![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What would happen if there is an injury of the facial nerve distal to the stylomastoid foremen.
|
Bell's Palsey - a paralysis of the muscles of facial expression. Pt won't be able to smile, close eyes; there will be a fascial droop; drooling;
|
|
|
Trigeminal has three major divisions:
There are two major divisions: |
CNV1 - ophthalmic
CNV2 - maxillary CNV3 - mandibular C2 and C3 are major divisions. |
|
|
Sensory information in the face is transmitted via what nerve? What about motor neuron?
|
Sensory = trigeminal
Motor = facial |
|
**Pix has nothing to do with this Q**
Describe how the facial dermatomes lay on the face. There are three (I'm referring to the face diagram with red blue and green) |

Red = ophthalmic
Blue = maxillary Green = mandibular |
|
|
Where does the trigeminal come off the brain?
|
The mid-point of the pons.
|
|
|
The twitch she talked about in pts with trigeminal neuralgia, "tic de la rue" happens in which dermatome?
|
Maxillary.
|
|
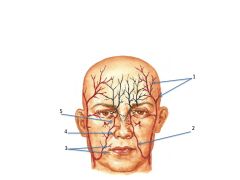
What are the red and black vessels a major branch from?
|
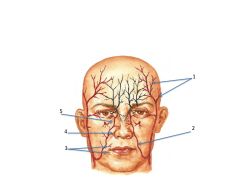
Black = Internal Carotid
Red = External Carotid 1. Superficial temporal 2. facial 3. inferior/superior labial 4. lateral nasal 5. angular artery |
|
|
What is the major blood supply to the face?
|
facial artery
|
|
|
Don't forget to study the structures mentioned in class but not on our structure list. I list them in netter's, pink highlight, and pink mini post its on top
|
Don't forget to study the structures mentioned in class but not on our structure list. I list them in netter's, pink highlight, and pink mini post its on top
|
|
|
Why don't the veins of the face have valves?
|
Bc they are above the heart.
|
|
|
What is the Danger Triangle?
|
It is a region on the face, including the angular vein, with veins that make connections with the superior/inferior ophthalmic veins that make connections with the cavernous sinus (intracranial) that can cause a meningitis. This is made worse bc the veins in the face do not have valves.
|
|
|
Where does ALL of the lymph vessels of the face drain to?
|
The deep cervical lymph nodes the surround the Internal Jugular Vein and are deep to the SCM.
|
|
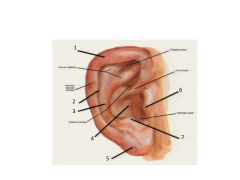
name
|
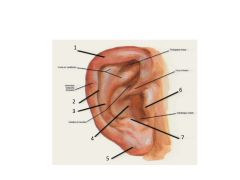
1. Helix
2. Scaphoid Fossa 3. Antihelix 4. Concha of auricle 5. Lobule of auricle 6. Tragus 7. Antitragus |
|
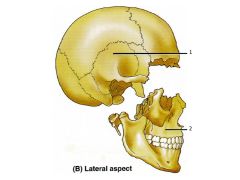
What is the "cap" of the skull called that includes the frontal, parietal, and some of the occipital bone?
|
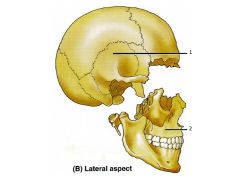
The cap = the Calvaria
1. Neurocranium 2. Viscerocranium |
|
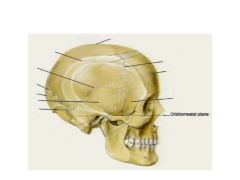
How is the Orbitomeatal plane defined?
|
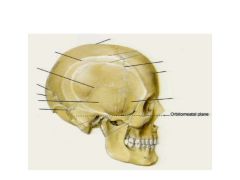
The inferior margin of the orbital cavity and the superior margin of the external acoustic meatus are in the same horizontal plane.
