![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 3 general characteristics of carbohydrates?
|
-polyhydroxyl aldehydes or ketones
-empirical formula (CH2O)n-hydrates of carbon -more CHO than any other organic matter |
|
|
Two ways to classify carbohydrates and examples of each.
|
Classified by size (CH2O)n n = 3-9
5 = pentose 6 = hexose Classified by nature of carbonyl group Aldehyde = aldose ketone = ketose |
|
|
Sugars have at least one ____ carbon
|
asymmetric
|
|
|
How are sugars oriented in Fisher projections?
What info can you see on this for Hayworth projections? |
C1 is at the top (the aldehyde or ketone), C6 or C5 is at the bottom.
Hydroxyls on left will be up, right down. Orientation of hydroxyl furthest down tells L (left)/D (right -> down) |
|
|
What is the structure of D-Glc in a Fisher projection?
|
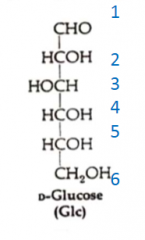
|
|
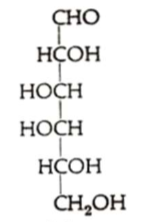
What sugar is this?
|
D-galactose
|
|
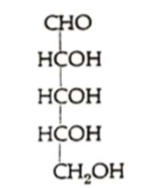
What sugar is this?
|
D-ribose
|
|
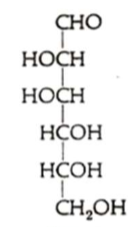
What sugar is this?
|
D-mannose
|
|
|
Draw all the sugars we learned.
|
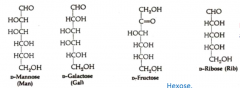
|
|
|
What is an epimer by definition?
|
isomers that differ in confirmation around one chiral carbon
|
|
|
D-Glc is an epimer of
|
D-Man and D-Gal
|
|
|
D-Gal is an epimer of
|
D-Glc
|
|
|
Linear sugars form rings by making a ____ bond between the former ____ and ____
|
hemiacetal
aldehyde and hydroxyl |
|
|
How do you tell the difference between alpha and beta sugars?
|
Look at anomeric carbon and what way the OH is pointing. Same as the acetyl group is Beta. Down away is alpha
|
|
|
Which is more predominant alpha or beta D-glc?
|
Beta 2/3
Alpha 1/3 |
|
|
What is the interconversion of alpha to beta called?
What are you swapping between? |
mutarotation
anomers |
|
|
Draw all the sugars as Hayworth projections.
|
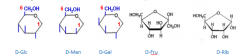
|
|
|
What is the term for a 5-membered ring sugar? 6?
|
furanose
pyranose |
|
|
Is a hexose always going to be a pyranose?
|
Nope e.g. fructose is hexose that commonly forms furanose
|
|
|
Onic Acids
What is it? What is the Glc derived onic acid? Draw that structure |
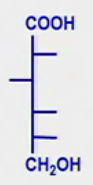
C1 is a carboxyl group (as opposed to aldehyde or ketone)
Gluconic acid (makes gluconate salt) |
|
|
Uronic acid
What is it? What is the Glc derived uronic acid? Draw that structure |
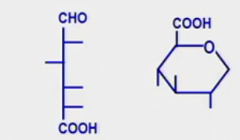
Last numbered carbon is a carboxyl group (as opposed to the hydroxyl carbon)
Glucuronic acid (glucoronate) |
|
|
Which sugar acid can form Hayworth projections?
|
The uronic acids (still have aldehyde)
not the case for onic acids |
|
|
What kind of molecules are rich in uronic acids?
|
GAG glycosaminoglycans made of proteoglycans
|
|
|
Sialic acids
What are they? Fact about it What is the example we learned? |
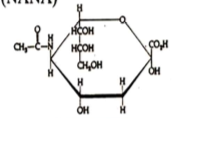
nine carbon carboxylic acid (on C1)
It's never free in the cell but always attached to proteins NANA (N-acetylneuraminic acid) |
|
|
Amino sugars: how do they work?
|
Have an amino group instead of a hydroxyl group on C2
|
|
|
Two examples of amino sugars
These are both These are (?) charged in water? |
glucosamine and galactosamine
hexoamines Yes. The amino group becomes protonated. |
|
|
What products do you get from our two amino sugar examples when the amino group gets acetylated?
What are two facts about them? |
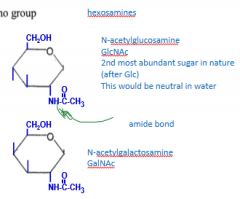
N-acetylglucosamine GlcNAc and
N-acetylgalactosamine GalNAc GlcNAc is second most abundant sugar Both would be neutral in water |
|
|
What disease has to do with hexosamines?
|
Tay-Sach's. A sphingolipidosis disease: hexosaminidase isn't available to cleave GalNAc off of GM2 ganglioside.
Normal development for 6 months then degeneration cherry red spot. Jewish and French Canadians |

