![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
139 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Carbachol:
Drug class |
Direct cholinergic agonist
|
|
|
Atropine:
Drug Class |
Cholinergic antagonist
|
|
|
Ipratroprium:
Drug Class |
Cholinergic antagonist
|
|
|
Benztropine:
Drug Class |
Cholinergic antagonist
|
|
|
Oxybutynin:
Drug Class |
Cholinergic antagonist
|
|
|
Glycopyrrolate:
Drug Class |
Cholinergic antagonist
|
|
|
Epinephrine:
Receptors affected |
alpha1, alpha2
beta1, beta2 |
|
|
Norepinephrine:
Receptors affected |
alpha1, alpha2
beta1 |
|
|
Dopamine:
Receptors affected |
D1=D2 > beta1 > alpha 1
|
|
|
Tertbutaline:
Receptors affected |
Beta2>beta1 (AGONIST)
|
|
|
Phenylephrine:
Receptors affected |
alpha1>alpha2
|
|
|
Doenepezil:
Drug class |
AChE-inhibitor (indirect cholinergic agonist)
|
|
|
Hexamethonium:
Drug class |
Nicotinic antagonist
|
|
|
Pralidoxime:
Drug class |
Regenerates cholinesterase ; impt for organophosphate poisoning
|
|
|
Agents that inhibit presynaptic uptake of NE
|
Cocaine
TCAs Amphetamines |
|
|
Loss of forearm pronation
|
Median nerve
|
|
|
Cannot abduct or adduct fingers
|
Ulnar nerve
|
|
|
Weak lateral rotation of arm
|
Suprascapular nerve (infraspinatus muscle)
Axillary nerve (via deltoid) contributes too |
|
|
Unable to abduct arm initial 10 degrees
|
Suprascapular nerve
|
|
|
Peptidoglycan:
Function |
Provides support, protects against osmotic pressure
Present in both gram poz and neg bacteria |
|
|
Crystal violet stain: purple
What is this staining? What does it identify? |
Gram-positive bacteria; stains peptidoglycan
|
|
|
Safranin counterstain: pink
What is this staining? What does it identify? |
Gram-negative bacteria; stains peptidoglycan
|
|
|
Acute phase cytokines:
Which are they? |
IL-1
IL-6 TNFalpha |
|
|
Bacterial cell wall serves as a surface antigen in ________ bacteria.
|
Gram positive
|
|
|
LPS acts as a surface antigen in _______ bacteria.
|
Gram negative
Note: LPS aka outer membrane aka Endotoxin |
|
|
Role of plasma membrane in bacteria.
|
Oxidative and transport enzymes
|
|
|
What is a periplasm?
Which class of bacteria has it? |
Periplasm = space between cytoplasmic membrane and peptidoglycan wall
Location of beta-lactamases! GRAM NEGS |
|
|
Beta-lactamases are located in ________.
|
Periplasm of gram negative bacteria
|
|
|
Function of capsules in bacteria.
Which specific bacteria have a capsule? |
Protects against phagocytosis
Some Killers Have Nice Shiny Bodies Step pneumo Klebsiella Haemophilus influenzae (B) Neisseria meningitdis Salmonella Group B Strep |
|
|
______ serves as antigens in vaccines.
|
Bacterial Capsules
|
|
|
Quelling test
|
Determines whether bug is encapsulated; if encapsulated bug present, capsule swells (Quelling-->swelling)
|
|
|
Role of pilus/fimbriae in bacteria.
|
Mediates adhesion of bacteria to cell surface
Sex pilus forms attachment b/t 2 bacteria during conjugation (exchange DNA) |
|
|
Organisms that form spores.
|
Bacillus (anthracis)
Clostridium (perfringens, tetanus) Coxiella burnetti |
|
|
Role of plasmids in bacteria.
|
DNA particles present in cytoplasm--contain genes for abx resistance, toxins
This DNA is separate from main DNA Exchanged during conjugation |
|
|
Role of glycocalyx in bacteria.
|
Mediates adherence to surfaces, esp foreign surfaces (indwelling catheters)
|
|
|
Teichoic acid is found in _____ and causes release of _____.