|
|
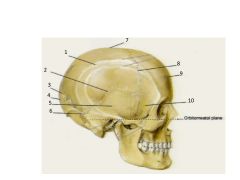
Name these bones and sutures. Also name the two processes of the temporal bone. Also, check out the Ethmoid bone on p37 of Rohan - she included it here but you can't see it.
|
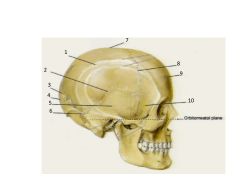
1. Parietal - "Wall" (paired)
2. Squamous suture 3. Lambdoid suture 4. Occipital 5. Temporal (paired) with zygomatic and mastoid processes 6. Sutural - (if additional pieces = wormian) 7. Sagittal suture (think Sagitarius, being pierced by arrow) 8. Coronal suture 9. Frontal 10. Sphenoid |
|
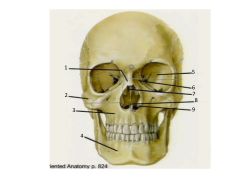
Name these structures.
|
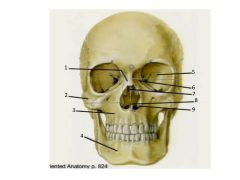
1. Nasal (paired)
2. Zygomatic (paired) 3. Maxillae (paired) 4. Mandible 5. Sphenoid 6. Lacrimal (paired) 7. Ethmoid (note perpendicular plate in nasal cavity) 8. Vomer 9. Inferior nasal concha (paired) |
|
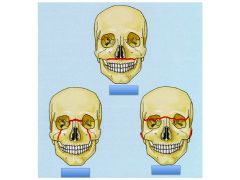
Name these injuries
|
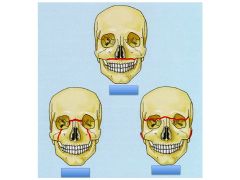
Le Fort I
Le Fort II Le Fort III |
|
|
Gaping scalp wounds are indicative of:
|
A deep cut through the aponeurosis.
|
|
|
Why is the loose areolar connective tissue layer called the "dangerous area"?
|
Bc it is often associated with infection - including infections inside the scull.
|
|
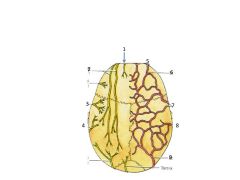
Name nerves and arteries
|
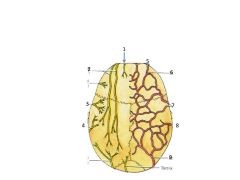
1. Supratrochlear
2. Supraorbital 3. Auriculotemporal n 4. Lesser occipital 5. Supratrochlear 6. Supraorbital 7. Superficial temporal artery 8. Posterior auricular artery 9. Occipital artery |
|
|
What nerve innervates the muscles of mastication? What are the muscles of mastication?
|
CN V3 (mandibular division of trigeminal nerve)
1. Temporalis 2. Masseter 3. Medial pterygoid 4. Lateral pterygoid |
|
|
What is the buccinator pierced by? Although it is a muscle of fascial expression, what else does it function as?
|
The parietal duct. It is also an accessory muscle of mastication. It holds food in place for mastication.
|
|
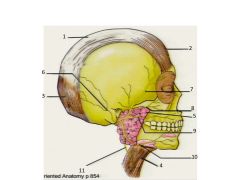
Structures 6 - 11 are nerve branches of what cranial nerve?
|
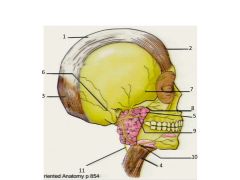
Cranial N VII - Facial Nerve.
1. Epicranial Aponeurosis 2. Frontalis m 3. Occipitalis m 4. Platysma 5. Parotid 6. Posterior auricular 7. Temporal n 8. Zygomatic 9. Buccal 10. Marginal mandibular 11. Cervical Pat Tillman Zzzz's, Bad Marine Corp |
|
|
What is the name of the foremen that CNVII comes out of?
|
Stylomastoid foremen
|

