![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
153 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the extrahepatic effects of liver failure?
|
Coma (hepatic encephalopathy)
Scleral icterus SPider nevi (estrogen effect) Gynceomastic (estrogen effect) Jaundice Testicular atrophy Coarse hand tremor Bleeding tendency (dec'd prothrombin and clotting factors) Ankle edema |
|
|
What are the lab values of liver failure?
|
Low PLT
Elevated PT, INR Dec'd lipids |
|
|
Micro vs Macronodular Cirrhosis:
Criteria Causes |
Micronodular--nodules <3mm; uniform size
Due to metabolic insult (EtOH, hemochromatosis, Wilson's Dz) Macronodular: Nodules >3mm, varied size Due to significant liver injury leading to hepatic necrosis (postinfectious or drug-induced hepatitis); inc'd risk HCC |
|
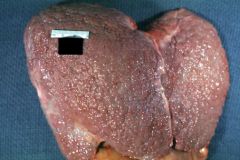
|
Micronodular cirrhosis of liver; from EtOH pt.
|
|
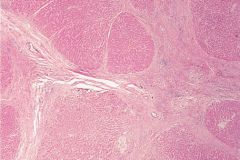
|
Cirrhosis; regenerative lesions surrounded by fibrotic bands of collagen (bridging fibrosis), forming characteristic nodularity
|
|
|
Serum Albumin: Ascites Gradient:
What is it? What does it tell you? |
SAAG + serum albumin - ascites albumin
If SAAG >1.1-->portal HTN If SAAG <1.1-->cancer, nephrotic syndrome, TB, panc/biliary dz, CT dz |
|
|
When is alkaline phosphatase elevated?
|
Obstructive liver dz (HCC), bone dz, bile duct dz
|
|
|
When is GGT elevated?
|
GGT =gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; elevated with verious liver dz; esp heavy EtOH consumption
|
|
|
AST/ALT:
Changes based on dz |
ALT > AST - viral hepatitis
AST > ALT - EtOH AST elevated - MI |
|
|
Reye's Syndrome;
Pathophys Presentation |
Childhood hepatoencephalopathy
Presents with mitochondrial abnlts, fatty liver dz, hypoglycemia, coma Assocd w/viral infeciton (VZV, H flu B) treated with ASA ASA metabolites dec beta-oxidation by inhibiting mitochondrial enzyme |
|
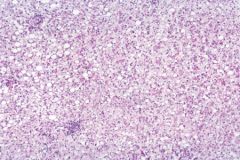
|
Fatty liver; early reversible change assocd w/EtOH consumption. Fat-filled vacuoles, no inflammn due to fibrosis of more serious alcoholic liver damage.
|
|
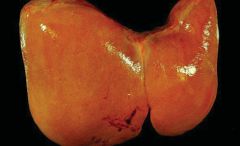
|
Fatty liver, gross specimen showing enlarged yellow appearance.
|
|
|
When do mallory bodies present?
|
After sustained, long-term EtOH consumption.
(note: fatty liver dz is reversible) |
|
|
Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Lab values Presentation Method of spread |
Inc'd AFP
Presents with jaundice, tender hepatomegaly, ascites, polycythemia, hypoglycemia Spread via hematogenous route May lead to Budd-Chiari syndrome |
|
|
Nutmeg liver:
Cause |
Due to backup of blood in liver
Commonly caused by right-sided heart failure and BUdd-Chiari syndrome |
|
|
Budd-Chiari Syndrome:
Pathophys Associated with? |
Occlusion of IVC or hepatic veins-->centrilobular congestion and necrosis
-->Congestive liver dz (hepatomegaly, ascites, abdominal pain, liver failure) Assocd w/hypercoag state, polycythemia vera, pregnancy, HCC |
|
|
alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency:
Pathophys Effects Diagnostics |
Misfolded gene protein product accumulates in hepatocellular ER-->dec'd elastic tissue in lungs-->panacinar emphysema
Leads to elevated PAS-positive globules in liver |
|
|
What are causes of increased bilirubin production?
|
Hemolytic anemia
Sickle cell anemia Hematoma breakdown (newborn delivered by vacuum delivery and develops hematoma on scalp) |
|
|
What are causes of impaired bilirubin uptake and storage?
|
Postviral hepatitis
Drug rxns |
|
|
What are causes of decreased UDP-GT activity?
|
Gilbert's
Crigler-Najjar Neonatal Jaundice--more common in premies |
|
|
When is impaired bilirubin transport seen?
|
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
Rotor Syndrome |
|
|
When is biliary epithelial damage seen?
|
Hepatitis
Cirrhosis Liver Failure |
|
|
When is extrahepatic biliary obstruction seen?
