstruction |
|
|
What are the different types of Lefort fractures |
Type 1: fracture of upper jaw which is maxillary bone Type 2: fracture of the upper jaw which is maxillary bone and nasal bone Type 3: fractures of the upper jaw which is maxillary bone + nasal bone + zygomatic bone eye orbit fracture |
|
|
What is the treatment for this |
Plates and screws |
|
|
What is proganthic |
Protruding lower jaw |
|
|
What is microganthia |
Very small lower jaw |
|
|
What is a adrenalectomy |
If there is a tumor of the adrenal gland we have to remove the glass and then we have to put patient on hormone replacement therapy for steroids and Catecholamines |
|
|
What is catecholamines |
Epinephrine and nor epinephrine |
|
|
What does the adrenal glands secrete |
Outer part called cortex which secretes steroids to cope with stress
Interpart called medulla which secretes Catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine |
|
|
What if there is only a tumor of the adrenal medulla |
We call it " pheochromocytoma" which secretes alot.of. epi and nor which can lead to very high BP in patient |
|
|
What position is the patient in |
Lateral with bean bags which holds the body in the lateral position when we vaccum the air out of the bag |
|
|
How do we protect the axillary nerves in this procedure |
With axillary rolls |
|
|
What is differently done position wise if its the right adrenal gland precedure |
Position is left lateral because the left side will touch the table |
|
|
When is the kidney rest elevated |
Kidnet rest is Elevated for the procedure to expose incision site |
|
|
When do you bring down the kidney rest |
At the end of the procedure the kidney rest is brought down to have the close proximity of the skin edges for closure |
|
|
What incision is done |
Flank The latimus dorsi external oblique internal oblique muscles are transected with the electrocautery grotas facia which surrounds the kidney and the adrenal gland is also open |
|
|
Which kidney is the perferred donor kidney and why |
Left side kidney is a preferred donor kidney because it has longer renal artery and renal vein which will facilitate to anastomosis of these vessels with the recipient iliac artery and vein |
|
|
What dont we remove |
We don't remove recipient diseased kidneys in order to avoid extra trauma to the patient recipients will have his or her kidney transplanted in iliac region |
|
|
What is the incision called |
Gibson |
|
|
What is zenker diverticulum |
Zenker's diverticulum is an esophageal pouch that develops in the upper esophagus that causes dysphagia difficulty swallowing and regurgitation of food |
|
|
How do we fix this |
Contemporary treatment of Zenker's diverticulum involves an "endoscopic approach" and division of the common party wall between the esophagus and diverticulum. Endoscopic approach refers to the approach to the diverticulum through the mouth. An "open approach", where an incision is made on the neck to expose and remove the diverticulum is rarely necessary. The success of the endoscopic approach is highly dependent on the experience of the surgeon. Endoscopic surgery generally leads to a shorter hospital stay and an earlier time to resuming food by mouth. In addition, laser surgery is able to completely divide more of the common party wall as compared to the endoscopic stapling techniques. |
|
|
What clamp do we use |
Then pennington clamp |
|
|
What suction is used |
Frazier |
|
|
What positon |
Trendelenburg positon |
|
|
What scope is used |

If endoscopically diverticuloscope |
|
|
What is the endoscopic treament of zenkers |
Goal is to divide the party wall and perform a diverticulotomy. Zenkers sac persists ( not resected)but food is now able to drain into the esophagus without collecting in the pouch |

