![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CA derivative
|
A cmpd that can be hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions to give related CA: can all be conceptually derived by replacing a small part of the CA structure w other groups
|
|
|
All CA derivatives contain
|
a carbonyl group except nitriles
|
|
|
The cyano group of nitriles reactivity resembles
|
a carbonyl group
|
|
|
Esters are named as derivatives of their parent CA by
|
the group attached to carb O named first as simple alkyl or aryl group followed by name of parent carboxylate
|
|
|
Substitution is indicated by numbering
|
the acid portion of the ester in CA nomenclature starting w carbonyl as C-1 (substitutive) or w adjacent as a-position (common)
|
|
|
primary vs secondary vs tertiary amide
|
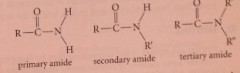
|
|
|
Substitution on nitrogen in secondary & tertiary amides is designated w
|
the letter N italicized or underlined
|
|
|
lactams
|
cyclic amides
|
|
|
gamma-lactam
|
five membered ring
|
|
|
beta lactam
|
four membered ring
|
|
|
Imides
|
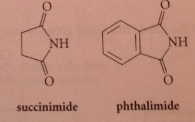
nitrogen analogs of anhydrides
|
|
|
priorities for citing principal groups in a CA derivative
|
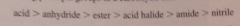
|
|
|
The nitrile bond length is ___ than the C=_C bond length
|
shorter (smaller atoms)
|
|
|
In an amide, both the carbonyl C and the amide N have
|
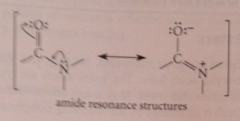
trigonal planar bonding due to db character
|
|
|
Which predominates in secondary/tertiary amides, E or Z conformation?
|
Z bc VDW avoided
|
|
|
The interconversion of E & Z forms of amides is
|
rapid @ room temp but slow compared to ordinary C-C sb rotation
|
|
|
Esters are polar mlcs but lack
|
the capability to donate H bonds like CA
|
|
|
Lower esters are
|
volatile, fragrant liquids that have lower densities than H2O - most insoluble in H2O
|
|
|
Most lower anhydrides & acid chlorides are
|
dense, water-insoluble liquids w acrid piercing odors & bp not very diff. from those of other polar mlcs of about the same mlclr mass/shape
|
|
|
Simplest anhydride, formic anhydride & simplest acid chloride, formyl chloride are
|
unstable, cannot be isolated under ordinary conditions
|
|
|
Nitriles are
|
polar, high bp
|
|
|
Is acetonitrile miscible w h2o?
|
yes
|
|
|
higher nitriles soluble in h2o?
|
no
|
|
|
useful polar aprotic solvent
|
acetonitrile
|
|
|
The lower amides are
|
water-soluble, polar mlcs w high bp
|
|
|
primary & secondary amides like CA tend to associate into
|
H-bonded dimers or higher aggregates in the solid state, pure liquid, or solvents that do not form H bonds
|
|
|
along a series in which H in primary amides replaced by methyl groups, bp
|
decrease w inc substitution
|
|
|
Esters are readily differentiated from CA, aldehydes or ketones by
|
unique ester carbonyl absorption at 1735-1745 cm-1
|
|
|
Lactones, lactams & cyclic anhydrides like cyclic ketones have
|
carbonyl absorption frequencies that inc significantly as ring size dec
|
|
|
Anhydrides + some acid chlorides have
|
two carbonyl absorptions due to symm + unsymm stretching of carbonyl
|
|
|
carbonyl absorptions of amides occur at much ___ freq than other carbonyl cmpds
|
lower
|
|
|
The C-=N stretching absorption of nitriles occurs in the triple bond region and are ___ than the C-=C absorptions of alkynes
|
stronger: large bond dipole of C-N triple bond @ higher frequencies
|
|
|
The a-proton resonances of all CA derivatives are obesrved in the
|
1.9-3 region of proton NMR spectrum
|
|
|
In esters, the chem shift of protons on the alkyl C adjacent to the carboxylate O are 0.6 ppm ___ than analogous proton in alcohols and ethers
|
greater due to electroneg character of carbonyl group
|
|
|
N-alkyl protons of amides have chem shifts in the ___ chem shift region
|
2.6-3
|
|
|
NH proton resonances of primary/secondary amides are observed in the
|
7.5-8.5 region
|
|
|
the resonances for protons like CA OH protons are sometimes
|
broad: slow chem exchange w protons of other protic substances (like moisture) & unresolved splitting w 14N, which has a nuclear spin
|
|
|
Amide NH resonances can be washed out by
|
exchange w d2o
|
|
|
The two N-methyl groups in N,N-dimethylacetamide have
|
diff. chem shifts & appear as 2 closely spaced singlets: chem. nonequiv because of db character = smaller rate internal rotation about this bond. time scale of NMR measurement so small that IR about CN bond appears frozen, so N-methyls behave like substituents on a db (one is cis and one is trans)
