![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DNA is ________-charged because of ______.
|
DNA is negatively charged bc of Phosphate groups
|
|
|
Purines vs Pyrimidines
|
PURe As Gold: PURine
A,G CUT the PY (pie): PYrimidines C, T, U |
|
|
This nucleotide is found exclusively in RNA.
|
Uracil
|
|
|
Which nucleotide bonds have two bonds? Which have three?
|
TA: 2 bonds
GC: 3 bonds |
|
|
Which amino acids are essential to PURINE synthesis?
|
GAG
Glycine Aspartate Glutamine |
|
|
What is required for PYRIMIDINE synthesis?
|
ATP, CO2, Glutamine
|
|
|
What is the rate limiting enzyme of pyrimidine synthesis?
|
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPSII)
|
|
|
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I vs II:
Location Pathway Nitrogen Source |
I:
Location--mitochondria PW: Urea cycle Nitrogen Source: ammonia II Location--cytosol PW: pyrimidine synthesis Nitrogen Source: glutamine |
|
|
Orotic aciduria:
Pathophys Presentation Treatment |
Inability to convert orotic acid to UMP (de novo pyrimidine synthesis PW) due to defect in either orotic acid phosphoribosyltransferase or orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase
Will find inc'd orotic acid in urine, megaloblastic anemia that does n't improve with admin of B12 or folic acid, no hyperammonemia Tx: Oral uridine |
|
|
Ribonucleotide reductase:
Role Relevant drug |
Ribonucleotide reductase:
UDP-->dUDP Inhibited by hydroxyurea, thus, no more pyrimidine synthesis |
|
|
Thymidylate synthase:
Role Relevant Drug |
Thymidylate synthase:
dUMP-->dTMP REQUIRES FOLIC ACID Inhibited by 5-fluorouracil (dec'd dTMP, dec'dp pyrimidine synthesis) |
|
|
Dihydrofolate reductase:
Role Relevant Drug |
Dihydrofolate reductase:
DHF-->THF (trihydrofolate = active folic acid) Active folic acid then feeds into thymidylate synthase for dTMP production Methotrexate (in eukaryotes) and Trimethoprim (in bacteria)both inhibit dihydrofolate reductase, causing dec'd dTMP and dec'd pyrimidine synthesis |
|
|
PRPP Synthetase:
Role Relevant Drug |
PRPP synthetase
Ribose 5-P-->PRPP Required for PURINE synthesis Inhibited by 6-mercaptopurine; blocks de novo purine synthesis |
|
|
What is the rate-limiting step in purine synthesis?
|
Glutamine PRPP aminotransferase (comes right after Ribose 5-P-->PRPP)
|
|
|
What is the rate-limiting step in pyrimidine synthesis?
|
CPS II
|
|
|
What are the sources of carbons in the formation of purines?
|
CO2
Glycine THF (aspartate and glutamine provide nitrogens) |
|
|
What are the sources of carbon in pyrimidine synthesis?
|
Aspartate
CO2 Glutamine for nitrogen |
|
|
What accounts for the positive charge of histones?
|
Lysine
Arginine |
|
|
What accounts for the negative charge of DNA?
|
Phosphate groups
|
|
|
How many adenine residues are found in a molecule of DNA if one strand contains A=2000, G=500, C=1500, and T=1000?
|
A pairs to T, one strand of DNA is double-strand
3000 adenine residues |
|
|
What strand of DNA nucleotides opposes this DNA strand:
5'-ATTGCGTA-3' |
5'-TACGCAAT-3'
|
|
|
Which drug:
Inhibits ribonucleotide reductase |
Hydroxyurea
|
|
|
Which drug:
Inhibits DHF reductase |
Trimethroprim
MTX |
|
|
Which drug:
Inhibits thymidylate synthase |
5-FU
|
|
|
Which drug:
Inhibits inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase |
Mycophenylate
|
|
|
Which drug:
Inhibits PRPP synthetase |
6-MC
|
|
|
What are the characteristic features of orotic aciduria?