|
Teichoic acid found in gram positive bacteria
Induces TNF-alpha and IL-1 release |
|
|
Endotoxin is found in _____ and causes release of _____.
|
Endotoxin is unique to gram neg organisms and induces release of TNF-alpha and IL-1
|
|
|
How are bacteria that produce spores killed?
|
Autoclaving
|
|
|
Endotoxin:
Which bacteria have it? Region of endotoxin that mediates immune response What is the immune response? |
Endotoxin = LPS
cell wall of gram neg bacteria and listeria (exception bc it's gram poz!) Lipid A component of LPS-->macs act'd and release IL-1 (fever); TNF (fever, hemorrhagic necrosis), NO (vasodilation-->shock!) Complement: C3a-->releases histamine (hypotn, edema due to vasc perm-->anaphylaxis) C5a-->nphil chemotaxis Hageman factor-->DIC |
|
|
Endotoxin vs Exotoxin:
Location Site of DNA coding for it Fatality (low/high) Antigenicity (poor/good) |
Endotoxin vs Exotoxin:
Endotoxin: surface of gram neg and listeria; LPS Encoded by bacterial chromosome Low fatality (fever, shock, edema) Poorly antigenic Exotoxin: proteins that bacteria spit out; polypeptides Encoded by plasmid/bacteriophage (virus that infects bacteria) Highly fatal Highly antigenic (used as vaccines) |
|
|
Super antigens:
What are they? Which organisms exhibit superantigens? |
Superantigens are exotoxins that bind directly to MHC II and T-cell receptor-->activate large numbers of T cells to stimulate IFN-gamma and IL-2 release
Superantigens: Staph aureus Strep pyogenes |
|
|
Sperantigens of staph aureus.
Effects? |
Staph aureus:
alpha-toxin-->hemolysis beta-toxpin-->sphingomyelinase (degrades portion of cell membrane) gamma-toxin-->A+B proteins of it-->hemolysin; B+C-->leukocidin Enterotoxins A-E-->food poisoning TSST-1-->cytokine release-->toxic shock Epidermolytic/exfoliative-->epithelial cell lysis-->scalded skin syndrome |
|
|
Superantigens of strep pyogenes.
Effects? |
Strep pyogenes (Group A Strep)
Streptolysin O: hemolysis Streptolysin S: hemolysis Erythrogenic/pyrogenic toxins-->skin rash, fever of scarlet fever (respectively) |
|
|
ADP Ribosylating Exotoxins:
Effect |
B component (Binding) binds host cell, enables endocytosis
A (active) component attaches ADP-ribosyl (ADP ribosylation) to host cell protein, altering its function |
|
|
This bug's exotoxin inactivates elongation factor 2 (EF-2).
Effects? |
Corynebacterium diphteriae
Causes pharyngitis, pseudomembrane in throat This is an ADP-Ribosylating Exotoxin (alters fn of a protein) |
|
|
This bug's exotoxin stimulates adenylyl cyclase.
Effect? |
Vibrio cholerae
Stimulate adenylyl cyclase-->Inc'd Cl- into gut, dec'd Na+ absorption-->rice-water diarrhea This is an ADP-Ribosylating Exotoxin (alters fn of a protein) |
|
|
This bug's exotoxins stimulates adenylate and guanylate cyclase.
Effect? |
E. coli
Causes watery diarrhea Labile like the Air, Stable like the Ground: Heat-labile toxin-->Adenylate cyclase stimulation Heat-stable toxin-->Guanylate cyclase stimulation This is an ADP-Ribosylating Exotoxin (alters fn of a protein) |
|
|
This bug's exotoxin inhibits the alpha subunit of Gi receptors.
