![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
211 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of vaccine uses a live virus that has lost it virulence?
What are some examples of live virus vaccines? |
Live attenuated:
MMR Sabine Polio-oral VZV Yellow fever Smallpox Intranasal flu |
|
|
Which HIV medications cause pancreatitis?
|
Didanosine
Zlacitabine Stavudine Ritonavir |
|
|
Which HIV medications cause rash?
|
NNRTIs: nevirapine, delaviridine, efavirenz
Abacavir: hypersens rxn |
|
|
Which HIV medications cause peripheral neuropathy and lactic acidosis?
|
Lactic acidosis: NRTIs but not abacavir
Peripheral neuropathy: didanosine, zalcitabine, stavudine |
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Necrotizing granulomas of lung and necrotizing GN |
Wegener's
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Necrotizing immune complex inflammation of visceral/renal vessels |
Polyarteritis Nodosa
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Young Asian women |
Takayasu's
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Young asthmatics |
Churg-Strauss
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Infants and young children; involved coronary arteries |
Kawasaki Dz
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Most common vasculitis |
Temporal
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Associated with Hepatitis B infection |
Polyarteritis nodosa
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Antiepithelial cell antibodoies |
Pemphigus
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Anti-BM |
Goodpasture's
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Cough, conjunctivitis, coryza, fever |
Measles
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Councilman bodies |
Apoptotic liver cells seen in viral hepatitis (yellow fever)
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Green/yellow pigment just within the corneoscleral margin |
Wilson's Dz
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Anticentromere antibodies |
CREST
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Dementia, eosinophilic inclusions in neurons |
Lewy Bodies (PD)
Pick bodies (Pick's dz) |
|
|
Which pathology:
Anti-ds-DNA antibodies |
Renal Dz of Lupus
|
|
|
What type of antipsychotic is often the first line of treatment for psychosis?
Which antipsychotic should be reserved for severe, refractory cases because of agranulocytosis? |
Risperidone = first line (atypical antipsychotic)
Clozapein = agranulocytosis |
|
|
What part of the viral life cycle is blocked by amantadine?
|
Uncoating
|
|
|
What part of the viral life cycles is blocked by acyclovir?
|
Nuc synthesis (inhibits viral DNA polymerase)
|
|
|
In which causes of vaginal discharge/vaginitis will pH be high?
|
Bacterial vaginosis, trichomonas
|
|
|
In which causes of vaginal discharge/vaginitis will pH be low?
|
Physiologic, candida
|
|
|
Which antibiotics are safe during pregnancy?
|
PCNs, Cephalosporins
Macrolides Metronidazole after 1st trimester Nitrofurantoin |
|
|
Describe phase I drug metabolism.
|
Phase I (cyp450):
Reduction Oxidation Hydrolysis -yields slightly polar, water soluble metabolites Phase II: |
|
|
Primaquine:
Drug class |
Anti-malarial
|
|
|
Saquinavir:
Drug class |
Protease inhibitor
|
|
|
Betaxolol:
Drug class |
selective beta blocker (beta-1)
|
|
|
Prazosin:
Drug class |
alpha-1 antagonist
|
|
|
Thiopental:
Drug class |
Barbiturate
|
|
|
Tranylcypromine:
Drug class |
MAOI
|
|
|
Sertraline:
Drug class |
SSRI
|
|
|
Temazepam:
Drug class |
Benzo
|
|
|
Desipramine:
Drug class |
TCA
|
|
|
Captopril:
Drug class |
ACE-i
|
|
|
Busulfan:
Drug class |
Anti-cancer
|
|
|
Mortifloxacin:
Drug class |
Fluroquinolone
|
|
|
Zanamivir:
Drug class |
Anti-viral
|
|
|
Miconazole:
Drug class |
Anti-fungal
|
|
|
Drug AE:
Teeth discoloration |
Tetracycline
|
|
|
Drug AE:
Tendonitis |
Fluroquinolones
|
|
|
Drug AE:
Red man syndrome |
Vanco
|
|
|
Drug AE:
Gray baby syndrome |
Chloramphenicol
|
|
|
Drug AE:
Cartilage damage in children |
Fluoroquinolones
|
|
|
Drug AE:
Nephrotoxicity with cephalosporins, ototoxicity with loop diuretics |
Aminoglycosides (vanco, loop diuretics, cisplatin)
|
|
|
Drug AE:
Pseudomembranous colitis |
Ampicillin, clindamycin
|
|
|
Drug of choice for gonorrhea.
