![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
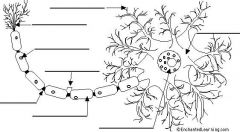
Label the Neuron
|
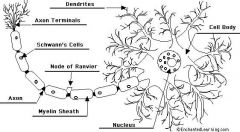
See above labeled Neuron
|
|
|
What are the four functional zones of a neuron?
|
Receptive zone
Trigger zone Conducting zone Secretory zone |
|
|
Receptive zone consists of...
|
Dendrites and Cell body
|
|
|
Trigger zone consists of...
|
Axon Hillock
|
|
|
Conducting zone consists of...
|
Axon
|
|
|
Secretory zone consists of...
|
Telodendria and terminal boutons
|
|
|
Amitotic
|
Unable to go through mitosis.
|
|
|
What accumulates in the terminal bouton?
|
(K+) Potassium
|
|
|
What are the three ways to get rid of extra neurotransmitters?
|
Reuptake
Phagocytosis Enzymatic degradation |
|
|
_____ are pumped out for every _____ that are pumped in.
|
3 Na+ for every 2 K+
|
|
|
What will happen if Na+ and K+ reach equilibrium across these cells? What prevents this?
|
You will die.
The pumps. |
|
|
Voltage
|
Voltage is a measure of the amount of difference in electrical charge between two points.
|
|
|
Where are Ligand gates found?
|
Only found in cell body and dendrites
|
|
|
Where are Voltage gates found?
|
Only found on axon hillock, axon, telodendria, and terminal boutons.
|
|
|
Resting membrane potential
|
The potential across the membrane when the cell is at rest (i.e. when there is no signaling activity. -70mV
|
|
|
Polarized
|
?
|
|
|
Current
|
The flow of electrical charge from point to point.
|
|
|
In the body, electrical currents are due to what?
|
Are due to the movement of ions across cellular membranes.
|
|
|
What is a reflex?
|
A reflex is a reaction to stimuli; involuntary motor responses.
|
|
|
Somatic reflex
|
Reflexes that activate skeletal muscle.
(rapid withdrawl of hand from hot object) |
|
|
Examples of somatic reflexes are?
|
Abdominal, Achilles, Corneal, crossed extensor, gag, patellar, and plantar reflexes.
|
|
|
Simple stretch reflex
|
Two-neuron, monosynaptic reflex arc.
|
|
|
Examples of simple stretch reflexes are?
|
Achilles and Patellar reflexes
|
|
|
Examples of superficial cord reflexes are...
|
Abdominal and plantar reflexes.
|
|
|
Autonomic reflexes
|
Reflexes that activate smooth or cardiac muscle and/or glands.
|
|
|
Examples of autonomic reflexes are...
|
Ciliospinal and pupillary light reflexes.
|
|
|
Name two cord-mediated reflexes
|
Plantar and Achilles reflexes.
|
|
|
Name two somatic reflexes in which the higher brain centers participate
|
Corneal & gag reflexes
or abdominal & plantar reflexes. |
|
|
Name the division of the autonomic nervous system responsible for these reflexes..
Ciliospinal? Salivary? and Pupillary light? |
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic Parasympathetic |
|
|
Somatic
|
Voluntary
|
|
|
Autonomic
|
Involuntary
|
|
|
What is the difference between Basic and Learned reflexes
|
Basic you are born with (breathing) and learned you learned (like walking).
|
|
|
3 factors that may modify reaction time to a stimulus...
|
How sensitive are your receptors, how fast are your nerves, and the number of nerves responding.
|
|
|
What are the 5 components of a reflex arc?
|
Receptor
Sensory neuron Integration center Motor neuron Effector |
|
|
Receptor
|
is the site of stimulus action
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
transmits afferent impulses to the CNS
|
|
|
Integration center
|
consists of one or more synapses in the CNS
|
|
|
Motor neuron
|
Conducts efferent impulses from the integration center to an effector organ.
|
|
|
Effector
|
Responds to efferent impulses characteristically (by contracting or secreting respectively).
|
|
|
Stretch reflexes
|
are for maintaining posture, balance, and locomotion.
|
|
|
Crossed extensor reflex
|
Consists of flexor or withdrawl reflex followed by extension of the opposite limb.
|
|
|
Superficial cord reflexes
|
Are initiated by stimulation of the receptors in the skin or nucosae.
|
|
|
Can a cell body and cell body synapse with each other?
|
No
|
|
|
Neurons can be classified structurally by the number of processes extending from their cell body. Which is the most common neuron type in humans?
|
Multiplolar
(Over 99% of neurons in humans are multipolar.) |
|
|
Somatic sensory afferents transmit impulses from the _________to the CNS.
|
The skin
|
|
|
The interior of a nerve cell has a slight excess of negative charge because
|
Potassium diffuses out of the cell.
|
|
|
The Nissl bodies seen in the neuron cell body represents which cellular organelle?
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulium
|
|
|
Bundles of neuron processes are called _____in the CNS and ______ in the PNS.
|
Tracts in CNS
Nerves in PNS |
|
|
Describe the membrane situation in the resting state in the neuron?
|
All the voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed
|
|
|
What lines the central cavities of the brain and spinal cord and provides a barrier between the CSF and nervous tissue?
|
Ependymal cells
|
|
|
Is slow conduction of nerve impulses associated with a myelinated nerve fiber?
|
No
|
|
|
Is direct flow of ions from one neuron to the next involved in the transfer of information across a chemical synapse?
|
No
|
|
|
Which of the following electrical event occurs when a certain threshold is reached?
|
a
|
|
|
Which of the following factors is associated with increased conduction velocity in an axon?
|
a
|
|
|
Hyperpolarization is produced which spreads to the axon hillock is a characteristic of the action of an______ but not in an ______ ?
|
IPSP not EPSP
|
|
|
A potential of –--90 mV would be considered to be
|
Hyperpolarized
|
|
|
During which phase of an action potential are voltage-gated K channels open, while voltage gated Na channels are closed?
|
Hyperpolarization
|

