![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common source of acute iron poisoning?
|
OD'ing on multivitamins
|
|
|
What are the relevant pharmacodynamics of iron?
|
A - only ~10% is absorbed
D - generally bound to transferrin, but following OD this becomes saturated and free iron that is toxic circulates |
|
|
How can the total amount of elemental iron be approximated?
|
Number of tablets x fraction of elemental iron
|
|
|
What levels of acute iron ingestion result in toxicity?
|
<20mg/kg / <350mcg/dL - no symptoms
20-60mg/kg / 350-500mcg/dL - mild-moderate symptoms >60mg/kg / >500mcg/dL - severe morbidity |
|
|
Where does iron have its toxic effects?
|
The gastric mucosa and cellular metabolism
|
|
|
What effect does iron have on the gastrointestinal system?
|
It causes caustic injury to the mucosa resulting in N/V/D/abd pain, bleeding, perforation and peritonitis
|
|
|
What effect does iron have on cellular metabolism?
|
Damages lipid membranes through peroxidation
Uncouples oxidative phosphorylation - |
|
|
What are the stages of iron poisoning?
|
1 - V/D/caustic GI injury (90 minutes)
2 - Apparent recovery (1 day) 3 - Recurrance of GI symptoms, decreased mental status, AGMA, leukocytosis, coagulopathy, renal failure and cardiovascular collapse (1-2 days) 4 - Fulminent hepatic failure (2-5 days) 5 - Pyloric scarring/obstruction; liver recovery |
|
|
What are the lab findings in iron poisoning?
|
Phase 1/2 nothing
Phase 3 - lactate AGMA, elevated coags, elevated creatinine, hypoglycemia, leukocytosis Phase 4 - elevated coags, transaminitis |
|
|
When should peak serum iron levels be drawn to quantify the extent of the ingestion?
|
3-5 hours
Sustained/enteric coated preparations 6-8 hours |
|
|
What is the efficacy of an abdominal radiograph in iron ingestion?
|
Many tablets are radiopaque. The presence of tablets correlates with ingestion severity. Can not rule it out.
|
|
|
Are activated charcoal, gastric lavage, whole bowel irrigation, chelation or dialysis useful in iron poisoning?
|
AC does not bind iron.
GL does not get tabs because they clump together. WBI is indicated Dialysis is not effective secondary to a large Vd Exchange transfusion may be useful in severe OD |
|
|
How can chelation be used to treat iron poisoning?
|
Deferoxamine forms a water-soluble, renally excretable compound (ferrioxamine)
100mg = 9.35mg of elemental iron Continuous infusion 15-30mg/kg/h for 24 hours (watch for hypotension, fine in pregnancy) |
|
|
What happens to the urine when deferoxamine is used?
|
It becomes a "vin rose" color
|
|
|
What are the indications for admission for iron poisoning?
|
<20mg/kg ingestion or <350mcg/dL peak level (6h observation)
Pills visible on radiograph (requires WBI) |
|
|
Which basic laboratory tests are highly specific for iron levels >300mcg/dL?
|
Elevated glucose and WBC
However, these are not sensitive. |
|
|
What are the most common sources of iron poisoning?
|
Historically: lead-based paint and gasoline
Moonshine Imported herbs and products |
|
|
When do children present with lead poisoning?
|
1 - post ingestion
2 - symptomatic with a compatible history 3 - for management of an elevated lead level |
|
|
When do adults present with lead poisoning?
|
Following workplace (smelting, battery manufacture, radiators, bridge/ship construction, weldeing, etc) or hobby (pottery, fishing sinkers, home remodels) exposure.
|
|
|
How does lead cause toxicity?
|
Binds to sulfhydryl groups and interferes with enzymatic reactions.
|
|
|
What systems does lead affect most prominently?
|
Hematopoietic
Neurologic Renal |
|
|
What are the hematopoietic manifestations of lead poisoning?
|
Normo or hypochromic anemia due to inhibition of heme synthesis
|
|
|
What are the neurologic manifestations of lead poisoning?
|
Acute - lead encephalopathy and cerebral edema
Demyelination and degeneration of motor axons - peripheral neuropathy, wrist drop, foot drop In children, neuropsychiatric disorders, decreased IQ, hyperactivity, learning disabilities, aggressive behavior and hearing loss. |
|
|
What are the renal manifestations of lead poisoning?
|
"Lead nephropathy" characterized by fibrosis of the proximal tubules
Hyperuricemic gout due to increased reuptake of uric acid |
|
|
What are the laboratory findings of lead poisoning?
|
Elevated lead level (>10mcg/dL toxic for children)
Also: basophilic stippling on peripheral smear, transaminitis |
|
|
Are activated charcoal, gastric lavage, whole bowel irrigation, chelation or dialysis useful in lead poisoning?
|
AC does not bind lead
GL does not get tabs because they clump together WBI is indicated Dialysis is not effective secondary to a large Vd |
|
|
When is chelation indicated for lead poisoning? What agents should be used?
|
>70mcg/dL or encephalopathy: parenteral dimercaprol and CaNa2EDTA.
