![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 components of image quality
|
spatial resolution
signal noise contrast Measure of flow and spatial resolution |
|
|
The sensitivity ("speed") of a film is based on what inherent feature of the silver halide crystal?
Is a high speed (more, less) grainy |
size. The larger the crystal, the less light is required to produce the same opitical density therefore is more "sensitive"
more |
|
|
What two "particles" can activate a silver halide crystal?
Which of the two is more effective? |
photon (light)
xray xray |
|
|
What is the role of a phosphor
A thicker phosphor layer (increases, decreases) the probability of xray interaction? The thicker the phosphor layer, the (less, more) lateral dispersion of photons? |

convert incident xrays into visible light photons
increases more |
|
|
(Film, digital) detector have a narrower exposure curve and are therefor more prone to exposure errors
|
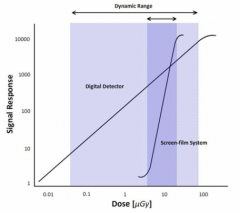
Film
|
|
|
What are discreet sampling and intensity resolution?
|
spatial resolution in terms of pixel pitch (spacing between pixel element centers) ie pixels/mm
bit depth, the maximum number of grayscale pixel values to describe exposure |
|
|
How does indirect digital imaging work?
|
xrays activate a phosphor or scintillator which in turn emits visible light which is digitally measured and stored on a sensor. Image readout/display occurs as a separate process.
|
|
|
How does CR work?
|
An xray stimulates a storage phosphor. This excites the phosphor atom to a metastable state which can exist for several days. The excited phosphor will emit blue green light if it interacts with a visible red light photon. This occurs in the reader and the emitted blue green light will be digitally measured and stored.
|
|
|
why is CR considered a digital technique?
|
because it produces digital data prior to image display
|
|
|
How does a flatpanel scintillator-CCD work?
|
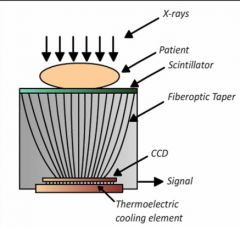
incident xrays strike a sintillator and the emitted light is "focused" by fiberoptic filaments onto a charge coupled device which is usually much smaller than the field of view.
this requires a demagnification step and results in loss of image quality |
|
|
How does a flatpanel scintillator-TFT device work?
|
The TFT array is a 2D charge measuring device. Visible light induced charge separation occurs in a photodiode layer formed in the alpha Si above the TFT array
|
|
|
Fundamentally, indirect imaging is based on converting xrays to __________________
|
visible light
|
|
|
What's the difference between direct and indirect aSe-TFT detectors?
which is more efficient, produces less scatter and can therefore reduce patient dose? |
indirect will store/measure charge based on emitted light
direct will store/measure charge based on incident xrays DIrect sensors are more efficient |
|
|
How does a photon counting detector work
|
Linear array of detector cells which continuously measure charge separation from absorbed xrays which produce a voltage spike (photon counting) relative to background noise.
this improves efficiency, minimizes scatter (1D setup) and sig reduces dose. "micro-dose mammography" |
|
|
What is more efficient? Storage phosphors or scintillators?
|
Scintillators
|
|
|
Light dispersion (increases, decreases) with phosphor/scintillator thickness and results in (gain, loss) of spatial resolution)
Absorption Efficiency is directly/indirectly proportional to phosphor/scintillator thickness? |
increases, loss
Directly Therefor: inverse relationship between absorption efficiency and spatial resolution |
|
|
What are two ways to overcome lateral dispersion?
|
phosphor/scintillator sandwhich
"/" columation |
|
|
Charge separation is an important step in:
Direct Indirect both |
both
|
|
|
What type of detector performs continuous measurement of charge separation?
|
photon counter. All others provide a summed charge during the entire exposure
|
|
|
Fill factor in TFT arrays are an issue in direct/indirect systems
|
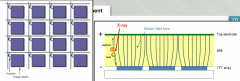
indirect: a large portion (up to 60%) is occupied by a transistor which does not detect xrays and therefor results in significant loss of detection efficiency.
Direct systems have curving electric field lines which eliminate this problem |
|
|
photon counting detectors have least noise and offer potential for mltiple energy imaging in a single exposure
|
...
|
|
|
What is MTF?
|
Modulation transfer function: a measure of loss of contrast as a function of spatial resolution
ie. spatial resolution performance |
|
|
What is DQE?
|
Detective Quantum Efficiency: Not yet standardized was of assessing detector performance with respect to noise AND spatial resolution
|
|
|
All digital imaging methods are based on measuring charge separation.
whether it requires generation of visible light determines if it is direct or indirect |
...
|
|
|
Approximately 30% of absorbed xray energy is stored in the metastable form of a storage phosphor
|
...
|
|
|
Visible light dispersion is the greatest source of spatial resolution loss
|
...
|
|
|
Amorphous selenium is able to produce charge seaparation as a result of xray absorption
|
...
|