|
|
|
13 CNMR: carbonyl chem shifts of CA derivatives in
|
165-180 range like CA
|
|
|
chem shifts in 13C NMR are in
|
115-120 range but greater than those of acetylenic carbons
|
|
|
CA derivatives are weakly
|
basic: can be protonated on carbonyl O by strong acids
|
|
|
Nitriles are weakly
|
basic at nitrogen
|
|
|
The basicity of an ester is ___ as the basicity of the corresponding CA
|
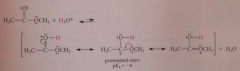
the same
|
|
|
amides are considerably more ___ than other CA derivatives
|
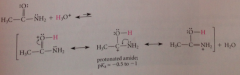
basic: reflects reduced electroneg of N relative to O -
|
|
|
Both esters & amides protonate on the
|
carbonyl oxygen
|
|
|
protonation of esters on the carboxylate oxygen or of amides on the nitrogen would
|
give a cation that is not resonance stabilized & destabilized by e-attracting polar effect of carbonyl group
|
|
|
Nitriles are very weak ___
|
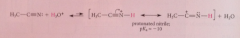
bases
|
|
|
rxn of CA & derivatives as Bronsted base is reaction type
|
1a: often first step in acid-catalyzed rxns of CA derivatives
|
|
|
As with CA, the major carbonyl group rxn of CA derivatives is a reaction of type
|
1b
|
|
|
Acyl substitution
|
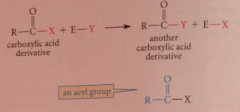
substitution at the carbonyl C: acyl group transferred between x and y group
|
|
|
addition rxn of nitriles
|
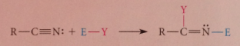
sometimes stable prod, usually react further
|
|
|
All CA derivatives undergo hydrolysis
|
cleavage rxn w h2o to yield CA
|
|
|
Saponification of esters
|
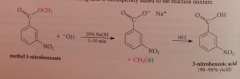
Cleavage w hydroxide ion to yield carboxylate salt and alcohol - CA formed when strong acid added
|
|
|
Mech ester saponification
|
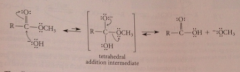
rxn nuc hydroxide ion @ carbonyl C to give tetrahedral addition intermediate from which alkoxide ion expelled and reacts w acid to give carboxylate salt & alcohol
|
|
|
Mech 2
|
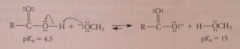
equilibrium lies to the right bc CA is a much stronger acid than methanol - Le Chateliers principle: rxn removes CA from equilibrium as salt driving hydrolysis to completion
|
|
|
Is saponification reversible?
|
No
|
|
|
Saponification solvent
|
can be alcohol despite alcohol as a prod
|
|
|
Acid catalyzed ester hydrolysis
|
esters hydrolyzed to CA in aq. soln of storng acid - mostly slow, excess h2o (esters insoluble)
|
|
|
Saponification followed by acidification is more convenient because
|
it is faster, irreversible, carried out in water & variety of solvents even alchols
|
|
|
Saponification mechanism
|
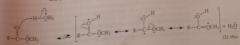
reverse of mechanism of acid-catalyzed esterification - ester first protonated by acid catalyst
|
|
|
Saponification mech 2
|
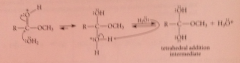
h2o as nuc reacts at carbonyl carbon, loses proton to give tetrahedral addition intermediate
|
|
|
Mechanism acid-catalyzed hydrolysis 3
|
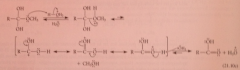
protonation of leaving O - lose group - protonated CA from which proton removed to give CA itself
|
|
|
Diff btwn acid-catalyzed hydrolysis & ester saponification
|
in ACH, carbonyl C reacts w weak nuc h2o bc carbonyl O protonated. In base, carbonyl O unprotonated, so stronger base than h2o required to react at carbonyl C. acid catalyzes ester hydrolysis, but base is consumed in rxn. saponification is irreversible
|
|
|
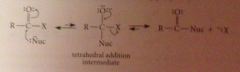
Nucleophilic acyl substitution mechanisms
|
substituting group reacts as nuc at carbonyl C - nuc approach the carbonyl C from above/below plane of carbonyl group, first interacting with n* MO of carbonyl group - tetrahedral intermediate - LG expelled departing from above or below plane of new carbonyl group
|
|
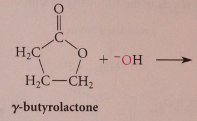
Lactones
|
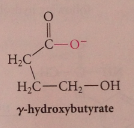
cyclic esters - undergo saponification - converted into carboxylate salt of corresponding hydroxy acid
|
|
|
Upon acidification, the hydroxy acid forms, but if a hydroxy acid is allowed to stand in acidic solution,
|
it comes to equilibrium w the corresponding lactone
|
|
|
The formation of a lactone from a hydroxy acid is nothing more than an
|
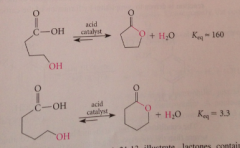
intramolecular esterification & is acid catalyzed
|
|
|
Lactones containing five and sex membered rings are ___ at equilibrium
|
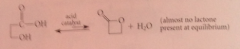
favored over corresponding hydroxy acids
|
|
|
amides can be hydrolyzed to CA & ammonia or amines by
|