|
Ceftriaxone
|
|
|
Drug class for Lyme disease or Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
|
Tetracycline
|
|
|
Used to treat Giardia Lamblia
|
Metro
|
|
|
Can treat MRSA and C. diff colitis
|
Vanco or linezolid
|
|
|
Treatment for gram negative rods in patients with renal insufficiency
|
Azteonam
|
|
|
Effective against gram positive cocci, gram negative rods, and anaerobes
|
Meropenem
OR Imipenim with cilastatin |
|
|
Prophylaxis in AIDS patients against PCP pneumonia
|
TMP/SMX
Dapsone Pentamidine |
|
|
Used as solo prophylaxis against TB
|
Isoniazid
|
|
|
Developmental milestones:
Birth-15m |
Birth-3mo: Rooting reflex, orients to voice
3mo: holds head up, social smile 7-9mo: sits alone, crawls; stranger anxiety 15mo: Walks, Babinski disappears; few words, separation anxiety |
|
|
Developmental milestones:
12-36m |
12-24: Climbs stairs, stacks 3 blocks at 1 year, 6 blocks at 2 years (number of blockst stacked = age in years x 3); object permanence; 200 words and 2-word sentences at age 2
24-36mo: core gender identity, parallel play |
|
|
Developmental milestones:
30m-4y |
30-36-mo: Stacks 9 blocks; toilet training at 3 (pee at 3)
3 years: Rides tricycle (3 wheels), copies line of circle drawing; 900 words and complete sentences 4 years: simple drawings (stick figure), hops on 1 foot; cooperative play, imaginary friends, grooms self, brushes teeth, buttons and zips |
|
|
Dysplasia vs Anaplasia
|
Dysplasia--abnl growth with loss of cell orientation, shape, size; commonly preneoplastic
Anaplasia: abnl cells lacking differentiation, like primitive cells of same tissue; little or no resemblance to tissue of origin |
|
|
Histologic features of anaplastic cells
|
High nucleus:cytoplasm ratio
Prominent nucleoli Nuclear chromatin clumping Many mitotic figures |
|
|
Vimentin stain:
Utility in oncology |
Stains sarcomas (CT)
|
|
|
Desmin stain:
Utility in oncology |
Identifies rhabdomyosarcome or leiomyosarcoma (muscle)
|
|
|
Cytokeritin stain:
Utility in oncology |
Identifies carcinomas (epithelial cells)
|
|
|
Neurofilament stain:
Utility in oncology |
Identifies adrenal neuroblastoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor (stains neurons)
(more adrenal than CNS) |
|
|
Adenoma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Benign epithelial tumor
|
|
|
Papilloma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Benign epithelial tumor
|
|
|
Adenocarcinoma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Malignant epithelial tumor
|
|
|
Papillary carcinoma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Malignant epithelial tumor
|
|
|
Hemangioma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Benign BV tumor
|
|
|
Angiosarcoma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Malignant BV tumor
|
|
|
Leiomyoma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Benign smooth muscle tumor
|
|
|
Leiomyosarcoma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Malignant smooth muscle tumor
|
|
|
Rhabdomyoma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Benign skeletal muscle tumor
|
|
|
Rhabdomyosarcoma:
Benign/Malignant Tissue type |
Malignant skeletal muscle tumor
|
|
|
Mature vs immature teratoma:
General Differences in men/women |
Mature teratoma in women = benign tumor of >1 cell type
Mature teratoma in men = malignant tumor of >1 cell type Immature teratoma = malignant tumor of >1 cell type |
|
|
Down Syndrome:
Associated neoplasms |
ALL (we ALL fall Down)
AML |
|
|
Xeroderma pigmentosum:
Associated neoplasms |
Melanoma, BCC, squamous cell carcinoma of skin
|
|
|
Tuberous sclerosis:
Associated neoplasms |
Astrocytoma
Angiomyolipoma Cardiac rabdomyoma |
|
|
Actinic keratosis:
Associated neoplasms |