Presentation? Labs? |
Pancreatic neoplasms
Choledocholithiasis Pancreatitis Cholangiocarcinoma All result in inc'd pressure in intrahepatic ducts-->injury/fibrosis and bile stasis Presents as pruritus, jaundice, dark urine, HSM, light-colored stool Elevated conj'd bilirubin, inc'd cholesterol, inc'd alk phos |
|
|
When is intrahepatic biliary obstruction seen?
|
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Sclerosins cholangitis Drugs |
|
|
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis:
Pathophys Labs Presentation Associated conditions |
Autoimmune reaction-->lymphocytic infiltrate + grnaulomas
Leads to inc'd serum mitochondrial Ab including IgM 60% positive p-ANCA Presents as pruritus, jaundice, dark urine, HSM, light-colored stool Ascod w/CREST, RA, Celiac Dz |
|
|
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis:
Pathophys Labs Presentation Associdated conditions |
Unkonwn cause of concentric onion skin bile duct fibrosis-->strictures and dilation with beading of intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts on ERCP
BEADING Presents as pruritus, jaundice, dark urine, HSM, light-colored stool Labs show elevated IgM Assocd w/ulcerative colitis; can lead to secondary biliary cirrhosis |
|
|
Wilson's Disease:
Patphophys Presentation Treatment |
inadequate hepatic copper excretion
Presents with: Asterixis Dec'd Ceruloplasmin Corneal deposits Cirrhosis Carcinoma Dementia Tx: Copper pennies-->Penicillamine |
|
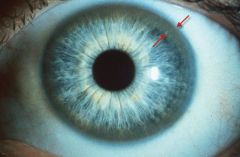
|
Kayser-Fleischer ring in Wilson's Dz
|
|
|
Hemochromatosis:
Pathophys Presentation Labs |
Iron deposition
Bronze diabetes (skin pigmentaiton and DM) Results in CHF, inc'd risk HCC May be primary (AR inheritance) or secondary to chronic transfusion tx (beta-hthal major) Labs: Inc'd ferritin Inc'd Iron Dec'd TIBC Inc'd transferrin saturation |
|
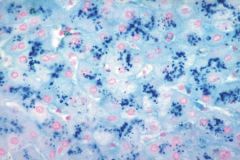
|
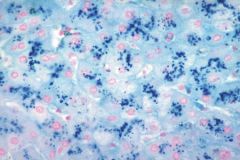
Hemochromatosis with cirrhosis. Prussian blue iron stain shows hemosiderin in liver parenchyma.
|
|
|
A young man presents with ataxia and tremors. He has brown pigmentation in a ring around the periphery of his cornea.
What treatment should he receive? |
Penicillamine
|
|
|
An 80 year-old woman comes to your clinic because her family is concerned about her yellowing skin. Exam reveals yellowing of the skin including the palms and soles but no scleral icterus.
What question could you ask the patient that would most likely identify the cause of the yellowing? |
Jaundice always results in scleral icterus.
Sounds like carotenemia, ask if eating carrots. |
|
|
A 20 year-old man contracts influenza then presents with an idiopathic hyperbilirubinemia.
Cause? |
Gilbert's
|
|
|
What is the fate of bilirubin after it's conjugated and secreted into the GI tract?
|
Acted upon by gut bacteria, forming urobilinogen
Some urobilinogen excreted, some reabs'd |
|
|
A patient presents complaining of pain in the right upper quadrant that he can point to with one finger. The area is tender to light touch and pain is worsened when the patient is asked to raise his arms above his head.
