![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
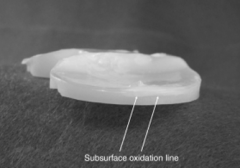
Which of the following manufacturing techniques of UHMWPE results in the < susceptibility to fatigue crack formation and propagation in joint arthroplasty bearings? 1-Ram bar extrusion with secondary machining into the desired product
2-Hot isostatic pressing into bars with secondary machining ; 3-Irradiation with 10 Mrad of radiation achieiving a polyethylene crystallinity of >90% 4. Direct compression molding from PE powder to the desired product; 5-Addition of calcium stearate to the polyethylene resin followed by compression molding into bars with secondary machining into the desired product |
compression molding and ram extrusion of polyethylene (PE) exhibit equivalent wear rates, but compression molding has a lower susceptibility to fatigue crack formation and propagation. (Of note, Miller's Review states direct compression molding consistently produces better wear rates). With direct compression the resin is directly molded into the finished part. During ram bar extrusion polyethylene resin is extruded through a die (along with heat and pressure) to create a cylindrical bar that is subsequently machined into the final product. Calcium stearate was once used to prevent corrosion on PE machine parts but resulted in unfused PE particles (fusion defects) which subsequently lowered the mechanical properties of the PE. High dose irradiation (5-15 Mrad) prompts the amorphous regions of the PE to cross-link.Ans4
|
|
The posterior condylar axis may be used to determine the rotation of the femoral component in TKA. Which of the following describes the nl relation of the posterior condylar axis: 1-Parallel to the transepicondylar axis; 2-Perpendicular to the anteroposterior axis (Whiteside's line) ; 3-3 deg ER to the transepicondylar axis; 4-3 deg IR to the transepicondylar axis; 5-7 deg ER to the transepicondylar axis
|

recreate an appropriate rectangular flexion gap, the femoral component should be aligned parallel to the transepicondylar axis. The transepicondylar axis is perpendicular to the anteroposterior axis (Whiteside's line). The posterior condylar axis is normally 3 degrees internally rotated to the transepicondylar axis. Thus, the posterior femoral cut should be made in 3 degrees of external rotation from the posterior condylar axis in order to produce a rectangular flexion gap.Ans4
|
|
Hx:18yo M w/severe hip OA and pain from a missed SCFE. You decide that a hip arthrodesis is the best treatment option. What is the optimum position for a hip arthrodesis to maximize function and prevent complications? 1-0° ER, 0° add, 0° hip flex; 2-5°ER, 0° add, 20° hip flex; 3-5° ER, 15° abd, 5° hip flex; 4-15°ER, 0° add, 20° hip flex; 5-15° ER, 15° abd, 5° hip flex
|
Hip arthrodesis is a salvage procedure for pts w/ hip arthritis w/OUTt ipsilateral knee, contralateral hip, or lumbar spine pathology.
optimal position for hip arthrodesis = 0-5 deg of add, 0-5 deg ER, 20-35 deg of hip fle.Ans2 |
|
|
A 66-year-old male is undergoing a total knee arthroplasty using a fixed bearing posterior stabilized component. During intraoperative trialing of the components it is noted that the flexion gap is loose, and extension gap is appropriate. If this is not corrected, what post-operative complication is this patient at risk of having? 1. Spin out of the polyethylene
2. Periprosthetic fracture 3. Posterior knee dislocation 4. Osteolysis 5. Patellar instability |
A posteriorly stabilized knee has a post built into the polyethylene bearing that articulates with the box of the femoral component in flexion to act as a cam mechanism. If the knee is too loose in flexion, it is possible for the femoral component to "jump the post", causing a posterior dislocation.Ans3
|
|
|
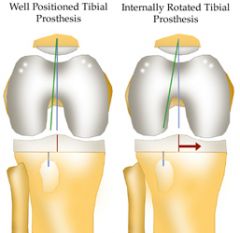
Following a left total knee arthroplasty, all of the following can cause the condition seen in Figure A EXCEPT: 1. Internal rotation of the femoral prosthesis
2. Internal rotation of the tibial prosthesis 3. Lateralization of the femoral prosthesis 4. Medialization of the tibial prosthesis 5. Lateralization of the patellar prosthesis |
Lateralization of the femoral prosthesis would not lead to lateral patellar subluxation. However, lateralization of the patella or the tibial tray could lead to lateral patellar subluxation.
The Malo article reviewed the common issues regarding the patellofemoral compartment after TKA. Patellar instability & maltracking can result from malpositioning of the component, prosthetic design, improper patellar preparation, or soft-tissue imbalance. Patellar instability & maltracking most often occurs due to internal malrotation of the femoral or tibial components, lateralization of the patellar component, or medialization of the femoral or tibial components. Medialization, not lateralization of the femoral prosthesis will increase the Q angle and lead to lateral subluxation of the patella.Ans3 |