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Paget's Disease of Bone:
Associated neoplasms |
secondary osteosarcoma dn fibrosarcoma
|
|
|
Acanthosis nigricans:
Associated neoplasms |
(acanthosis nigricans = hyperpigmentation and epidermal thickening along nape, armpit)
Visceral malignancy (stomach, lung, breast, uterus) |
|
|
Achalasia:
Associated neoplasms |
Precursor to squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus
|
|
|
Sjogren's Syndrome:
Associated neoplasms |
B cell lymphoma
|
|
|
Ras oncogene:
associated neoplasms (be specific) |
K-RAS: Kolon, panKreatic, lung
H-RAS: bladder, kidney (Hematuria) N-RAS: melanomas, heme malignancies |
|
|
abl:
associated neoplasms |
CML
|
|
|
c-myc:
Associated neoplasms |
Burkitt's lymphoma (gain of function mutation)
|
|
|
bcl-2:
Associated neoplasms |
follicular and undiff lymphomas
(gain of function mutation) |
|
|
erb-B2:
Associated neoplasms |
Breast, ovarian, gastric carcinomas
(gain of function mutation) |
|
|
ret:
Associated neoplasms |
MEN II, III
(gain of function mutation) |
|
|
c-kit:
Associated neoplasms |
GIST--gastrointestinal stromal tumor
(gain of function mutation) |
|
|
Retinoblastoma:
Sporadic vs Heritable Pathophys |
Heritable: inherit one hit to Rb gene (loss of function), and acquire second hit
Sporadic: acquire both hits |
|
|
BRCA1 vs BRCA2
|
BRCA1: breast, ovarian cancer
BRCA2: breast cancer |
|
|
p53:
Role Associated neoplasms |
Involved at G1/S checkpoint and G2/M checkpoint;
Associated with most human cancers |
|
|
APC:
Associated neoplasms |
Familial adenomatous polyposis
|
|
|
CEA antigen:
Clinical utility |
GI tumor marker--colorectal, pancreatic, gastric; also breast and thyroid medullary carcinomas
|
|
|
alpha-fetoprotein:
Clinical utility |
HCC
Yolk sac tumor of testis (nonseminomatous germ cell) |
|
|
beta-hCG:
Clinical utility |
Hydatidiform moles
Choriocarcinomas |
|
|
Alkaline phosphatase:
Clinical utility |
Mets to bone, obstructive biliary dz, Paget's dz of bone
|
|
|
Tartate-resistant acid phosphatase:
Clinical utility |
TRP the hairy animal--Hairy cell leukemia (B cell neoplasm)
|
|
|
EBV:
Associated neoplasm |
Burkitt's lymphoma
|
|
|
HHV-8:
Associated neoplasm |
Kaposi sarcoma
|
|
|
Strep bovis:
Associated neoplasm |
Colon cancer
|
|
|
Schistosoma hematobium:
Associated neoplasm |
Bladder cancer
|
|
|
What neoplasm can result in Cushing's syndrome?
|
Small cel lung carcinoma
|
|
|
What neoplasm can result in SIADH?
|
Small cell lung carcinoma
|
|
|
What neoplasm can result in hypercalcemia?
|
Hypercalcemia via a PTH-related peptide; squamous cell lung carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, breast carcinoma
|
|
|
What neoplasm can result in polycythemia?
|
Renall cell carcinoma
Hemngioblastoma HCC Pheochromocytoma via EPO obvs |
|
|
What neoplasm can result in Lambert-Eaton syndrome (muscle weakness)?
|
Thymoma, small cell lung cancer; bc of ab's against presynaptic Ca2+ channels at N/M Jn
|
|
|
What neoplasms can result in gout?
|
Leukemia, lymphoma result in hyperuricemia due to excess nucleic acid turnover (cytotoxic tx)
|
|
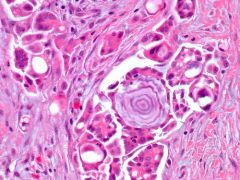
Associated neoplasms
|
Psamomma body (rings on a tree)
PSaMMoma Papillary (thyroid) adenoca Serous cystadenoca of ovary Meningioma Malignant mesothelioma |
|
|
When is ESR elevated?
|
Infections
Inflammn Cancer Pregnancy SLE |
|
|
When is ESR decreased?
|
Sickle cell (altered shape)
Polycythemia (too many) CHF (unknown) |
|
|
What cancers metastasize to brain?
|
Lots of Bad Stuff Kills Glia:
Lung Breast Skin (melanoma) Kidney (Renal CC) GI 50% of brain tumors are from mets! |
|
|
What cancers metastasize to liver?
|
Cancer Sometimes Penetrates Benign Liver
Colon > Stomach > Pancreas > Breast > Lung |
|
|
What cancer metastasize to bone?