Diagnosis? |
Points to with one finger-->musculoskeletal pain, rectus abdominis tear
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Most common cause of acute RLQ pain |
Appendicits
|
|
|
Diagnose:
50 year-old female presents with pruritis without jaundice, lab reveals (+) AMA |
PBC
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Most common cause of acute LLQ pain |
Diverticulitis
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Gluten sensitivity |
Celiac Sprue
|
|
|
Diagnose:
A patient with Gl bleeding has buccal pigmentation |
Peutz-Jeghers
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Colonoscopy reveals very friable mucosa extending from the rectum to the distal transverse colon |
Ulcerative colitis
|
|
|
Diagnose:
A small intestinal mucosa laden with distended macrophages in the lamina propria (that are filled with PAS(+) granules and rod-shaped bacilli seen by electron microscopy) |
Whipple Dz
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Most common cause of RUQ pain |
Cholecystitis
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Liver biopsy on a 23 year-old female with elevated levels of LKM-1 antibodies, no alcohol history, and no viral serologic markers reveals infiltration of the portal and periportal area with lymphocytes |
Autoimmune hepatitis
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps following a course of antibiotics |
Pseudomembranous colitis
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Fatal disease of unconjugated bilirubin resulting from a complete lack of UDPGT activity |
Crigler-Najjar I
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Radiography reveals a "string-sign" in the terminal ileum |
Crohn's
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Nonfatal disease of unconjugated bilirubin resulting from low levels of UDPGT activity |
Gilbert's or Crigler-Najjar II
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Elevated levels of serum ferritin and increased transferrin saturation |
Hemocrhomatosis
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Alpha-fetoprotein levels >1 000 pg/mL |
HCC
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Elevated serum copper, decreased serum ceruloplasmin, and elevated 24-hr urinary copper |
Wilson's
|
|
|
Diagnose:
Liver disease+ lung emphysema |
alpha1-antitrypsin dz
|
|
|
Diagnose:
ERCP reveals alternating strictures and dilation |
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
|
|
|
Diagnose:
60 year-old female with rheumatoid arthritis and no alcohol history presents with fatigue and right abdominal pain, lab studies reveal high levels of ANA and ASMA, elevated serum lgG levels, and no viral serologic markers |
Autoimmune hepatitis
|
|
|
Diangose:
Total or subtotal atrophy of the small bowel villi, plasma cells and lymphocyte infiltration into the lamina propria and epithelium, and hyperplasia/elongation of crypts |
Celiac Sprue
|
|
|
Cholelithiasis:
Risk Factors Presentation Effects |
4F's:
Female, fat, fertile, forty (Feathers--Pima Indians) Presents with jaundice, fever, RUQ pain; positive Murphy's sign--inspiratory arrest on deep palpation due to pain Can cause cholecystitis; ascending cholangitis, acute pancreatitis, bile stasis |
|
|
Biliary colic:
Pathophys |
Obstruction of common duct by gallstones causes biel duct contraction--cause bile duct obstruction which results in bile duct contraction
|
|
|
Cholesterol vs Pigment Gallstones:
Appearance on ultrasound Frequency Causes |
Cholesterol--radiolucent with 10-20% opaque due to calcifications
Assocd w/obesity, Crohn's, CF, age, fibrates, estrogen, Native American origin Pigment stones: radiopaque; seen in pts w/chronic hemolysis, alcoholic cirrhosis, age, biliary infection |
|
|
Acute pancreatitis:
Causes Presentation Effects (acute vs chronic) |
Gallstones, EtOH***
Trauma Steroids Mumps ERCP** Sulfa Drugs, some HIV drugs Presentation: Epigastric abdominal pain radiating to back Labs: elevated amylase, lipase (higher specificity), can lead to DIC--this is life-threatening! If chroniic-->pancreatic insuff; steatorrhea, fat-soluble vitamin def., DM |
|
|
What is the most common cause of chronic pancreatitis?
|
ALCOHOL
|
|
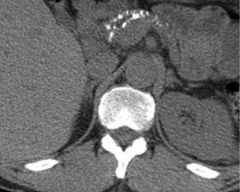
|
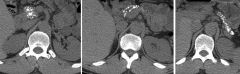
Chronic pancreatitis; CT shows punctate calcifications in head, body, and tail of pancreas
|
|
|
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma:
Most common site Presentation |
Most common in pancreatic head-->obstructive jaundice
Presents with PAINLESS JAUNDICE; abdominal pain radiating to back Weight loss Migratory thrombophlebitis--redness and tenderness on palpation of extremities |
|
|
Ondansetron:
MOA Use |
5-HT3 antagonist.
