![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
142 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
HIV:
Structure GPs and roles RR5 vs X4 |
RNA virus (uses reverse transcriptase)
Diploid genome--2 molecules of RNA p24--capsid protein gp41: fusion and entry gp120--attachment to host T cell (these gp 's are envelope proteins) RR5--binds CCR5 and and CD4 on MACS X4--binds CXCR4 and CD4 on T cells |
|
|
Viral tropism
|
Which viruses cells can infect
|
|
|
Homozygous CCR5 vs Heterozygous CCR5 Hosts
|
Homozygous CCR5 hosts-->immune against HIV
Heterozygous CCR5 mutation-->Slower course |
|
|
HIV:
Diagnosis |
Screen: ELISA
Confirmatory: Western Blot |
|
|
Structural genes in HIV.
What do they code for? |
env: gp120 and gp41
gag: p24 pol: reverse transcriptase |
|
|
Diagnosis of AIDS
|
CD4+ <200 (normal 500-1500)
RIsk pneumocystis jiroveci infection! |
|
|
Classic opportunistic infections in patients with AIDS
|
Cryptococcal meningitis
Toxoplasmosis CMV encephalopathy CMV retinitis Thrush PCP pneumonia Shingles KAPOSI'S SARCOMA (HSV-8) |
|
|
Antibiotics given to AIDS patients based on CD4 count.
What are you trying to prevent? |
CD4+ at 200-->Bactrim to prevent PCP pneumonia (or Dapsone)
CD<100: Add azitrhomycin; worry about thrush, toxo, histo CD<50: Fluconazole if develop cryptococcal meningitis (?) |
|
|
Highly active antiretroviral therapy:
What is it? When is it used? |
2 nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) + 1 protease inhibitor
OR 2 NRTIs + 1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor AIDS-defining illness (PCP pneumonia) CD4+ below 350 |
|
|
Viral Proteases:
Suffix MOA AE |
NAVIR TEASE a proTEASE
-vir (saquinavir, ritonavir, etc.) HIV-1 protease cleaves mRNA into functional parts is inhibited by these drugs AE: GI intolerance, inhibit cyp450 (making HAART drugs last longer!) Lipodystrophy Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors:
MOA Examples AEs |
Competitively inhibit nucleotide binding to reverse transcriptase; need to be phosphorylated (activated) by thymidine kinase
Ex: Zidovudine (AZT), didanosine, zalcitabine AEs: BM suppression (reversed with EPO, G-CSF), peripheral neuropathy, lactic acidosis, rash, hepatosteatosis |
|
|
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors:
MOA Examples AEs |
Nevirapine, Efavirenz, Declaviridine
Binds reverse transcriptase at site different from NRTIs; do not require phosphorylation Never Ever Deliver nucleosides (NED) AEs the same as NRTIs: AEs: BM suppression (reversed with EPO, G-CSF), peripheral neuropathy, lactic acidosis, rash, hepatosteatosis |
|
|
Fusion inhibitor:
MOA Examples AEs |
Only one drug: EnFUvirtide (FU --> fusion)
Binds viral Gp41 subunit; inhibits fusion with CD4 cells (thus preventing entry and replication) AE: Hypersens rxn, inc'd risk bact pneumonia... |
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
SE: lactic acidosis |
NRTIs
|
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
SE: GI intolerance |
Protease inhibitors
|
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
SE: pancreatitis |
Ritonavir
Didenosine Zalcitabine Stavudine |
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
SE: megaloblastic anemia |
Zidovudine
|
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
SE: rash |
NNRTIs
|
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
SE: hyperglycemia, DM, lipid abnormalities |
Saquinavir
Indinavir |
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
SE: Bone marrow suppression |
Zidovudine
|
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
Give to pregnant women with HIV |
Zidovudine
|
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
Regimen for occupational HIV exposures |
Zidovudine
|
|
|
Which antiretroviral:
Combination of different classes of medication used to attack HIV at different point in its replication/infection cycle in order to control the infection and avoid resistance |
HAART
|
|
|
Which class of HIV drugs causes redistribution of fat into a buffalo hump on the back of the neck?