Which are lytic? Blastic? |
PT Barnum Loves Kids
Prostate (blastic) Thyroid, Testes Breast (lytic and blastic) Lung (Lytic) Kidney |
|
|
What drugs are used to treat testicular cancer?
|
Eradicate Ball Caner
Etoposide Bleomycin Cisplatin |
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Hashimoto's thyroiditis |
Lymphoma
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Down Syndrome |
ALL, AML
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Plummer-Vinson Syndrome |
Squamous cell of esophagus
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Tuberous Sclerosis |
Cardiac rhabdomyoma
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Ataxis telangectasia |
Leukemia, lymphoma
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Paget's disease of bone |
Osteosarcoma, fibrosarcoma
|
|
|
Among men and women, compare the most common cancers and the most common cancers causing mortality.
|
Men:
Common: Prostate, lung, colorectal Mortality: Lung, prostate, colorectal Common (Women): Breast, lung, CRC Mortality: Lung, breast, CRC |
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Rb |
Retinoblastoma
Osteosarcoma |
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
DPC |
Pancreatic ca
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
p53 |
Almost all ca's
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
APC |
CRC
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
WT1 |
Wilms Tumor
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
BRCA1 and BRCA2 |
Breast, Ovarian
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Nitrosamines |
Esophageal, stomach ca
|
|
|
Associated tumor marker:
Colon Cancer |
CEA
|
|
|
Associated tumor marker:
Astrocytoma |
S100
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of hypercalcemia?
What cancers may cause it? |
Most common cause: primary hyperparathy
|
|
|
Associated neoplasm:
ACTH-->Cushing's |
Small cell lung ca
|
|
|
Associated tumor marker:
EPO-->polycythemia |
RCC
Hemangioblastoma |
|
|
Associated tumor marker:
ADH-->SIADH |
Small cell lung ca
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Asbestos |
Mesothelioma
Bronchogenic ca |
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Naphthalene |
Bladder transitional cell cancer
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Arsenic |
Squamous cellc ancer of skin
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
EBV |
Burkitt's
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
HPV |
Cervical, vulvar, anal, genital ca
|
|
|
Associated neoplasms:
Schistoma haematobium |
Squamous cell ca of bladder
|
|
|
Associated tumor marker:
Hepatocellular carcinoma |
AFP
|
|
|
Associated tumor marker:
Ovarian cancer |
CA125
|
|
|
Associated tumor marker:
Pancreatic cancer |
CA99
CEA |
|
|
Associated tumor marker:
Melanoma |
S100
|
|
|
Describe the events of the cell cycle and where cancer drugs act.
|
G1: synthesis of components needed for DNA synthesis
S phase: DNA synthesis; antimetabolites work here; as does etoposide G2: synthesis of component needed for mitosis; bleomycin and etoposide work here M: mitosis; vinca alkaloids and and and taxols work here |
|
|
What rapidly growing cells are targeted by cancer drugs?
|
Cancer
Hair follicles GI tract Bone Marrow |
|
|
Methotrexate:
MOA Use AE |
Folic acid analog that inhibits DHF reductase (dec'd DNA and protein synthesis)
Use: Leukemias, lymphomas, choriocarcinoma, sarcomas ABORTION, ECTOPIC PREGNANCY, RA AE: Myelosuppression reversible with leucovorin (FOLINIC ACID) "rescue" |
|
|
Which antibiotic shares its MOA with methotrexate?
|
Trimethoprim
|
|
|
5-flurouracil:
MOA Use |
Pyrimidine analog converted to 5F-dUMP-->complexes with folic acid; inhibits THYMIDYLATE SYNTHASE (dec'd dTMP-->dec'd DNA and protein synthesis)
Use: Colon cancer, BCC, synergy with MTX |
|
|
6-mercaptopurine:
MOA Use |
Purine analog-->dec'd de novo purine synthesis; act'd by HGPRTase
Use in leukemias, lymphomas (not CLL or Hodgkin's) |
|
|
This drug exhibits increased toxicity with allopurinol.
|
6-mercaptopurine
|
|
|
Cytarabine:
MOA Use |
Pyrimidine antagonist-->inhibition of DNA polymerase
AML, ALL |
|
|
Dactinomycin:
MOA Use |
Intercalates in DNA; use in pediatric tumors (dACT; children ACT out)--Wilms', Eqing's, rhabdomyosarcoma
|
|
|
Doxorubicin:
MOA AE |
Generates free radials
AE: cardiotoxic |
|
|
Daunorubucin:
MOA AE |
Generates free radicals to induce breaks in DNA
Cardiotoxic |
|
|
Bleomycin:
MOA Use AE |
Induces free radical formation-->breaks in DNA strands
Use in testicular cancer Pulm fibrosis |
|
|
Etoposide:
MOA Use |
Inhibits topoisomerase II-->inc'd DNA degradation
Use in testicular cancer |
|
|
Cyclophosphamide:
MOA AE |
Alkylating agent; interstrands DNA at guanine, must be act'd by liver
AE: Hemorrhagic cystitis |
|
|
Nitrosoureas:
Suffix MOA Use AE |
Nitro on your mustang-->ends in mustine
Alkylating agents Use: Cross BBB to tx brain tumors AE: CNS tox |
|
|
Busulfan:
MOA AE |
Alkylates DNA
Pulm fibrosis |
|
|
Vincristine:
MOA |
Block polymerization of MTs
|
|
|
Vinblastin:
MOA |
Block polymerization of MTs
|
|
|
Palitaxel:
MOA |
Palitaxel drug class end in -TAXols
Hyperstabilize polymerized MTs in M-phase so mitotic spindle can't break down TAXing to stay polymerized! |
|
|
What drugs interfere with microtubules?