<70mcg/dL: oral DMSA OR Penicillamine Chelation allows renal/hepatic excretion |
|
|
How are the chelation agents dosed in severe lead poisoning?
|
-Dimercaprol 3-5mg/kg IM q4h x 2 days, q6h x 2 days, q12h x 2 days
-The 2nd dose of Dimercaprol is followed by Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (CaNa2EDTA) 75mg/kg/d IV/IM divided bid-qid. |
|
|
What are the contraindications and side effects to dimercaprol?
|
-Contraindicated in peanut allergy
-Relative contraindication in G6PD deficiency (hemolysis) -Side effects are N/V/urticaria/HTN |
|
|
What are the contraindications and side effects to CaNa2EDTA?
|
-Have not already given dimercaprol (concern that more lead may cross the BBB and increase toxicity if given first)
-Inadequate renal function (requires concurrent hemodialysis -Renal tubular injury and chelation of other metals (iron and zinc) |
|
|
When should penicillamine be used for lead poisoning?
|
Ingestions <70mcg/dL when oral DMSA is not tolerated
|
|
|
When must adults with occupational lead exposure be removed from work?
|
Lead levels >50mcg/dL
|
|
|
What are the most common sources of arsenic poisoning?
|
Historically used in homicide
Smelters/power plants Rodentisides Contaminated drinking water in 3rd world countries |
|
|
How does arsenic cause toxicity?
|
Binds to sulfhydryl groups preventing enzyme function (disrupts oxidative phosphorylation). Also causes massive hemolysis (mechanism unknown).
|
|
|
How does arsenic poisoning present?
|
Severely - mortality 25-30%
GI effects initially - N/C/D/abd pain/metallic taste Massive hemolysis and renal tubular injury ARDS, dysrhythmias, cardiovascular collapse May be dx'd as gastroenteritis or sepsis |
|
|
What are the chronic effects of arsenic poisoning?
|
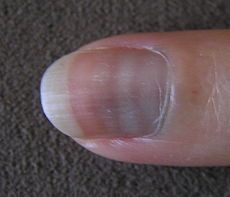
Triad: H/O severe GI illness, rash & peripheral neuropathy.
See Mees' lines on nails Painful sensorimotor neuropathy Hyperkeratosis of palms and soles |
|
|
What are the laboratory findings in arsenic poisoning?
|
Arsenic level in blood (>5mcg/L) or urine (>50mcg/24h - spot urine lots of false negatives; seafood lots of false positives)
Anemia & basophilic stippling, elevated creatinine, transaminitis |
|
|
How does seafood falsely elevate urinary arsenic levels?
|
It contains arsenobetaine which does not result in arsenic toxicity
|
|
|
How can chronic arsenic poisoning be confirmed?
|
Using hair and nail specimens
|
|
|
Are activated charcoal, gastric lavage, whole bowel irrigation, chelation or dialysis useful in arsenic poisoning?
|
-AC will not absorb
-GL or WBI could be considered for recent ingestion/radioopaque material on x-ray -Exchange transfusions should be considered -Chelation with dimercaprol or DMSA -Hemodialysis is useful in context of renal failure |
|
|
What are the most common sources of mercury poisoning?
|
Sphygmomanometers
Flourescent lights, batteries Fish |
|
|
What are the different kinds of mercury and how are we exposed to them?
|
Metallic mergury - inhaled as a vapor but NOT GI causing resp problems
Inorganic mercury salts - Acute GI absorption/damage and renal toxicity Organic mercury - Chronic GI and dermatologic absorption |
|
|
How does metallic mercury cause toxicity?
|
Retained in the lungs causing pneumonitis and ARDS. Also can affect renal and CNS.
|
|
|
How does inorganic mercury cause toxicity?
|
Acute
GI absorption along with corrosive gastroenteritis and hemorrhage Renal toxicity caused by direct and immune damage. Chronic Neurologic(neurasthenia), renal (nephrotic syndrome), GI (gingivostomatitis, loose teeth, burning sensation in mouth) |
|
|
How does organic mercury cause toxicity?
|
Has chronic (not acute) toxicity
GI and dermatological absorption result in delayed neurotoxicity with ataxia/tremor/dysarthria/tunnel vision. Carcinogen |
|
|
What are the laboratory findings in mercury toxicity?
|
Organic - positive serum levels (>35mcg/L)
For other exposures use urine levels |
|
|
Are activated charcoal, gastric lavage, whole bowel irrigation, chelation or dialysis useful in mercury poisoning?
|
AC - absorbs little, not recommended
GL - try for mercury salts with milk/egg whites Chelation - dimercaprol for inorganic mercury but NOT organic mercury; DMSA for organic mercury. |