|
Protease inhibitors; saquinavir, ritonavir
|
|
|
Which virus:
Conjunctivitis or diarrhea |
Adenovirus
|
|
|
Which virus:
Fever, jaundice, black vomit |
Yellow Fever
|
|
|
Which virus:
Enlarged cell with owl's eye inclusions |
CMV
|
|
|
Which virus:
Identified with Pap smear |
HPV
|
|
|
Which virus:
Barking seal cough |
Croup/parainfluenza
|
|
|
Which virus:
Brassy cough |
RSV
|
|
|
Which virus:
Negri bodies |
Rabies
|
|
|
Which virus:
Hides in trigeminal ganglia |
HSV-1/2
VZV |
|
|
Which virus:
Diarrhea in children during winter months |
Rotavirus
|
|
|
Which virus:
Cause of common cold |
Rhinovirus
Coronavirus |
|
|
Which virus:
Downey cells |
EBV
|
|
|
Which virus:
Aseptic meningitis |
Echovirus
Coxsackie virus |
|
|
What causes a steeple sign on x-ray?
|
Parainfluenza
|
|
|
What causes a thumb sign on x-ray?
|
H. flu B (not seen a lot bc of immunizations)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for the different herpes viruses?
|
HSV1, HSV2, EBV, VZV all treated with cyclovir
CMV: ganciclivir, but if doesn't work, use foscarnet |
|
|
For what infections is interferon used?
|
HBV, HCV, Kaposi's
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
Inhibits CMV DNA polymerase |
Ganciclovir
Foscarnet |
|
|
Which antiviral:
Used in treatment for chronic HCV |
Ribavirin
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
Blocks viral penetration and uncoating |
amantidine and ramantidine
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
Treats both influenza A and B |
Zanamivir
Oseltamivir These inhibit neuraminidase (cell entry?) |
|
|
Which antiviral:
Second-line for CMV retinitis |
Foscarnet
|
|
|
Identify HBV status:
HBsAg Negative HBsAb Positive HBcAb Positive |
Recovery
|
|
|
Identify HBV status:
HBsAg Negative HBsAb Negative HBcAb Positive |
Window Phase
|
|
|
Identify HBV status:
HBsAg Positive HBsAb Negative HBcAb Positive IgM |
Acute
|
|
|
Identify HBV status:
HBsAg Positive HBsAb Negative HBcAb Positive IgG |
Chronic
|
|
|
Identify HBV status:
HBsAg Negative HBsAb Positive HBcAb Negative |
Immunized
|
|
|
Prion diseases:
What are they? |
Infectious protein particles
Mad cow, ataxia |
|
|
Normal flora:
Skin |
Staph epidermidis
|
|
|
Normal flora:
Nose |
S. epidermidis, Staph aureus
|
|
|
Normal flora:
Oropharynx |
Strep viridans
|
|
|
Normal flora:
Dental plaque |
Strep mutans (viridans)
|
|
|
Normal flora:
Colon |
Bacteroides > E coli
|
|
|
Normal flora:
Vagina |
Lactobacillus, colonized by E coli and Group B Strep
|
|
|
Which bug:
Ocean water shellfish Diarrhea |
Vibrio cholera
|
|
|
Which bug:
Reheated rice |
Bacillus
|
|
|
Which bug:
Meats, mayonnaise, custard Preformed toxin |
Staph aureus
|
|
|
Which bug:
Reheated meat |
Clostridium perfringens
|
|
|
Which bug:
Improperly canned foods (bulging cans) |
Clostridium botulinum
|
|
|
Which bug:
Undercooked meat |
E. coli
|
|
|
Which bug:
Poultry, meat, eggs |
Salmonella
|
|
|
Which bugs cause bloody diarrhea?
|
Campylobacter
Salmonella Shigella Enterohemorrhagic E coli Enteroinvasive E coli Yersinia enterocolitica C. diff Entamoeba histolytica |
|
|
Which bugs cause watery diarrhea?