|
Vincristine
Vinblastine Taxols Bendazoles (antihelminthic) Griseofulvin Colchicine |
|
|
Cisplatin:
MOA Use AE |
Cross-link DNA
Testicular, bladder ca Nephrotoxic, acoustic nerve damage |
|
|
Hydroxyurea:
MOA |
Inhibits ribonucleotide reductase-->dec'd DNA synthesis
|
|
|
Trastuzumab:
MOA Use |
MAB x HER2 (erb-B2) positive breast cancer
Cardiotoxic |
|
|
Imatinib:
MOA Use |
bcr-abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Use in CML, GIST |
|
|
Rituximab:
MOA Use |
MAB x CD20 for NHL (most B-cell neoplasms)
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Forms complex between topoisomerase II and DNA |
Etoposide
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Aklylates DNA, AE: pulm fibrosis |
Busulfan
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Fragments DNA, AE: pulm fibrosis |
Bleomycin
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Blocks purine synthesis, metabolized by xanthine oxidase |
6-MC
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Cross-links DNA Nephrotoxic, ototoxic |
Cisplatin, carboplatin
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Nitrogen mustart, alkylates DNA |
cyclophosphamide
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Folic acid analog that inhibits dihydrofolate reductase |
MTX
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Prevents tubulin disassembly |
Taxols
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Intercalates DNA, produces oxygen free radicals, cardiotoxic |
Doxarubacin, daunarubacin
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
DNA alkylating agents used in brain cancer |
Nitrosureas
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Prevents tubulin assembly |
Vincristine, vinblastine
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Inhibits thymidylate synthase-->dec'd nucleotide synthesis |
5-FU
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
SERM--blocks estrogen binding to ER+ cells |
Tamoxifen, raloxifene
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
MOA similar to acyclovir and foscarnet |
Citeravine
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
MOA similar to fluoroquinolones |
Etoposide
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
MOA similar to trimethoprim |
MTX
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
MAB against HER-2 |
Trastuzumab
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Free radical induced DNA strand breakage |
Bleomycin, -rubacins
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Inhibitor of PRPP synthetase |
6-MC
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Reversible with leucovorin |
MTX
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Treatment for choriocarcinoma |
MTX
Vinristine, vinblastine |
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Treatment for AML |
Cyterabine
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Treatment for CML |
Busulfan
Imatinib |
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Prevents breast cancer |
Tamoxifen, raloxifen
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Applied topically for AKs and BCCs |
5-FU
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Treatment for childhood tumors |
Dactinomycin
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Inhibits ribonucleotide reductase |
Hydroxyurea
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
AE: hemorrhagic cystitis |
Cyclophosphamide
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Ab against Philadelphia chromosome |
Imatinib
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
What are the potential side effects of prednisone? |
Cuhsing's
Immunosuppression Cataracts Acne Peptic ulcers Insomnia |
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Somatosensory from body |
VPL
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Communicates with prefrontal cortex |
MD (medial dorsal)
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Cerebellum (dentate nucleus) and basal ganglia-->motor cortex |
VL (ventral lateral)
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Trigemniothalamic and taste pathways to somatosensory cortex |
VPM
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Retina-->occipital lobe |
Lateral geniculate body
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Basal ganglia-->PFC, premotor, and orbital cortices |
Ventral Anterior (VA)
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Mamillothalamic tract-->cingulate gyrus |
Anterior nucleus
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Integration of visual, auditory, and somesthenic input |
Pulvinar nucleus
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Memory loss results if destroyed |
Medial Dorsal nucleus
|
|
|
Which thalamic nucleus:
Auditory info of inferior colliculus-->primary auditory cortex |
Medial geniculate body
|