Powerful central-acting antiemetic. Controls postop vomiting and in pts undergoing chemo. You will not vomit with ONDANSetron, so you can go ON DANCing. |
|
|
What are some of the risk factors for esophageal cancer?
|
Achalasia, Alcohol
Barrett's Corrosive esophagitis, Cigarettes Diverticuli Esophageal web Familial GERD Hot dogs (nitrosamines) |
|
|
What are the risk factors for colon cancer?
|
Tubular adenoma
Tubulovillous adenoma Villous adenoma High-fat, low-fiber diet Chronic IBD Age Cancer syndrome (FAP, HNCC, Peutz-Jeghers, juvenile polyposis) |
|
|
What are the signs of portal hypertension?
|
Esophageal varices
Hemorrhoids Caput medusa Ascites Hematemesis, melena Splenomegaly |
|
|
What is seen in Budd-Chiari syndrome?
What conditions are a/w Budd-Chiari syndrome? |
Occlusion of IVC or hepatic veins
A/W: Polycythemia vera Pregnancy |
|
|
What is the underlying problem in Wilson's disease?
What are the characteristics of Wilson's disease? What is the treatment for Wilson's disease? |
Impaired copper excretion through bile
Asterixis PD syx Dec'd serum ceruloplasmin Cirrhosis Kayser-fleischer rings Copper accumuln HCC Dementia Dyskinesia Dysarthria Tx: penicillamine |
|
|
What is the classic triad of symptoms in hemochromatosis?
What lab tests are used to diagnose hemochromatosis? What is the treatment for hemochromatosis? |
Bronze diabetes:
-Skin pigmentation -DM Cirrhosis Labs; Inc'd ferritin, inc'd transferrin saturation Inc'd serum Fe, dec'd TIBC Tx: Phlebotomy |
|
|
What are the possible etiologies of acute pancreatitis?
|
GET SMASHED
Gallstones EtOH Trauma Steroids Mupms Autoimmune Scorpion stings Hypercalcemia Hyperlipidemia Drugs |
|
|
What is the typical presentation of a pt with pancreatic insufficiency?
What is the treatment for pancreatic insufficiency? |
Diarrhea, steatorrhea, weight loss, weakness, fat soluble vitamin def (ADEK)
Tx: limit fat intake, replace pancreatic enzymes |
|
|
What are the risk factors for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma?
|
HBC, HCV
Wilson's Hemochromatosis alphta1-antitrypsin def Hepatic adenoma Alcoholic cirrhosis |
|
|
What is the difference between primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
Primary Biliary Sclerosis:
+AMA Middle-aged female Auto-immune dz Assocd w/other auto-immune dz Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Etiology UNK 60% assocd w/+P-ANCA Males >40 Assocd w/UC and cholangiocarcinoma ERCP findings of BEADING and STRICTURING |
|
|
What is the most common salivary gland tumor?
What is the second most common salivary gland tumor? What is the most common location for a salivary gland tumor? |
1) Pleomorphic adenoma
2) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Most common location = parotid gland |
|
|
What are the five 2's of Meckel's diverticulum?
|
2 inches long
2 feet from ileocecal vlve 2% of populn Commonly presents in first 2 years of life 2 types of epihelium--gastric and pancreatic |
|
|
What are the tumor markers for pancreatic cancer?
|
CEA
CA19-9 |
|
|
What is the typical histological neoplastic progression of colon cancer?
|
Tubular adenoma-->
Tubulovillous adenoma--> Villous adenoma--> Carcinoma |
|
|
List the names of the B vitamins.
|
The Rich Never Pan Pyrite Filled Creeks
B1 - Thiamine B2 - Riboflavin B3 - Niacin B5 - Pantothenic acid B6 - Pyridoxine B9 - Folic acid B12 - Cobalamin |
|
|
Name of vitamin A.
|
Retinol, retinal
|
|
|
Name of vitamin E.
|
alpha-tocopherol
|
|
|
Name of vitamin C.
|
Ascorbic acid
|
|
|
What is the most common vitamin deficiency in the US?
|
Folic Acid--vit B9
|
|
|
What is the functionally active form of thiamine?
|
Thiamine = vit B1
Active form = Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) |
|
|
In what reactions does thiamine pyrophosphate have a role? List enzymes.
|
Pyruvate-->acetyl coA (Pyruvate DH)
alpha-ketoglutarate-->succinyl CoA (alpha-ketoglutarate DH)--TCA Ribose 5-P<-->Glyceraldehyde 3-P (Transketolase)--HMP |
|
|
How is thiamine deficiency diagnosed?
|
By an increase in RBC transketolase activity observed upon addition of thiamine
|
|
|
What characterizes dry beriberi?