Effect? |
Bordetella pertussis
Leads to inc'd cAMP-->whooping cough; inhibits chemokine receptor-->lymphocytosis This is an ADP-Ribosylating Exotoxin (alters fn of a protein) |
|
|
This bug's exotoxin is a bacterial adenylate cyclase.
|
Bacillus anthracis
DIRECTLY increases cAMP |
|
|
Clostritidum perfringens:
Exotoxin Effect |
alpha toxin (lecithinase)
Gas gangrene |
|
|
C. tetani:
Exotoxin effects |
Blocks GABA release-->lockjaw
|
|
|
C. botulinum:
Exotoxin effects |
Blocks release of Ach-->Dry as a bone, hot as hare, bloated as toad
Elevated HR, elevated temp |
|
|
Bug found in canned food
|
C botulinum
|
|
|
Honey causes floppy baby. Why?
|
C botulinum
|
|
|
Bacillus anthracis:
Exotoxin effects |
Exotoxin = Edema factor (a bacterial adenylate cyclase)-->inc'd cAMP
|
|
|
Shigella:
Exotoxin effects |
Shiga toxin-->cleaves host rRNA (inactivates 60S ribosome)-->enhances cytokine release causing hemolysis, uremia (hemolytic uremic syndrome)
|
|
|
Inhibits ACh release:
Toxin |
Botulinum
|
|
|
Lecithinase:
Toxin |
C perfringens (gas gangrene)
|
|
|
Inhibits inhibitor of adenylate cyclase:
Toxin |
Pertussis
|
|
|
Stimulates adenylate cyclase:
Toxin |
Cholera
Heat labile E Coli (ETEC: enterotoxic E Coli) |
|
|
Destroys leukocytes
|
Leukocidin (staph aureus)
|
|
|
Edema factor, lethal factor, protective antigen
|
Bacillus anthracis
|
|
|
Rice-water diarrhea
|
Cholera
Heat labile enterotoxin |
|
|
Scarlet Fever
|
Strep pyogenes
|
|
|
Toxic shock syndrome
|
TSST1 of staph aureues
|
|
|
Inactivates EF-2
|
Diphtheria
|
|
|
Blocks releases of glycine
|
Tetanus
|
|
|
What 5 bacteria secrete enterotoxins?
|
Cholera
ETEC (heat labile toxin) Staph aureus Salmonella Shigella |
|
|
This bug requires dark field microscopy to identify.
Why? |
Treponemes--too thin to be visualized
|
|
|
Which bugs don't appear on gram stain?
|
These Rascals May Microscopically Lack Color
Treponema Rickettsia (intracell parasite) Mycobacteria (high-lipid content of cell wall requires acid fast stain) Mycoplasma (no cell wall) Legionella (intracellular) Chlamydia (intracellular) |
|
|
This bug requires a silver stain to identify.
Why? |
Legionella
bc it's primarily intracellular |
|
|
Which bugs are obligately intracellular?
|
Stay inside when it's Really Cold
Rickettsia Chlamydia can't make their own ATP :( |
|
|
Which bugs are facultatively intracellular?
|
Legionella
(don't worry about others) |
|
|
Ziehl-Neelsen stain
|
AKA Acid-fast stain (mycobacteria)
|
|
|
India ink stain
|
Cryptococcus
|
|
|
Silver stain
|
Legionella
Fungi (pneumocystis) |
|
|
Congo Red Stain
|
Stains amyloid; amyloidosis
|
|
|
Chocolate agar
|
H flu
|
|
|
Löwenstein-Jensen Agar
|
Mycobaterium tuberculosis--takes 3-4 weeks to culture!
Should really do acid fast stain. |
|
|
Patients with this bug should be in airborne isolation.
|
TB
|
|
|
MacConkey's agar
|
Gram poz WILL NOT GROW
Lactose fermenters turn pink Non-lactose fermenters stay white BOTH ARE GRAM NEGZ |
|
|
Blue-black colonies with metallic sheen.
|
E. coli
|
|
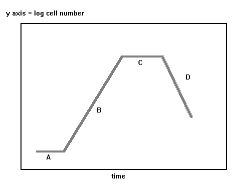
Label this bacterial growth curve.
Describe events. |
A = lag; metabolic activity, no division
B = Log phase; rapid cell division C = Stationary phase; nutrient depletion, slow growth. SPORE formation D = death phase: prolonged nutrient depletion, waste buildup |
|
|
Define bacterial transformation.
Bacteria that utilize this? |
Take up DNA from environment.