|
Orotic acid in urine
Megaloblastic anemia not correctable by B12 or folate Failure to thrive No elevation of ammonia level |
|
|
Lesch-Nyan Syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation Treatment |
Defective purine salvage (breakdown) owing to absence of HGPRT, which converts hypoxanthine to IMP and guanine to GMP
results in excess uric acid production Findings: retardation, self-mutilation (lip biting), aggression, hyperuricemia, gout Tx: Allopurinol |
|
|
Adenosine deaminase deficiency:
Pathophys Presentation |
Excess ATP and dATP-->negative feedback-->inhibits ribonucleotide reductase (UDP-->dUDP)-->prevents DNA synthesis and thus dec'd lymphocyte count
Major cause of SCID (severe combined immunodef dz--happens to kids) |
|
|
What is a silent mutation?
|
Same aa, often change in 3rd position of codon (tRNA wobble)
|
|
|
What is a missense mutation?
|
Changed aa (conservative--new aa is similar in chemical structure)
|
|
|
What is a nonsense mutation?
|
Change results in EARLY STOP codon--STOP THE NONSENSE
|
|
|
How does UV light damage DNA?
|
Creates thymine dimers on same strand of DNA
|
|
|
Topoisomerase:
Role Relevant drug |
Creates nick in helix to relieve supercoils created during replication
Fluoroquinolones inhibit DNA gyrase--a specific prokaryotic topoisomerase Etoposide inhibits eukaryotic topoisomerase (cancer drug) |
|
|
Which eukaryotic DNA polymerase:
Repicates lagging strand |
alpha
|
|
|
Which eukaryotic DNA polymerase:
Synthesizes RNA primer |
alpha
|
|
|
Which eukaryotic DNA polymerase:
Replicates mitochondrial DNA |
gamma
|
|
|
Which eukaryotic DNA polymerase:
Replicates leading strand DNA |
delta
|
|
|
Which eukaryotic DNA polymerase:
Repairs DNA |
beta, epsilon
|
|
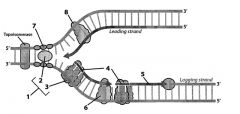
Label
|
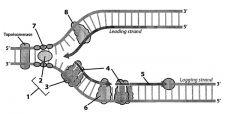
1. Primosome (lays down RNA primer); composed of DNA helicase and Primase
2. DNA Helicase 3. Primase 4. RNA primers made by 6 5. Okazaki frag 6. DNA polymerase 7. ssBP stabilizing DNA while complementary strand synthesized 8. DNA polymerase on leading strand |
|
|
Xeroderma pigmentosum:
Pathophys Presentation |
Lack nucleotide excision repair; can't repair thymidine dimers
Hypersensitive to UV light-->1000x inc'd risk of skin cancer |
|
|
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer:
Pathophys |
Inability to perform mismatch repair--unmethylated, newly synthesized string is recognized, mismatched nucleotides are removed, and gap is filled and resealed
|
|
|
How is double-stranded DNA repaired?
|
Nonhomologous end joining--brings together 2 ends of DNA fragments; no requirement for homology
|
|
|
Everything is synthesized __' to __'.
|
5' to 3' ALWAYS
|
|
|
Start codons
|
AUG
|
|
|
Stop codons
|
You are away
Yo go away You are gone UAA UGA UAG |
|
|
What is an operon?
|
Structural genes that are transcribed + promoter region + all regulatory genes
|
|
|
What are transcription factors?
|
Factors that must bind PROMOTER region (TATA box) in order for transcription to occur
|
|
|
What is an operator region?
|
Region of gene that binds repressor (stops transcription) or inducer (starts transcription) located between promoter region and start site
|
|
|
lac operon:
Role Regulation |
Controls expression of beta-galactosidase, which breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose
In presence of glucose, lac operon is turned off because lac repressor is bound In absence of glucose, CAP binds, but transcription of beta-galactosidase will only begin in presence of lactose Only when lactose is present and glucose is absent, will lac repressore release from lac operon. |
|
|
RNA polymerase I vs II vs III:
Role |
RNA pol I: makes rRNA
II: makes mRNA III: makes tRNA No proofreading function; ONLY present in eukaryotes |
|
|
rRNA is synthesized in the ______.
|
Nucleolus
|
|
|
mRNA is synthesized in the ______.