|
Enterotoxigenic E Coli
Vibrio Cholera C. perfringens Protozoa (Giardia, cryptosporidium--in immunocomp'd) Viruses (rotavirus, adenovirus, Nowralk virus--notovirus) |
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Food poisoning as a result of mayonnaise sitting out too long |
Staph aureus
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Diarrhea caused by Gram negative nonmotile organism that does not ferment lactose |
Shigella
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Rice water stools |
V. cholera or enterotoxigenic E coli
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Diarrhea caused by a C or S-shaped organism |
Campylobacter
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Diarrhea transmitted from pet feces |
Yersinia
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Food poisoning resulting from reheated rice (Chinese food) |
Bacillus cereus
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Diarrhea caused by Gram negative motile organisms that don't ferment lactose |
Salmonella
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Most common cause of traveler's diarrhea |
Enterotoxic E coli
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Diarrhea caused by gram negative lactose fermenting bacteria, no fever |
E Coli
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Diarrhea caused by gram negative comma-shaped organism, no fever |
V cholera
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Diarrhea Recept ingestion of water from a stream |
Giardia or entameba histolytica
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Food poisoning from undercooked hamburger |
E coli O57A7
|
|
|
Treatment for anaerobic pneumonia.
|
Clindamycin
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Common cause of pneuomnia in immunocompromised patients |
PCP
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Most common cause of atypical/walking pneumonia |
Mycoplasma pneumonia
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Most common fungal infection of lung in Texas/Gulf Coast region |
Histo
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Common causative agent for pneumonia in alcoholics |
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Can cause interstitial pneumonia in bird handlers |
Chlamydia psittaci
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Often cause of pneumonia in patient with history of exposure to bats and bat droppings |
Histo
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Fungal cause of pneumonia in a patient who has recently visited Southern California, New Mexico, or West Texas |
Coccidioides
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Pneumonia associated with currant jelly sputum |
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Q fever |
Coxiella burnetti
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Associated with pneumonia acquired from air conditioners |
Legionella
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Most common cause of pneumonia in children 1 year old or younger |
RSV
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Most common cause of pneumonia in neonate (birth-28 days) |
E coli or GBS
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Most common cause of pneumonia in children and young adults, including college students, military recruits, and prison inmates |
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Common cause of pneumonia in patients with other health problems |
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Most common cause of viral pneumonia |
RSV
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Causes a wool-sorter's disease (life-threatening pneumonia) |
Bacillus anthracis
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Endogenous flora in 20% of adults |
Strep pneumoniae
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Common bacterial cause of COPD exacerbation |
H flu
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Common pneumonia in ventilator patients and those with cystic fibrosis |
Psueudomonas
|
|
|
Which infectious agent:
Pontiac fever |
Legionella
|
|
|
CSF findings of:
bacterial meningitis |
Inc'd pressure
PMNs Inc'd protein Dec'd sugar |
|
|
CSF findings of:
Fungal meningitis |
Inc'd pressure
Lymphocytes Inc'd protein Dec'd sugar |
|
|
CSF findings of:
Viral meningitis |
Normal or inc'd pressure
Lymphocytes Normal or inc'd protein Normal sugar |
|
|
CSF findings of:
TB meningitis |
Inc'd pressure
Inc'd lymphocytes Inc'd protein Dec'd sugar |
|
|
Which bugs are urease positive?
|
Paricular Killerse Have Urease:
Proteus Klebsiella H pylori Ureaplasma |
|
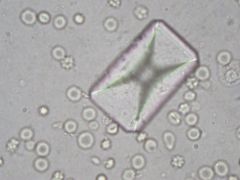
|
Struvite crystal
UREASE positive bacteria |
|
|
What is a ToRCH infection?
Specific bugs? Presentation? |
Microbes that pass from mother to fetus and result in deformation.