heating them in acidic or basic solution
|
|
|
In acid, ___ drives the hydrolysis equil. to completion
|
protonation of the ammonia or amine prod
|
|
|
The amine can be isolated by
|
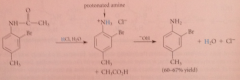
addition of base to the reaction mixture following hydrolysis
|
|
|
The conditions for acid & base-promoted amide hydrolysis are more ___ than corresponding rxns of esters
|
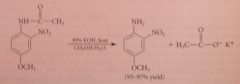
severe - amides are less reactive than esters
|
|
|
Mechanism of amide hydrolysis
|
nuc acyl substitution
|
|
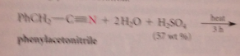
Nitriles are hydrolyzed to CA & ammonia by
|
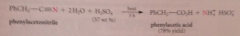
heating in strongly acidic or strongly basic solution
|
|
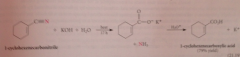
nitriles hydrolyze more ___ than esters & amides
|

slowly (requires more severe conditions)
|
|
|
Mechanism nitrile hydrolysis in acidic solution
|

protonation of the nitrogen, making nitrile C much more electrophilic
|
|
|
Mechanism nitrile hydrolysis in acidic solution 2
|
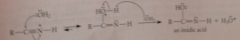
nuc rxn of h2o at nitrile C + loss of proton gives imidic acid intermediate
|
|
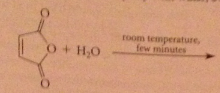
acid chlorides and anhydrides react rapidly w h2o even in absence of acids/bases
|
|
|
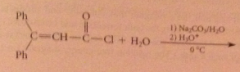
|
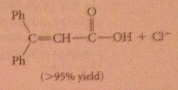
hydrolysis of acid chlorides/anhydrides almost never used to prepare CA bc usually prepared from acids
|
|
|
reactivities of carboxylic acid derivatives in nuc acyl sub rxns
|

|
|
generalized nuc sub rxn free energy diagram
|
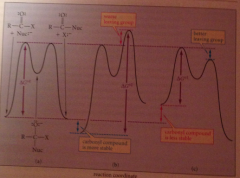
assume reactants/prod of comparable stability
|
|
|
How does the stability of the carbonyl cmpd affect the rate of carbonyl sub. rxn?
|
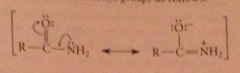
An amide is stabilized by the resonance interaction of unshared e pair of N w carbonyl group, inc energy diff btwn amide & tetrahedral addition intermed in which no resonance
|
|
|
How does the LG ability of X affect rate carbonyl sub rxn?
|
the difficulty in expelling a basic LG reflected in a higher free-energy barrier for the 2nd step => rate limiting
|
|
|
delta G for amide hydrolysis
|
diff btwn standard free energy of RLS & starting amide
|
|
|
Amide hydrolysis is a particularly __ rxn
|
slow
|
|
|
Why are prod less stable than reactants?
|
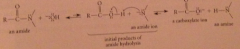
LG is more basic than nuc (last ionization & protonation drives base-promoted amide hydrolysis to completion)
|
|
|
What governs the reactant-stabilization effect?
|
The amide nitrogen's ability to donate e by resonance
|
|
|
Amides in which resonance is absent are
|
quite reactive
|
|
|
Esters are also stabilized by resonance
|
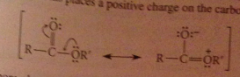
places pos charge on carboxylate o
|
|
|
Why is resonance interaction less important in an ester than an amide?
|
O is more electroneg than N
|
|
|
Why are esters more reactive than amides?
|
An alkoxide ion is much less basic than an amide ion
|
|
|
Why are acid chlorides stabilized much less by resonance than esters or amides?
|

Poor overlap of chlorine 3p orbital with carbon 2p orbital and polar effect of Cl destabilizes the carbonyl cmpd through unfavorable interaction of C-Cl bond dipole w partial pos charge on carbonyl C
|
|
|
LG effect in hydrolysis of an acid chloride
|
Cl is a weak base: decreased TS energy so first step (rxn w nuc) becomes RLS = much smaller overall delta G
|
|
|
Resonance stabilization of anhydride more important than in acid chloride but less important than an ester
|
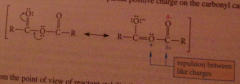
repulsion btwn pos charge on carboxylate O & partial pos charge on carbonyl C
|
|
|
LG in an anhydride
|
carboxylate anion more basic than Cl, less than alkoxide
|
|
|
Stabilization of the carbonyl cmpd ___ reactivity
|
decreases
|
|
|
Increasing reactivity
|
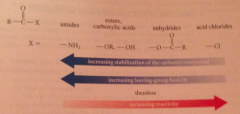
|
|
|
Why are reactions of nitriles in base slower than those of other acid derivatives?
|
N is less electroneg than O, accepts additional e less readily - nitriles have low basicity
|
|
|
What form of nitrile reacts w nuc in acid soln?
|
protonated - so little that rxn rate is small
|

