![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sensory Deficits |
Impaired or absent functioning in one of more senses -impaired sight or hearing -altered taste -numbness and paralysis -impaired kinesthetic sense
NOTE: sometimes reversible, sometimes permanent |
|
|
Sensory Problems |
Everything has it's wonders, even darkness and silence, and I learn, whatever state I may be in, therein, to be content. -Helen Keller |
|
|
Eye and Vision Problems |
Whatever you may look like, marry a man your own age - as your beauty fades- so will his eyesight. -Phyllis Diller |
|
|
Vision Statistics |
US -currently 3.3 million over age 40 with low vision -2020 projected to be 5.5 million -cataracts (prominent problem) -molecular degeneration (prominent problem)
|
|
|
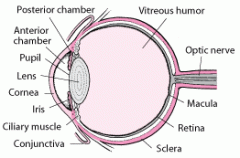
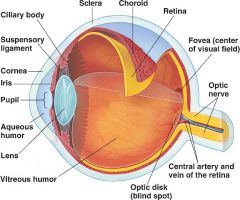
The cornea coats the exterior of the anterior eye |
True |
|
|
The lens is a circular transparent structure behind the iris |
True |
|
|
The retina is an inner thin layer made of sensory receptors |
True |
|
|
The macula is a segment of the retina that allows perception of fine detail |
True |
|
|
The aqueous humor is the thin watery fluid that fills the space between the cornea and iris (anterior chamber) and the posterior of the eye. It lubricates the iris. |
True |
|
|
The vitreous humor is a clear thick gel that maintains the eye's shape |
True |
|
|
Which term indicates a problem with distance vision? |
Myopia (near sightedness - can't see far) |
|
|
Emmetropia |
Normal near & far vision |
|
|
Hyperopia |
far sightedness (can't see near) |
|
|
Astigmatism |
distortion of cornea (contact lens damage) |
|
|
Presbyopia |
increased near point vision - objects must be placed far from the eye to be seen. |
|
|
|
|
|
Age Related Changes |
Sclera: yellow or blue Cornea: flattens and curve becomes irregular |
|
|
Age Related Changes |
-decreased muscular tone -decreased ability to focus -relaxation of eyelids |
|
|
Age Related Changes |
-Iris has decreased ability to dilate -Lens has decreased elasticity, yellow, hard and small -Tears have reduced production |
|
|
Age Related Changes |
Color vision -decreased blue, green, violet discrimination |
|
|
Cornea Damage |
comes from infection and degeneration |
|
|
blurred vision |
caused by reduced refractory power |
|
|
Lens |
loss of transparency leads to cataracts & vision loss (lens looks cloudy) |
|
|
Aqueous humor |
-H2o flow -maintains IOP (interoptic pressure) -if blocked glaucoma and vision loss occur
|
|
|
Retina separation or detachment |
-vision loss -caused by punches or blows to the head and other trauma -pt states "somebody pulled curtain over my eye" |
|
|
Macula damage |
caused by capillary breakage or fluid build up and it causes central vision loss |
|
|
"I take the blue pill once daily and the green one twice daily." |
Not good -Age related vision changes states that older pts have loss of color discrimination. |
|
|
"Before I go to bed, I prepare the pills for the next day." |
Not good -Age related vision changes states that older pts have bad night vision and they should not be preparing any pills at night. |
|
|
"If I close my right eye, I can read the labels easier." |
Not good -This is a compensatory mechanism and is not a safe accommodation for age related vision changes. |
|
|
"Every Sunday, my son puts my weekly pills into daily dosing containers." |
Good -this pt statement indicates safe accommodation for age related vision changes. |
|
|
Assessment - Targeted History |
Age -presybyopia: inability for muscles to get lens to focus |
|
|
Assessment - Targeted History |
Gender -men: retinal detachments (occupations where head can get hit) -women: dry eyes |
|
|
Assessment - Targeted History |
Occupation -sustain an eye injury -computer eye strain -working outdoors (cataracts)(outside in the light) |
|
|
Assessment - Targeted History |
Medical Problems -diabetes -htn (damage to vessels) -lupus -retinopathy |
|
|
Assessment - Targeted History |
Drugs -antihistamines -anticholenergics -steroids (increase inner ocular pressure and mask infection which sets pt up for super infection) |
|
|
Assessment - Targeted History |
Nutrition -vitamin A -vitamin C -vitamin E -Zinc -Copper -vitamin deficiency leads to macular degeneration |
|
|
Assessment - Targeted History |
Genetics -glaucoma -refractory problems
|
|
|
Assessment - Targeted History |
Current Health -loss of vision suddenly |
|
|
Increases with age |
-glaucoma -cataracts -macular degeneration (loss of vision in the center of the visual field) |
|
|
Physical Exam |
Compensatory actions -do you close one eye to see better -do you move the paper further from your face to see better |
|
|
Physical Exam |
Appearance of eye -symmetry -color ( is the cornea transparent?) -blink reflex (is it in tact?)