|
Nucleoplasm
|
|
|
tRNA is synthesized in the _______.
|
Nucleoplasm
|
|
|
What events must occur for RNA to leave the nucleus?
|
5' capping
3' poly A Splicing out of introns |
|
|
What structures removes introns from pre-mRNA?
|
Spliceosome!
|
|
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase:
Role |
"Matchmaker"; 1 per amino acid--scrutinizes aa before and after it binds to tRNA, then delivers it to ribosome
|
|
|
What are the steps of elongation in protein synthesis?
|
1. Aminoacyl-tRNA binds A site of ribosome (PREVENTED BY TETRACYCLINE)
2. Ribosomal rRNA catalyzes peptide bond formation via PEPTIDYL TRANSFERASE, transfers growing polypeptide to amino acid in A site of ribosome 3. Ribosome advances 3 nucleotides toward 3' end of RNA, moving peptidyl RNA to P site (translocation) |
|
|
How do eukaryotic ribosomes structurally differ from prokaryotic ribosomes?
|
Eukaryotes: 40S + 60S-->80S (EVEN EUK)
PrOkaryotes: 30S + 50S-->70S (ODD prO) |
|
|
Aminoglycosides:
MOA |
-micins
Inhibit formation of initiation complex (assembly of euk ribosome?) |
|
|
Chloramphenicol:
MOA |
Inhibits 50S peptidyltransferase (this enzyme catalyzed peptide bond formation in growing polypeptide being synthesized)
|
|
|
Macrolides:
MOA |
Bind 50S and block translocation
|
|
|
Clindamycin:
MOA |
Binds 50S and blocks translocation
|
|
|
Ribosomes are synthesized in the ______.
|
Nucleus (and then exported to cytoplasm)
|
|
|
Role of ubiquitin.
|
Attaches to defective proteins to tag them for breakdown (Proteasomal degradation)
|
|
|
Which antibiotic:
Inhibits 50S peptidyltransferase |
Streptogrammins
Chloramphenicol |
|
|
Which antibiotic:
Binds 50S, blocking translocation |
Macrolides
Lanezolide (sp?) |
|
|
Which antibiotic:
Binds 30S, preventing attachment of tRNA |
Tetracyclines
|
|
|
Which antibiotic:
Inhibits prokaryotic RNA polymerase |
Rifampin
|
|
|
Which antibiotic:
Inhibits prokaryotic topoisomerase |
Fluoroquinolones
|
|
|
Which antibiotic:
Inhibits prokaryotic dihydrofolate reductase |
Trimethoprim
|
|
|
What are the 3 mechanisms cell employ to break down proteins?
|
Ubiquitin mechanism
Lyososmal degradation mech Calcium-dependent enzyme mech |
|
|
What enzyme catalyzes peptide bond formation during protein synthesis?
|
Peptidyltransferase--a type of ribozyme
|
|
|
What enzyme matches amino acids to tRNA?
|
AMinoacyl tRNA synthetase
|
|
|
What are the mRNA stop codons?
|
UGA
UAA UAG |
|
|
What are the different RNA polymerases in eukaryotes?
|
RNA pol I: codes for rRNA
II: transcribed mRNA III: transcribes tRNA |
|
|
What amino acid frequently has more coding sequences in the mRNA than are represented in the peptide that is created from that mRNA?
|
Methionine--more AUG than methionine in a protein because AUG is the start sequence and it is commonly cleaved off
|
|
|
How is hnRNA processed before it leaves the nucleus?
|
5' cap
3' poly-A tail Splice out introns |
|
|
What is the characteristic sequence of the promoter region? What does a mutation in the sequence cause?
|
-25 TATA box
-75 CAT box Mutation-->dec'd amount of gene transcribed |
|
|
What enzyme is deficient in Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome?
What is the treatment? |
HGPRT
Tx: allopurinol |
|
|
What structural motifs allow for proteins to bind DNA?
|
Helix turn helix
helix loop helix Leucine zippers Zinc fingers |
|
|
Which drugs cause gynecomastia?
|
Some Drugs Create Awesome Knockers
Spironolactone Digitalis Cimetidine Alcohol Ketoconazole |

