![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what does blood pressure measure
|
the force of the blood pushing against the side of its container, the vessel wall
|
|
|
what are 8 factors that effect blood pressure
|
age
gender race diurnal rhythm weight exercise emotions stress |
|
|
what are 5 factors in your body that determine what the bp is
|
cardiac output
peripheral vascular resistance volume of circulating blood viscosity elasticity of vessel walls |
|
|
using a cuff that is too narrow yeilds a falsely low/high bp?
|
high
|
|
|
there is a 5 mm Hg difference between the left and right arm bp. is this ok?
|
yes. a difference of 10-15 mm hg would be significant
|
|
|
how many mm Hg should you go above the brachial artery obliteration?
|
20-30 to avoid missing an auscultatory gap
|
|
|
use the bell or diaphragm for blood pressure?
|
bell. diaphragm will work but bell is better
|
|
|
what are the five korotkoff sounds
|
tapping
swooshing knocking abrupt muffling sielence |
|
|
systolic pressure
|
the maximum pressure felt on the artery during left ventricular contraction
first sound heard on bp measurement |
|
|
diastolic pressure
|
the elastic recoil or resting pressure that the blood exerts constantly between each contraction
the last sound heard on bp measurement |
|
|
pulse pressure
|
the difference between the systolic and diastolic and reflects stroke volume
|
|
|
systolic normas
|
normal: 119 or less
high normal: 120-139 high: 140 or more |
|
|
diastolic norms
|
normal: 79 or less
high normal: 80-89 high: 90 or more |
|
|
how much time do you seperate between bp's
|
2 mins
|
|
|
steps to taking bp
|
pt may be sitting or lying
feet must be flat palpate brachial artery center cuff 2.5 cm above brach artery palpate radial inflate until obliterated deflate wait 30 seconds place bell over brachial inflate 20-30 above obliteration deflate @ 2mm hg/heartbeat korotkoff sounds |
|
|
what does the allens test measure
|
lateral circulation of hand
|
|
|
how to do allens test
|
press ulner and radial
pump fist release one side look for blood return to hand repeat on other side |
|
|
what does the homans sign assess for
|
DVT
|
|
|
do you dorsally flex or pedally flex the foot for homans sign
|
dorsal
|
|
|
what is the S1 sound
|
first heart sound
closure of AV valves marks begining of systole |
|
|
what is the S2 sound
|
closure of semilunar valves
signals end of systole |
|
|
what type of fever puts someone at risk for heart disease
|
rhuematic fever
|
|
|
what to assess for when doing HPI chest pain
|
progression
radiation quality onset relief measures |
|
|
what to assess for when doing HPI irregular heart beats
|
pounding feeling
skip a beat? |
|
|
what to assess for when doing HPI on SOB
|
orthopnea
|
|
|
what to assess for when doing HPI on cough
|
sputum
timing activity |
|
|
what is a common vauge sign of heart dz
|
fatigue
|
|
|
what to assess for when doing HPI on edema
|
location
pitting what brings it on |
|
|
what are s/s of arterial insufficiency
|
pain on activity in the calves
change in characteristics of skin pain is worse when legs are propped up |
|
|
crucial hx for cardio assessment
|
meds: beta blocker/caffeine
age occupation: standing/stress lipid levels |
|
|
risk factors for heart disease
|
diabetees
murmurs htn stroke obesity smoking |
|
|
landmarks for cardio assesment on chest
|
sternal notch
sternal angle (louis) xyphoid intercostal space midsternal line midclavicular line anterior axillary line PMI |
|
|
where to palpate on cardio assessment
|
aortic
pulmonic erbs tricusp mitral PMI |
|
|
where to palpate for cardio assessment
|
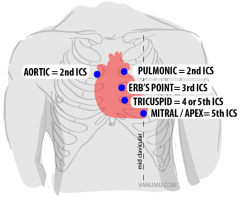
|
|
|
when you're listening to sammy's chest, if you heard buzzing, how would you describe it?
|
as looooovveeeee
psych its a thrill! not good |
|
|
diaphragm hears _____ sounds
|
high pitched
|
|
|
bell hears ______ sounds
|
low pitched
|
|
|
S1 heart sound
|
closure of tricuspid and mitral valve
|
|
|
S2 heart sound
|
closure of aortic/pulmonic valve
|
|
|
where is S1 heard the loudest
|
at the apex
|
|
|
where is S2 heard the loudest
|
the base of the heart
|
|
|
1+ edema is..
|
mild pitting
slight indentatation no perceptible swelling |
|
|
2+ edema is...
|
moderate pitting
indentation subsides rapidly |
|
|
3+ edema is ...
|
deep pitting
indentation remains for a sort time leg looks swoll |
|
|
4+ edema is...
|
very deep pitting
indentation lasts a long time leg looks very swollen |
|
|
3 areas to asses with pulses
|
rate
rhythm quality |
|
|
1+ pulse is..
|
weak
|
|
|
2+ pulse is..
|
normal
|
|
|
3+ pulse is..
|
full
|
|
|
4+ pulse is..
|
bounding
|
|
|
locations to check pulses
|
carotid
brachial radial femoral popliteal posterior tibial dorsal pedis |
|
|
bell or diaphragm for bruits?
|
bell
|
|
|
what angle for JVD
|
45
|
|
|
how big should JVD be?
|
3 cm or less
|
|
|
what are the layers of heart muscle
|
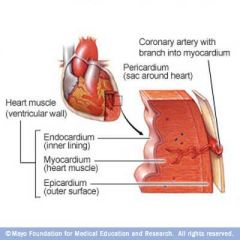
|
|
|
what are the heart chambers and valves?
|
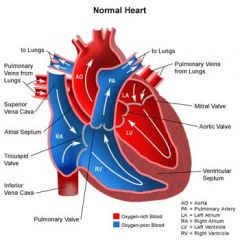
|
|
|
describe the route of pulmonary artery
|
blood leaves the right ventricle, bifurcates, and carries the venous blood to the lungs
|
|
|
prevelance of heart disease
|
black>white
black women>black men white men> white women |
|
|
prevelence of smoking
|
white women>black women, latinas
black men=white men |
|
|
cool skin is associated with artery/vein dz
|
artery
|
|
|
leg ulcers occur with chronic arterial/venous dz?
|
both! gotchya
|
|
|
what is the cause of bi lateral edema?
|
systemic problem
|

