![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common globin mutation?
Resultant hemoglobinopathy Populations affected Effects Requirements for Disease State |
beta-26 mutation-->Hgb E
Present in SE Asians Leads to mild microcytic anemia; causes clinical dz when combined with beta-thal |
|
|
Hgb C:
Affected populations Mutation Effects Requirements for Disease State |
Found in African descent
Mutation at beta-6 (glutamate to lysine) Affects cellular hydration; MANY TARGET CELLS Dz state w/Hgb S |
|
|
Hgb S:
Mutation Effects Requirements for Disease State |
beta-6 mutation (glutamate to valine)
Mutation results in polymer formation in DEoxygenated state Dz state when combined w/second S gene or other Hgb mutations |
|
|
How does Hgb S contribute to increased risk of thrombosis?
|
Rigid, sickle shaped red cells with sticky membranes damage endothelium of vessels
Elevated platelet count (due to increased BM production in response to RBC death)-->high risk of thrombosing small vessels |
|
|
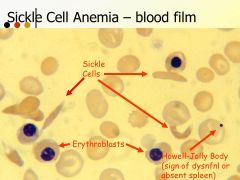
Hallmark of sickle cell disease.
|
Veno-occlusive crises:
PAIN with infarction of BM Splenic infarct/sequestration Acute chest syndrome: thromboses within lung BVs Priapism: painful erection due to inability to release blood from turgid penis |
|
|
Non-veno-occlusive crises of sickle cell disease.
|
Sepsis (poor splenic fn)
Gallstones (elevated hemolysis) Iron overload in transfusion tx |
|
|
If a baby shows on newborn screen to have sickle cell disease , but parents have no sickle cell disease, what do parents have?
|
Both parents have HgbAS (sickle cell trait)--infant has HbSS dz
OR One pt has HbAS (sickle cell trait) and other is HbA-beta-0thal (beta thal trait)--infant has HbS-Beta0 thal dz |
|
|
Medical management of sickle cell disease.
|
-PCN prophylaxis, vaccination
-Management of fever, pain -Erythrocyte transfusion (with non-sickled cells) -Hydroxurea -Stem Cell Transplantation (need match sibling donor) |
|
|
|

