![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What causes Pericarditis (infected pericardium): |
CARDIAC RIND- Collagen Vascular disease Aortic aneurysm Radiation Drugs (hydralasine) Infections Acute renal failure Cardiac infarction Rheumatic fever Injury Neoplasms Dressler's syndrome |
|
|
Pericarditis infections are commonly caused by what pathogens? |
VIRAL pathogens- Coxsackie A & B, echo, adeno, mumps virus (most common)
bacterial pathogens- pneumoccoccus, streptococcus--> gram (-) sepsis |
|
|
Clinical presentation of acute pericarditis: |
*pericardial friction rub (leather squeak) -chest pain radiates from L heart to trapezius (worsens when supine & during inspiration) -dyspnea (shallow breathing to avoid pain) -fever -effusion compressing lung & bronchi |
|
|
ECG findings for acute pericarditis |
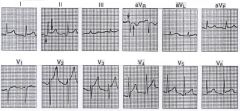
upsloping ST elevation in II, III, aVF, V2-V6
small downward PR deviation- in all except aVR (in PRecordial leads)
(pericarditiS- small p & a big S) |
|
|
Beck's triad is the manifestation of pericardial effusion w/ compression. What is Beck's triad? |
(cardiac tamponade)
3 D's: Distant heart sounds Distended jugular veins Decreased arterial pressure (hypotension--> dec Sv & CO) |
|
|
What is Cardiac tamponade (Beck's triad) caused by? |
fluid in the pericardium--> causes restricted heart contraction
(fluid may be due to trauma, pericarditis, myocardial rupture, uremia, hypothyroidism)
(if there is 200cc or > fluid, CXR will show cardiomegaly/distention) |
|
|
Pulsus paradox occurs in Beck's triad, what is pulsus paradox? |
when the systolic BP drops more than 10mmHg from expiration to inspiration |
|
|
Pericarditis should be treated if it leads to cardiac tamponade. How? |
pericardiocentesis |
|
|
Recurrent pericardial effusions may cause what? |
constrictive pericarditis = fibrosis & thickening of pericardium |
|
|
Clinical manifestations of constrictive pericarditis |
inc jugular venous pressure** diastolic pericardial knock hepatomegaly |
|
|
What may cause endocarditis (infected valves)? |
*prosthetic valves = Strep Viridans (most common)(or may be Staph epidermis) (endocarditis is common after valve surgery) -IV drug use= Staph Aureus -mitral valve prolapse (rare)
(know bacterial pathogens) |
|
|
Why is endocarditis dangerous? |
-bacterial valve damage -embolization of bland or septic fragments -hematologic seeding to remote sites -chronic antibody response, host rxn |
|
|
Endocarditis: diagnosis |
-+ bacterial blood cultures (strep viridans, staph aureus, staph epidermis) -visible vegetations or -2 major criteria or -1 major & 3 minor criteria (or 5 minor) |
|
|
Major Criteria for Endocarditis diagnosis |
-+ blood culture (2 or more + drawn 12 hrs apart) -visible vegetative lesions on echo (perivavlular abcess) -new valvular regurgitation |
|
|
Minor criteria for endocarditis diagnosis: |
-fever -vascular phenomena: emboli, stroke, splinter (conjunctiva) hemorrhages, anemia -immunologic phenomena: rheumatoid factor, Roth's spots, Osler's nodes, renal inflammation -thickened valves on echo w/o clear vegitations |
|
|
How is endocarditis treated? |
*antibiotics specific to the bacterial pathogen
-surgical excision of valve if causing bacteremia, if large vegetations, perivalvular abcess, recurrent emboli or severe valve destruction
|
|
|
Causes of Myocarditis (infected myocardial tissue) |
*VIRAL (Coxsackie sp- most common)
-parasitic (Chagas disease) = rare |
|
|
Clinical presentation of myocarditis |
-acute systolic LV dysfunction (seen on echo) -rapidly progressing CHF -cardiac arrhythmias (& other viral symptoms) |
|
|
Myocarditis: tx |
-tx symptoms (not virus)
-CHF- diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blocker -LV assist devices |

