![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What enables an electric current to pass round a circuit? |
Circuit must be complete Source of potential difference- battery forces charge carriers through conducting material and components |
|
|
Electric current (I) = |
rate of flow of charge in the wire/component |
|
|
Charged particles/ charge (Q) = |
charge carriers. in metals = electrons in a salt solution = ions |
|
|
The conventional direction of current in a circuit |
+ to - (convention was agreed long before electrons were discovered it was not known whether the current was due to a flow of positive charge from + to -, or if it was due to negative charge from - to +) |
|
|
Diagram showing current/electron flow |
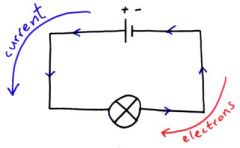
|
|
|
Unit of current |
Ampere (A) |
|
|
Unit of charge |
Coloumb (C) |
|
|
ΔQ = I * Δt |
- |
|
|
What is an insulator |
No current can pass through an insulator, because it yields no free electrons |
|
|
What is a metallic conductor |
When voltage is applied across the metal, delocalised electrons can carry the charge towards the positive end of the terminal |
|
|
What is a semiconductor |
no. of charge carriers increases with an increase of temp. ∴ resistance of semiconductor decreases, as temperature increases |
|
|
The work done by each electron is equal to |
its loss of energy |
|
|
Potential difference/voltage (V)= |
work done (or energy transfer) per unit charge (1 joule per coulomb) The battery is described as having the "potential" to transfer energy from its chemical store if the battery is not part of a complete circuit |
|
|
V= W/Q |
- |
|
|
The emf of a source of electricity = |
electrical energy produced per unit charge passing through the source. Measured in volts |
|
|
The electrical energy when charge Q passes through the source = |
Q * emf |
|
|
How does an electrical heater use electrical energy to produce heat? |
In a device that has resistence the work done on a device is transferred as thermal energy Charge carriers repeatedly collide with atoms in the device and transfer energy to them Atoms vibrate = resistor become hotter |
|
|
How does an electric motor use electrical energy to produce movement? |
The electrons are forced through the wires in a magnetic field, causes the coil of wire to spin |
|
|
How does a loud speaker use electrical energy to produce sound/vibrations?
|
Electrons are forced through the wires of the vibrating loudspeaker coil against the force on them due to the loudspeaker magnet. |