Presentation? |
Nonspecific peripheral neuropathy with myelin degeneration
Toe dorp, wrist drop, food drop Muscle weakness, hyporeflexia, areflexia |
|
|
What characterizes wet beriberi?
|
Peripheral vasodilation-->high output cardiac failure-->peripheral edema
Cardiomegaly (wet = blood) |
|
|
What are the biologically active forms of riboflavin?
What is the role of these molecules? |
Riboflavin = vit B2
Active forms: Flavin mononucleotide (FMN) Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) Used for red-ox rxns |
|
|
What are some of the symptoms associated with riboflavin deficiency?
|
Riboflavin = vit B2
Syx: Dermatitis Cheilosis--fissuring of corners of mouth Glossitis (smooth, purple tongue) |
|
|
What is angular stomatitis?
What population is this common in? |
Inflammn of corners of mouth
Common in those who wear dentures |
|
|
What nutrient deficiencies are a/w cheilosis, glossitis, and stomatitis?
|
Iron
Riboflavin Niacin Folate B12 (cobalamin) |
|
|
What are the biologically active forms of niacin?
|
Niacn = vit B3
Active forms: NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) |
|
|
What amino acid is required for the generation of niacin?
|
Tryptophan
|
|
|
What disease is caused by niacin deficiency? What are the symptoms of this disease?
|
Pellagra: Dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia
Can cause death! |
|
|
Why might pellagra be seen in a population that primarily eat corn?
|
Tryptophan can be metabolized to form niacin, and corn lacks tryptophan.
|
|
|
How is niacin effective in treating type IIb hyperlipoproteinemia?
|
Inhibits lipolysis in adipose tissues-->less circulating FFA's-->less FA's to liver-->less VLDL made-->less LDL prouced
|
|
|
What is the biologically active form of pyridoxine?
|
Pyridoxal phosphate
Pyridoxine = B6 |
|
|
What is the metabolic function of pyridoxal phosphate?
|
Coenzyme for enzymes of amino acid metabolism (transaminations and deaminations)
|
|
|
What drug can lead to a deficiency of B6 in addition to B3?
|
Isoniazid
|
|
|
What are the clinical findings of B6 deficiency?
|
Same as riboflavin deficiency + convulsions***, hyperirritability, peripheral neuropathy
|
|
|
What is the biologically active form of folic acid?
|
Tetrahydrofolate
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of folic acid deficiency?
|
NT defects
Growth failure Megaloblastic anemia |
|
|
What are the steps involved in the intake and absorption of B12?
|
Pepsin in stomach releases B12 from protein-bound form
B12 binds salivary vitamin B12 binding proteins (cobalophilins) R-B12 complex broken down in duodenum by panc protease Unbound B12 (in duodenum) binds IF secreted by parietal cells from stomach IF-B12 complex binds IF-specific receptors on cells of terminal ileum B12 transverses mucosal cell and picked up by plasma protein called transcobalamin II |
|
|
What specific organs are involved in the absorption of B12?
|
Salivary glands
Stomach Pancreas Distal Ileum |
|
|
Descibe the stages of the Schilling test and their diagnostic utility.
|
1. Administration of radiolabeled 812 without intrinsic factor (to determine if there is a problem absorbing B12)
2. Administration of radiolabeled B12 with intrinsic factor (to determine if a lack of intrinsic factor is the cause of the problem) 3. Administration of radiolabeled B12 with pancreatic supplements (to determine if a lack of enzymatic degradation of R protein is the problem) 4. Administration of radiolabeled B12 after administration of antibiotics (tetracycline) or anti-inflammatory drugs (prednisone) (to determine other causes of B12 malabsorption such as bacterial overgrowth) |
|
|
What is the metabolic role of biotin?
|
Apoenzyme in carboxylation reactions (buy-a-tin of CO2)
|
|
|
What can cause a deficiency of biotin?
|
Glycoprotein avidin found in egg whites prevents absorption of biotin (would need 20 egg whites per day)
Antibiotic use--gut bacteria make biotin |
|
|
What is the main metabolic reaction that vitamin C is involved in?
|
Hydroxylation of prolyl and lysyl residues
|
|
|
What are the major sources of vitamin C deficiency-scurvy?
|
Sore, spongy gums
Loose teeth Fragile BVs-->hemorrhages Swollen joints--bleeding into joint spaces Impaired wound healing Anemia |
|
|
What are the different forms of Vitamin A?
