![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gill arches AKA?
|
Branchial arches
Pharyngeal arches |
|
|
What cranial nerves did fish originally have?
|
I (olfaction), II (vision), VIII (balance/hearing)
|
|
|
Where were fish jaws derived from embryologically?
How is the jaw supported? Embryonic origin? |
Jaw derived from gill arch 1
Supported by hyoid-like bones derived from Arch 2 |
|
|
Divide the cranium into three sections. What does each section contain?
|
Neurocranium: brain (occipital, parietal, frontal, temporal bones)
Basicranium: Ethmoid (Olfactory), Sphenoid (Optic), Petrosal Temporal (Otic) ganglia Viscerocranium: sphenoid, incus ,maxilla, malleus, hyoid, thyroid, cricoid, arytenoid, styloid process Viscerocranium |
|
|
Bones of calvaria grow via ___________
|
intramembranous development (NCC important in forming; somitomeres too)
|
|
|
Bones of basicranium grow via ___________
|
endochondral bone development
|
|
|
Neural Crest Cells contribute to which region of the cranium?
|
Viscerocranial structures
|
|
|
What could failure of ordered neural crest migration result in?
|
Congenital defects:
NCC migration required for development of bones and connective tissue (Could have problem in the development of vessels!) |
|
|
What are somitomeres in relation to somites?
What role do somitomeres play in embryonic development? |
Somitomeres are premature somites (presomites)
Somitomeres (develop into somites?) and migrate to form muscles (extraocular, mm of mastication, stylopharyngeus, mm of pharynx) |
|
|
What specific embryonic layer are somites derived from?
|
Paraxial mesoderm (form muscles)
|
|
|
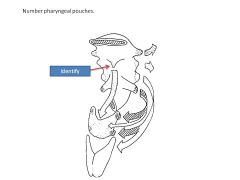
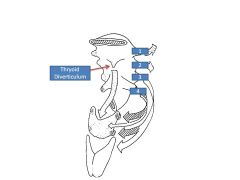
What is foramen cecum a remnant of?
|
Remnant of thyroid diverticulum
Thyroid diverticulum migrates to form thyroid at same time tongue migrates upward |
|
|
Which aortic (pharyngeal) arch does the branchiocephalic trunk form from?
|
4
|
|
|
Which aortic (pharyngeal) arch does the aortic arch form from?
|
4
|
|
|
Which aortic (pharyngeal) arch does the common carotid form from?
|
3
|
|
|
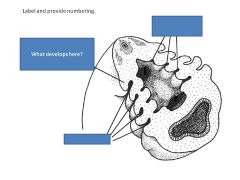
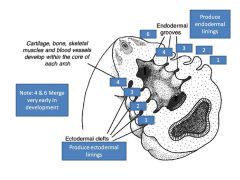
Pharyngeal Arch 1:
Arch Skeleton Cranial Nerve Muscles Pouch Derivatives |
1:
Arch skel: Mandible, maxilla, palatine, zygomatic, sphenoid (part), temporal (part), maleus, incus CN V Muscles: Mastication, jaw opening mm, ant digastric, mylohyoid, tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini Pouch derivs (LININGS): eustachian tube, ear canal, middle ear |
|
|
Pharyngeal Arch 2:
Arch Skeleton Cranial Nerve Muscles Pouch Derivatives |
Arch Skel: Hyoid (part), stapes, styloid process
CN VII Muscles: Facial expression, stapedius, stylohyoid, post digastric Pouch Derivs (LINING): Palatine Tonsils |
|
|
Pharyngeal Arch 3:
Arch Skeleton Cranial Nerve Muscles Pouch Derivatives |
Arch: Hyoid
CN IX Muscles: Stylopharyngeus Pouch derivs (LININGS): Thymus, parathyroid |
|
|
Pharyngeal Arches 4,6:
Arch Skeleton Cranial Nerve Muscles Pouch Derivatives |
Arch Skel: Laryngeal Cartilages
CN X Muscles: Pharyngeal constrictors, mm of larynx, cricothyroid, palatopharyngeus, palatoglossus Pouch derivs (LINING): part of parathyroid |
|
|
What are the symptoms of DiGeorge Syndrome? How can each be symptom be explained embryoligically?
|
DiGeorge Syndrome:
-Facial abnormalities: small jaw, cleft palate (arch 1 issue) -Deficiencies or absence of thymus and parathyroid glands (no thymus-->no mature T cells; no parathyroid-->low calcium levels): arch 3 problem, maybe arch 4 too -Cardiac abnormality (persistent truncus arteriosus) due to septation issue ALL ORIGINATE from pharyngeal arches; problems in their migration! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

