![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
intervertebral foramina
|
transmit the spinal nerves from the vertebrae
|
|
|
What innervates the deep muscles of the back and the skin of the back; Also posterior head and neck?
|
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
|
|
|
Extrinsic back (superficial and intermediate) and
Upper & Lower limbs are NN by what? |
ventral rami of spinal nerves
|
|
|
*dermatome
|
region of skin NN by a single spinal nerve
|
|
|
Is the vertebral column a part of the axial or appendicular skeleton?
|
axial, which also includes the cranium, rib cage, sternum; appendicular is all other bones
|
|
|
vertebral column tapers at which vertebra
|
SII
|
|
|
primary curves of the vertebral column
|
thoracic kyphosis and sacral ky; secondary are cervical and lumbar
think: primary, developed first |
|
|
hunchback v.s. swayback
|
excessive thoracic kyphosis (contributing: poor posture, compression fracture due to osteoporosis)
v.s. excessive lumbar lordosis (contributing: poor postural habit, muscle imbalances (weak abdominal muscles), large abdomen (obesity and pregnancy)) |
|
|
scoliosis
|
-lateral curvature of the spine in the frontal plane; always associated with rotation
-It causes a rib hump on convex side when a person bends forward (posterior view) -The spinous processes point toward the concavity of the abnormal lateral curvature |
|
|
scoliosis can result from:
|
-congenital disorders (e.g. hemivertebra)
-muscular disorders (cerebral palsy, poliomylitis) -idiopathic (unknown cause) |
|
|
spina bifida
|
vertebral arch open; s.b. occulta, commonest: asymptomatic, tuft of hair
|
|
|
type of joint for vertebral bodies and intervertebral disk
|
symphysis (secondary cartilaginous)
|
|
|
zygopaphysial joints are what type of joints?
|
synovial, fluid filled; inner synovial membrane produces nutrient rich fluid and outer fibrous membrane confers pain (nociception) and proprioception
|
|
|
inferior and superior to the vertebral bodies lies ___, before the intervertebral disk
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
annulus fibrosis composed of what?
|
layers of (fibrocartilage) concentric laminae, which consist of fibers which alternate directions for strength
|
|
|
nucleus pulposis is an embryonic remnant of what?
|
notocord
|
|
|
In what regions is the anterior part of the intervertebral disc is thicker than the posterior?
|
cervical and lumbar
|
|
|
a herniated L4-L5 intervertebral disk likely compress which spinal nerve?
|
L5 spinal nerve
|
|
|
joints of Luschka
|
-Uncovertebral joints, C3-C6
-Site of arthritic changes (spur formation) |
|
|
ligamentum flava
|
-between laminae
-made of mostly elastic fibers, therefore resists flexion & aids in extension |
|
|
What aspect of intervertebral disk is vulnerable to herniation?
|
posterolateral
|
|
|
Regional variation in articular facet planes: cervical
|
-region of most mobility
-flexion, extension, lateral bending, rotation -this region allows most flexion |
|
|
Regional variation in articular facet planes: thoracic
|
lateral bending, rotation, limited flexion extension
|
|
|
Regional variation in articular facet planes: lumbar
|
flexion extension, lateral bending, limited rotation
|
|
|
1/2 of all cervical roation is permitted by what one joint?
|
AA joint
|
|
|
nodding occurs mainly due to what joint?
|
atlantoccipital joint
|
|
|
rupture of the transverse ligament is likely to cause what?
|
spinal cord compression
|
|
|
tectorial membrane is an extension of what?
|
posterior longitudinal ligament
|
|
|
AA joint is what type of joint?
|
synovial
|
|
|
How many sacral vertebrae present in lumbarization?
|
4
|
|
|
How many sacral vertebrae present in sacralization?
|
6
|
|
|
Scottie dog
|
-neck: pars interarticularis
-eye: pedicle -ear: superior articular process -head & nose: transverse process -legs: inferior articular processes -body: spinous process |
|
|
spondylolysis
|
-scottie dog has a collar in oblique radiograph
-fracture of pars interarticularis |
|
|
spondylolisthesis
|
-scottie dog is decapitated
-bilateral fracture of par interarticularis -anterior shift of vertebra relative to the one below |
|
|
spinal stenosis
|
-abnormal narrowing of vertebral foramina
-may cause spinal cord or spinal nerve compression |
|
|
vertebral a. passes through what in cervical vertebrae
|
transverse foramina of C6-C1, * skipping the transverse foramen of C7
|
|
|
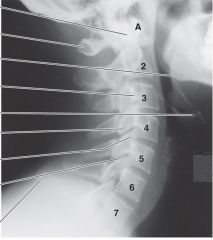
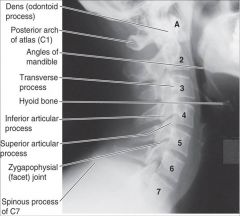
C3-C6
|
-bifid spinous processes &
-uncinate processes |
|
|
|
|
|
If you are checking a patient for a fracture of the dens, what view clearly demonstrates the atlas and axis vertebrae with the dens?
|
upper cervical AP radiograph
|
|
|
Superior costal facet articulates with what?
|
rib of same vertebral level, e.g. superior costal process of T2 articulates with 2nd rib
|
|
|
Articular facet on transverse processes articulates with what?
|
tubercle of corresponding rib
|
|
|
Ribs 11 & 12 articulate with what?
|
each articulates with a single costal facet of corresponding vertebra
|
|
|
unique processes of lumbar vertebrae
|
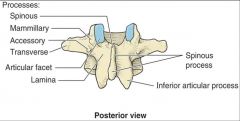
mammillary and accessory processes
|
|
|
what sacral structure is sometimes used to deliver epidural anesthesia?
|
sacral hiatus
|
|
|
Where does cauda equina reside?
|
sacral canal
|
|
|
Does sacrum contain intervertebral foramina?
|
yes, the sacral spinal nerves reside here
|
|
|
Where are the costal elements of cervical and lumbar vertebrae incorporated?
|
transverse processes
|