|
Retinol, retinal (used by body)
beta-carotene (cleaved in intestine to yield retinal) Retinoic acid (can't be reduced; unusable by body) |
|
|
What are the signs of vitamin A deficiency?
|
Night blindness
Xerophthalmia--pathologic dryness of conjunctiva and cornea-->corneal ulceration and blindness Keratomalacia--wrinkling, clouding of cornea Bitot's spots--dry, silver-grey plaques of bulbar conjunctiva |
|
|
What are the signs of hypervitaminosis A?
|
HA, n/v, stupor
Skin--dry, pruritic Liver--enlarged (possibly cirrhotic) Bone, joint pain Inc'd ICP |
|
|
T/F: Lack of vitamin A in pregnant women has the potential for causing congenital malformations.
|
False, excessive Vit A in pregnant women has potential for causing congenital malformations including:
-hydrocephalus -inhibited migration of NCC |
|
|
In which patient populations is vitamin A supplementation a bad idea?
|
Pregnancy-->teratogenic
Smokers-->inc'd risk lung ca |
|
|
What are the names for vitamin D deficiency in adults and in children?
|
Adults--osteomalacia
Children--rickets |
|
|
What is the principle role of vitamin K?
|
Post-translation modification of various clotting factors where it serves as a co-enzyme in the carboxylation of certain glutamic acid residues present in these proteins.
|
|
|
Which proteins are vitamin K-dependent?
|
Protein C
Protein S Prothrombin Factors 2,7,9,10 ALL require vitamin K for synthesis |
|
|
What is the primary function of vitamin E?
|
Antioxidant--prevents nonenzymatic oxidation of cell components (esp on RBCs) by molecular oxygen free radicals
|
|
|
What is another name for vitamin E?
|
alpha-Tocopherol
|
|
|
A patient presents with convulsions and irritability.
What vitamin deficiency is causing these symptoms in this patient? |
B6
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency results in gum bleeding, bruising, anemia, and poor wound healing?
|
C
|
|
|
Vitamin C is necessary for the hydroxylation of which amino acids in collagen synthesis?
|
Proline and Lysine
|
|
|
What vitamin in excess can cause hypercalcemia?
|
Vitamin D, also Vitamin A
|
|
|
What vitamins have a function similar to reduced glutathione?
|
(anti-oxidant = glutathione)
A, C, E = anti-oxidants |
|
|
An alcoholic develops a rash, diarrhea, and altered mental status.
What is the vitamin deficiency? |
B3 (niacin)
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Increased RBC fragility |
E
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Dermatitis, cheilosis, glossitis |
B2, B3, folate, B12, Fe
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Peripheral neuropathy, angular cheilosis, glossitis |
B12
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Hemorrhagic disease |
K
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Neural tube defects |
Foilc acid
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia |
B3--Niacin
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Megaloblastic anemia |
Folate or B12
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Pernicious anemia |
B12
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Bitot's spots, keratomalacia, xerophthalmia |
A
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Osteomalacia |
D
|
|
|
Which vitamin deficiency:
Rickets |
D
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Can be used to treat acne and psoriasis |
A
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Used in oxidation/reduction reactions |
B2 (riboflavin)--FAD/FMN
Niacin--NAD, NADP |
|
|
Which vitamin:
Used in carboxylation reactions |
Biotin
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Involved in the hydroxylation of prolyl residues |
C
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Requires intrinsic factor for absorption |
B12
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Deficiency may result from kidney disease |
D
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Used by pyruvate dehydrogenase and a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
B1, b2, b3, b5, lipoic acid
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Given prophylactically to newborns |
Vit K
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Can be used to elevate HDL and lower LDL |
B3--niacin
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Deficiency can be caused by isoniazid use |
B6
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Cobalt is found within this vitamin |
B12--cobalamine
|
|
|
Which vitamin:
Critical for DNA synthesis |
B12, Folate
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of zinc deficiency?
|
poor wound healing
|
|
|
What enzyme is inhibited by the drug fomepizole?
|
Alcohol DH
|
|
|
What is the difference between kwashiorkor and marasmus?
|
Kwashiorkor--protein malnutrition, skin lesions, edema, dec'd apolipoprotein synthesis; swollen belly
Marasmus--tissue wasting, global manlutrition |
|
|
What vitamins should vegetarians supplement in their diet?
|
B12
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of vitamin A toxicity?
|
Bitot's spots
Keratomalacia Xerophthalmia |