|
|
|
Physical Exam |
Pupils -PERRLA -3 to 5 mm are typical pupils -consensual (does the other eye do the same thing that the other eye is doing?) (pupils should be consensual) |
|
|
Visual Acuity |
Snellen -far vision Rosenbaum or Jaeger -near vision (Jaeger is the aircraft test for those that work with small parts) Visual fields -peripheral vision Cardinal fields of gaze -weakness in any field tells there is problem (good indicator for truck drivers to make sure they see whats going on around them) Ishihara -hidden colored number test |
|
|
Diagnostics |
Cultures -help identify infections Imaging -structure abnormalities, was there trauma? Did the trauma leave you with metal in your eye? Stay away from MRI or you are at risk for blindness. Slit lamp -magnifies eye structure, look at the structure of the eye (when you rest your chin in the chin rest) Tonometry -measures IOP Ophthalmoscope -dark room for good eye exam |
|
|
Metal in the eye is an absolute contraindication for which diagnostic test? |
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) |
|
|
Corneal Injury: Nursing Diagnoses |
-Acute Pain -Risk for Infection -Impaired Tissue Integrity |
|
|
Corneal Injury: Interventions |
-rest eye -put in dark room -patch both eyes, patch one eye -antibiotics (3 or more weeks) -teach correct technique wash hands use dropper no make up no contact lens don't touch eye don't touch dropper
NOTE: w/infection there is absolutely no makeup because it can get transferred to your makeup and keeps on getting back into your eye
|
|
|
Corneal Problems |
Abrasion -scratch -risk for infection -could be caused by placement of contact lens -tissue is still in tact |
|
|
Corneal Problems |
Ulcer -deeper disruption of the epilthelium -higher risk of permanent damage from infection -more serious, much deeper disruption -might come from striking of the eye -might come from sand in eye and therefore tears tissue deeper |
|
|
Corneal Problems |
Keratoconus -degeneration of corneal tissue -leading to changes in shape to cornea usually caused by trauma to the eye |
|
|
Corneal Problems |
Corneal Opacity -scarring and clouding -more cloudy of the cornea than scarring |
|
|
Corneal Problems |
Both Keratoconus and Corneal Opacity have same tx -corneal transplant
|
|
|
Corneal transplant |
-pressure patch worn for 24 hours and only removed by surgeon -patch will be removed and new one applied and changed daily -if you had surgery on right eye sleep on left side for decreased pressure -avoid activity for 8 weeks -stay away from tight shirts and socks (pressure causing) -use steroids if you think rejection is going on |
|
|
Nursing Diagnoses |
Impaired Tissue Integrity PC: Increased Intraocular Pressure (ICP) -eye patch -positioning -s/s graft rejection -activity restriction |
|
|
Anti-Infectives |
-kill or inhibit growth of bacteria, fungi, or viruses |
|
|
Anti-infectives |
Implications -proper technique -cleanliness
wash hands don't touch eye or dropper put in conjunctival sac put 30 seconds of pressure on tear duct to keep medicine on eye longer and doesn't travel to your throat |
|
|
Anti-infectives |
-gentamycin (garamycin) -tobramycin (Tobrex) -sulfacetemide (Bleph-10) -trifluridine (Viroptic) |
|
|
Anti-inflammatory |
control inflammation thereby reducing vision loss and scarring -decrease pressure, decrease pain resulting in masking infection |
|
|
Anti-inflammatory |
Implications -technique -steroids can increase sugar and mask infection -antibiotics are used w/these prophylactically just in case infection is present |
|
|
Anti-inflammatory Steroidal |
-prednisolone (PredForte) -dexamethasone (Maxidex) -can mask infection, impair healing |
|
|
Anti-inflammatory Non-steroidal |
-cyclosporine (Restasis) (dry eyes) -ketorolac (Acular) |
|
|
Anti-inflammatory Anti-allergic |
-odozamide (Alomide) |
|
|
Antibiotic-Steroid Combinations |
-Tobramycin with dexamethasone (Tobramax) -Neomycin sulfate with polymyxin B sulfate and dexamethasone (Maxitrol) -inflammation & infection all in one -2 medicines in one (drops) |
|
|
Cataract |
*Opacity of the lens that distorts the image projected onto the retina *Causes -Aging (50-80 years old) -Diabetes -Steroid use -Trauma -Congenital -genetic *Intervention indicated when visual acuity becomes unacceptable to the patient
NOTE: looks like a opacity in the center of your eye (opacity) leaving you with cloudy vision |
|
|
Clinical Manifestations |
-blurry, cloudy, colors faded, lights have halo, hard to distinguish real charachteristics -entire picture is cloudy |
|
|
Risk for Injury |
Early cataract -lighting -sunglasses Cataract removal and lens insertion -eye drops -eye shields -Minimize IOP (no bending, heavy lifting, sneezing, coughing or straining) -Report Pain |
|
|
Cataract surgery |
-implants can impair refractory -do not need glasses afterwards -best vision doesn't come back for 4-6 weeks post op -use combo drugs -wear eye shields to protect eye or eyes -itching is normal, pain is not normal |