Toxoplasma--chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications Rubella--PDA, cataracts, deafness, purpura CMV: *MOST COMMON*--asyx but develop unilateral hearing loss HIV: recurrent infections, chronic diarrhea HSV: Temporal encephalitis, herpetic (vesicular) lesions Syphilis--stillbirth, hydrops, facial abnlts (notched teeth, saddle nose, short maxilla) O for Parvo: hydrops |
|
|
Causes of pelvic inflammatory disease.
Risks? |
Starts with cervicitis-->salpingitis (fallopian tubes), works its way upward
Risk of ectopic pregnancy, infertility, adhesions. TOp bugs: Chlamydia Neisseria |
|
|
Adolescent presents with cough and rust-colored sputum.
What does gram stain of sputum show? |
Typical strep pneumo; gam positive diplococci
|
|
|
HIV+ patient with a CD4 count of 25 presents with signs of meningitis. Examination of the CSF reveals a heavily encapsulated organism.
What is the organism? |
Cryptococcus
|
|
|
An older male patient has blood in his urine and renal stones.
Organism responsible for stones? |
Proteus
|
|
|
50 year-old patent recovered from abdominal surgery performed 2 days ago and has had an internal catheter in place since that time.
He now has a fever of 100º. Cause? |
UTI
|
|
|
What are the most common causes of UTI?
|
E coli
Proteus Staph saprophyticus Klebsiella |
|
|
What are the most common causes of pneumonia for the following patient populations:
6w-18y 18y-40y 40y-65y Elderly |
6w-18y: strep pneumo, chlamydia pneumonia, RSV
18y-40y: mycoplasma, strep pneumo, chlamydia 40y-65y: strep pneumo, h flu, anaerobes Elderly: strep pneumo, gram neg rods, anaerobes |
|
|
Pathology:
Signet ring cells |
Gastric adenoca
|
|
|
Pathology:
Nutmeg liver |
Right sided HF
|
|
|
Pathology:
Maternal elevations of AFP |
Anencephaly
Spina bifida Omphalocele Gastrischesis |
|
|
Pathology:
RBC casts in urine |
Acute GN
|
|
|
Pathology:
Currant-jelly sputum |
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Pathology:
Dog or cat bite |
Pasturella
|
|
|
What are the TORCH infections?
|
Toxoplasma
O--parvo Rubella CMV HIV/HSV Syphilis |
|
|
STD:
Clue cells |
Bact vaginosis
|
|
|
STD:
Painless genital ulcer |
Syphilis
|
|
|
STD:
Flagellated cells |
Trichomonas
|
|
|
STD:
Strawberry cervix |
Trichomonas
|
|
|
What CSF findings would you see in a patient with TB meningitis?
|
Inc'd Pressure, inc'd protein, dec'd sugar
Inc'd lymphocytes |
|
|
Most common cause of atypical/walking pneumonia.
|
Mycoplasma
|
|
|
Common causative agent for pneumonia in alcoholics.
|
Klebsiella
Anaerobes if aspiration pneumonia |
|
|
Can cause interstitial pneumonia in bird handlers.
|
Chlamydia psitecci
|
|
|
Often cause of pneumonia in patient with history of exposure to bats and bat droppings.
|
Histo
|
|
|
Fungal cause of pneumonia in patient who has recently visited Southern California, New Mexico, or West Texas.
|
Cocciodes
|
|
|
Pneumonia associated with currant jelly sputum.
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Most common cause of pneumonia in children 1 year or younger.
|
RSV
|
|
|
Most common cause of pneumonia in neonate (birth-28 days).
|
Group B Strep
E coli |
|
|
Most common cause of pneumonia in children and young adults--including college students, military recruits, and prison inmates.
|
Mycoplasma
|
|
|
Drug class:
Ritonavir |
Protease Inhibitor
|
|
|
Drug class:
Didanosine |
NRTI
|
|
|
Drug class:
Declaviridine |
NNRTI
|
|
|
Drug class:
Zidovudine |
NRTI
|
|
|
Drug class:
Abacavir |
NRTI
|
|
|
Drug class:
Lamivudine |
NRTI
|
|
|
Drug class:
Nelfinavir |
PI
|
|
|
Drug class:
Efavirenz |
NNRTI
|