Seen in SHiN bacteria: S pneumoniae H flu Neisseria |
|
|
Generalized vs Specialized Transduction
|
Generalized transduction:
Lytic phage infects bacterium-->cleave bact DNA and synthesize viral proteins. Parts of bact chromosomal DNA may become packaged into viral capsid. Phage infects another bacterium and transfers these genes. Specialized: lysogenic phage infects bacterium, viral DNA integrated into bact chromosome; when phage DNA excised, flanking bact genes excised with it. Phage can infect other bacterium and transfer these flanking genes. |
|
|
Define bacterial transposition.
|
Segment of DNA excised and reincorporated from plasmid to chromosome and vice versa.
Flanking DNA may follow when excised in this process. |
|
|
Gram stain:
Purple |
Gram Positive
Can also appear blue! |
|
|
Gram stain:
Pink |
Gram Negative
|
|
|
Gram positive algorithm
|
Gram (+): Purple/blue
Cocci and Rods (bacilli): If cocci: Catalase (+)--Clusters or Catalase (-)--Chains Catalase (+): Staph If Staph: Coag (+): Staph aureus Coag (-): Staph epidermidis; Staph saphrophyticus If Catalase (-): Strep ---- If rods (bacilli): Clostridium Listeria Bacillus |
|
|
Function of bacterial catalase.
Which bacteria make it? |
Catalase degrades H2O2 before it can be converted to micorbicidal products by myeloperoxidase
Staph make catalase, strep do not. Staph make catalase because they have more staff. |
|
|
Function of bacterial coagulase.
Which bacteria make it? |
Coagulase: converts fibrinogen to fibrin; allows staph aureus to hang out in blood clotting
Made by Staph aureus; not S epidermidis, not S saprophyticus |
|
|
What population is at risk of repetitive infections with catalase-producing microbes? Why?
|
Those with chronic granulomatous dz; catalase-producing microbes (Staph) easily degrade what little H2O2 is present
|
|
|
Describe how catalase negative bacteria are classified.
|
Catalase neg (gram poz cocci) = strep
Categorized by hemolysis Partial hemolysis (green/alpha)-->S. pneumoniae (most common) Complete hemolysis (clear/beta)-->S pyogenes (GAS); Group B strep No hemolysis (gamma)-->Enterococcus faecalis |
|
|
This streptococcus exhibits a positive quelling test.
|
S. pneumoniae
Positive quelling means encapsulated! |
|
|
Gram-positive diplococci
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
Gramp-positive cocci in clusters
|
Staph aureus
Grapes! |
|
|
Bacillus is [aerobic/anaerobic].
|
Aerobic
|
|
|
Clostridium is [aerobic/anaerobic].
|
Anaerobic
|
|
|
Bacteremia vs Sepsis (General)
|
Bacteremia: bacteria in blood
Sepsis: bacteremia with signs of infection |
|
|
What toxin-mediated diseases are associated with staph aureus?
|
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSST-1)
Scalded skin syndrome (epidermolytic/exfoliative toxin) Gastroenteritis/food-poisoning (enterotoxins) |
|
|
Protein A:
Effects of this virulence factor Which bacteria exhibit this? |
Binds Fc region of Ig and prevents opsonization
Exhibited by Staph aureus |
|
|
IgA Protease:
Effects of this virulence factor Which bacteria exhibit this? |
Cleaves IgA
Secreted by S pneumo, H flu B, Neisseria in order to colonize respiratory mucosa (SHiN bacteria) |
|
|
This bacteria infects prosthetic devices and IV catheters by producing adherent biofilms.
|
Staph epidermidis
Component of normal skin flora! |
|
|
This bacteria is normally present on the skin but can cause endocarditis.
|
Staph epidermitis
|
|
|
Strep pneumo:
Associated illnesses Virulence factor |
MOPS
Meningitis Otitis media (in kids) Pneumonia Sinusitis Has IgA protease! |
|
|
M protein:
Effect of this virulence factor Bacteria that produce this? |
Prevents phagocytosis
Group A Strep |
|
|
Rusty sputum
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
Sepsis in sickle cell anemia and splenectomy
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
Pneumococcal vaccine:
Who gets it? |
65+
Asplenic Sickle Cell HIV poz Chronic lung dz (asthma, COPD) |
|
|
This is the most common organism of dental caries.
|
Viridans group strep-->Strep mutans
|
|
|
Viridans strep is ___-hemolytic.
|
Alpha
|
|
|
This bacteria is optochin resistant.
