![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What CNs do the Parasymphathics of the HN originate from?
|
CN 3977 or COPS:
Ciliary Otic Pterygopalatine Submandibular |
|
|
Where does the preganglions of X synapse?
|
In the organ walls itself - you already knew that about the vagus.
|
|
|
What are the COPS parasympathetics primarily responsible for?
|
Secretomotor to glands and motor to smooth muscles.
|
|
|
See lecture Nov 4th at 10 min/Pg 2 - you might want to copy that diagram
|
See lecture Nov 4th at 10 min/Pg 2 - you might want to copy that diagram
|
|
|
There are four major glands in the head - what are they and what are they innervated by and what are their preganglionic parasympathic fibers?
|
1. Parotid - CN9, Lesser Petrosal
2. Lacrimal - CN7, Greater Petrosal 3. Submandibular - CN7, Chorda Tympani 4. Siblingual - CN7, Chorda Tympani |
|
|
See lecture Nov 4th at 10 min/Pg 2 - you might want to copy that diagram
|
See lecture Nov 4th at 10 min/Pg 2 - you might want to copy that diagram
|
|
|
There are four major glands in the head - what are they and what are they innervated by and what are their preganglionic parasympathic fibers?
|
1. Parotid - CN9, Lesser Petrosal
2. Lacrimal - CN7, Greater Petrosal 3. Submandibular - CN7, Chorda Tympani 4. Siblingual - CN7, Chorda Tympani |
|
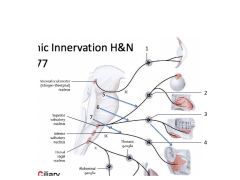
Name
|
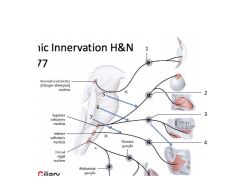
1. Ciliary Ganglion
2. Pterygopalatine Ganglion 3. Submandibular Ganglion 4. Otic ganglion 5. Greater Petrosal 6. Chorda Tympani 7. Lesser Petrosal |
|
|
What does CNVII innervate and how does Hoagland remember it?
|
All muscles of facial expression and Spits and Cries (salivary and lacrimal)
|
|
|
The Internal Acoustic Meatus has three canals - what are they? What would happen if a pt had a neuroma at that location?
|
1. Facial
2. Vestibular 3. Cochlear Neuroma here would cause facial drooping, no taste, no balance, and deaf in affected ear. |
|
|
All that is moist in the H&N are receiving what kind of nerve fibers (that's all he wants us to know)
|
Postganglionic parasympathetic
|
|
|
Where are the cell bodies for taste located?
|
Geniculate Gangion - (likely exam question)
|
|
|
What are the three branches of the facial n as it traverses the facial canal within the temporal bone?
|
1. Greater petrosal n
2. Nerve to the stapedius 3. Chorda tympani |
|
|
What are the 9 branches of the CNVII after exiting the stylomastoid foramen?
|
1. Posterior auricalar
2. Posterior digastric branch 3. Temporal Branch 4. Zygomatic Branch 5. Stylohyoid branch 6. Buccal branch 7. Marginal mandibular branch 8. Cervical branch |
|
|
For facial muscles of expression, remember "Two Zebras Bit My Coccyx"
|
Temporal
Zygomatic Buccal Marginal Mandibular Cervical |
|
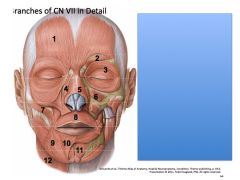
Label
|
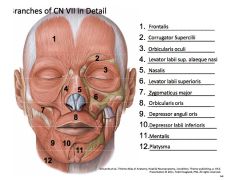
|
|
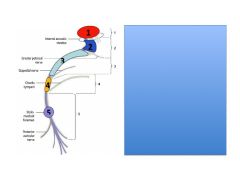
Describe symptoms with lesions at at each point
|
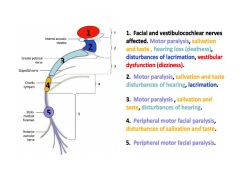
a
|