|
Viridans strep (mutans, sanguis)
|
|
|
This bacteria causes subacute bacterial endocarditis.
|
Strep sanguis (sanguis = blood; there's lots of blood in the heart)
|
|
|
This bacteria may enter circulation during dental procedures and cause heart problems for those with _________.
|
Strep mutans/sanguis
May cause subacute endocarditis in those w/turbulent flow heart problems (pre-existing(!!) endothelial damage) |
|
|
What skin infections can be caused by both strep pyogenes and staph aureus?
|
Folliculitis
Cellulitis Impetigo (honeycomb lesion) |
|
|
Strawberry tongue
|
Scarlet fever-->strep pyogenes
|
|
|
Pharyngitis:
Most common cause? Concern if untreated? |
Pharyngitis caused by strep pyogenes (Group A Strep)
If untreated-->autoimmune mediated glomerulonephritis (PHritis), rheumatic fever (PHever) |
|
|
Why is group B strep so common in neonates?
Types of infections caused? How can this be prevented? |
Normal vaginal flora in 25% of women!
Meningitis Sepsis Pneumonia (B is for babies!) Must give PCN or ampicillin DURING labor |
|
|
What are the most common BACTERIAL causes of neonatal death?
|
Group B strep
E coli Listeria |
|
|
Enterococci:
Gram -/+ Location Associated infections |
Gram (+)
Normal flora of gut Biliary tract infection UTI Note this is group D strep. |
|
|
Which bacteria are obligate anaerobes?
|
Clostridia
Bacteroides (in gut) Actinomyces Anaerobes Can't Breathe Air |
|
|
Lecithinase:
Effects Bug |
C. perfringens (alpha toxin)
Gas gangrene |
|
|
Drugs of choice for anaerobes
|
Metronidazole
Clindamycin |
|
|
Flaccid vs Spastic Paralysis:
Causes |
Flaccid Paralysis: C. botulinum (floppy baby after honey)
Spastic Paralysis: C. tetani |
|
|
Bacillus anthracis:
Gram -/+ Aerobe/Anaerobe Cutaneous vs Pulmonary |
Gram positive
Obligate aerobe Cutaneous: painless black skin lesion (eschar)-->bacteremia and death Pulmonary: inhalation of spores-->flu syx-->shock |
|
|
Which bacteria are obligate aerobes?
|
Bacillus
Nocardia Pseudomonas Mycobacterium tb |
|
|
Listeria:
Sources Associated illness |
Unpasteurized milk/cheese--pregnant women should avoid soft cheese
Vaginal transmission Neonatal (or immunocomp'd) meningitis Spontaneous abortion Amnionitis |
|
|
Actinomyces vs Nocardia:
Features Presentation Treatment |
Both are gram poz rods with long branching filaments; RESEMBLE fungi
Actinomyces israeli (yellow granules; Israel has yellow sand)-->oral/facial abscess, normal oral flora Nocardia--pulm infection in immunocomp' pts Treatment is a SNAP. Sulfa for Nocardia Actinomyces use PCN |
|
|
What organisms are most commonly implicated in subacute endocarditis?
|
Staph epidermitis
Enterococci Veridans group strep |
|
|
What organisms are most commonly implicated in acute endocarditis?
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
A woman that is breast-feeding develops redness and swelling of her right breast over a period of 2 hours. Examination reveals a warm, fluctuant mass.
What's the diagnosis? |
Mastitis due to staph auerues
|
|
|
What is the most common aerobic skin flora?
|
Staph epidermitis
|
|
|
White membrane on pharynx
|
Diphtheria
|
|
|
Most common cause of meningitis
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
Most common cause of osteomyelitis
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
Otitis media in children
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
Cellulitis
|
Strep pyogenes OR staph aureus
|
|
|
One hour after eating potato salad at a picnic, an entire family began to vomit. After 10 hours, they were better.
What's the organism? |
Staph aureus made exotoxins in potato salad, family digested toxins, but didn't develop infection.
|
|
|
What infections are caused by strep pyogenes?
|
Strep pyogenes = Group A Strep, so:
Pharyngitis Endocarditis Skin infections Necrotizing fasciitis, bacteremia Toxin-mediated dz Autoimmune-mediated dz |

