![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of Ring Strain
|
Bond angle strain E(θ) Torsional strain E(φ)- (repulsion from electrons and substituents on adjecent atoms (eclipsed, staggered etc)) Non-bonded interactions E(d) - if atoms or groups not directly bonded together are pushed close together (less than sum of Van der Waals radii) |
|
|
How can molecular strain be measured?
|
examining trends in heats of combustion (ΔHcomb) for a homologous series |
|
|
Which is more costly in energy bond length or bond angle?
|
Bond angle deformation is less costly than changes in bond length |
|
|
Conformational isomer?
|
different shapes of molecules resulting from the deformation of bonds (almost always rotation about single bonds) (no bonds are broken when converting between conformers) |
|
|
Configurational isomer?
|
Different connectivity of atoms within stereoisomers |
|
|
Draw cyclohexane chair conformation now
|
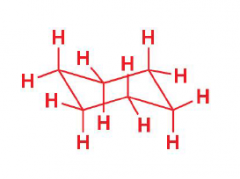
|
|
|
Total Strain in Cycloalkanes (graph)
|
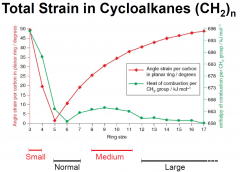
|
|
|
why is cyclopropane highly strained?
|
High bond angle stain + eclipsed C-H bonds(torsional strain) |
|
|
Cyclobutane strain (comments) |
bond angle starin is high, but distortion away from planarity means C-H bonds don't have to be eclipsed |
|
|
Cyclopentane strain(comments) |
although closest bond angle to 109.5, planar configuration results in eclipsed CH2 bonds therefore forms envelope or twist conformations (envelope is lower in energy) |
|
|
Cycloheptane strain (comments) |
Rings with > 6 atoms tend to be inherently more flexible
4 low-energy conformations |
|
|
Medium sized ring strain C8-C11 (comments) |
all significantly less stable than cyclohexane because of bond angle strain, torsional strain and transannular clashing e.g. cyclodecane -all internal H-atoms are 1.8A apart, less than sum of their Van der Waals radii (which is about 2.2A) |
|
|
Large sized ring strain >11
|
Called macrocycles, Transannular strain is diminished can adopt any number of conformers to become staggered and achieve optimum bond angle. |
|
|
What two distinct locations for substituents are there in cyclohexane chair conformation?
|
Axial and Equatorial positions |
|
|
Covalent bond homolysis (rough energies) |
200-460KJmol⁻¹ |
|
|
Hydrogen bond strength (rough energies) |
4-125 KJmol⁻¹ |
|
|
Cyclohexane chair flip barrier (rough energies) |
43 KJmol⁻¹ |
|
|
Butane rotational barrier (rough energies) |
6 KJmol⁻¹ |
|
|
NMR of cyclohexane signals C₆D₁₁H₁ |
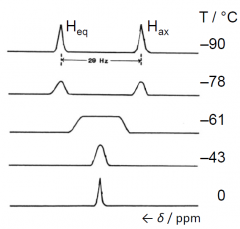
|
|
|
What conformers of monosubstituted cyclohexane where X≠H have the lowest energy?
|
Conformers with the largest substituent in an equatorial position are the generally the lowest energy
|
|
|
How do we quantify conformational equilibrium?
|
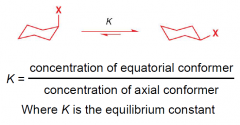
|
|
|
What is an 'A value'?
|
Energy difference between two conformers |
|
|
What do the A values (and equlibrium constants) depend on? |
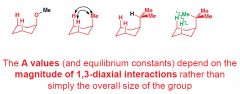
|
|
|
What is a conformational lock?
|
where it is energetically costly to occupy a particular conformer therefore doesn't really happen |
|
|
What position does a tBu group prefere to take on a cyclohexane ring? |
equitorial, as axial positions are very energetically costly
|
|
|
What is an E1 reaction? |
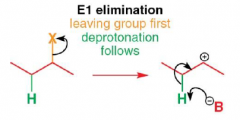
|
|
|
What is an E2 reaction?
|
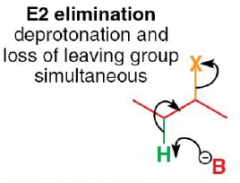
|
|
|
What is an E1cB reaction?
|
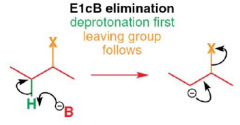
|
|
|
What nucleophiles favour elimination over substitution?
|
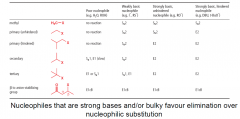
|
|
|
What geometry intermediate does E1 form?
|
Trigonal planar carbocation |
|
|
What happens if the geometry of a molecule prevents planarization of C-center in E1 reactions?
|
E1 is not possible |
|
|
What do you need for a E1cB mechanisms to occur?
|
a poor leaving group -OH or -OR and an acidic hydrogen (hydrogen on carbon atom adjacent to a carbonyl carbon atom or a H on a OH) |
|
|
What conformations gives good orbital overlap for E2 elimination?
|
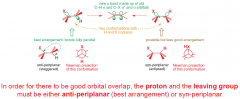
|
|
|
E2 elimination from cyclohexanes information (possibly break up into multiple questions in future) |
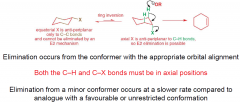
|
|
|
What products are most favoureud in elimination reactions under most circumstances?
|
|
|
|
1-chloro-1-methylcycloHexane, where will the double bond form on E2 elimination witha sterically hindered base? |
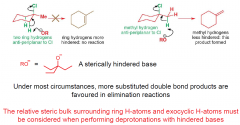
|
|
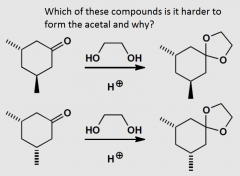
|
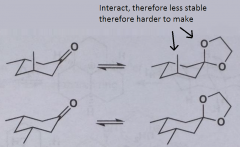
|
|
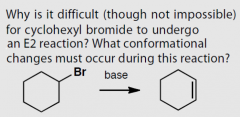
|
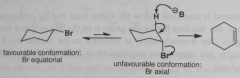
|
|
|
structure of cyclohexanone?
|
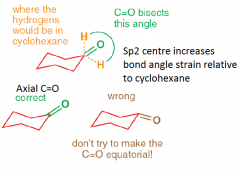
|
|
|
What isomer of cyclohexene is stable?
|
cis as trans would be too strained |
|
|
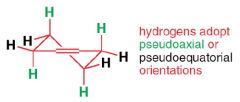
what positions do hydrogens in cyclohexene adopt? |
|
|
|
how many atoms lie in a plane in cyclohexene?
|
4 |
|
|
How do we know if a substituent on a di substituted cyclohexane is axial or equatorial?
|
We need to draw out the chair diagram, to give us a 3d representation from which we can then start to determine what the ideal position is |
|
|
How can we predict lowest energy conformation?
|
In general, the conformation with fewer axial substituents is lower in energy. If there are equal numbers of axial and equatorial substituents in two conformations, refer to the A values |
|
|
Anomalies to usual conformations in cyclohexane?
|
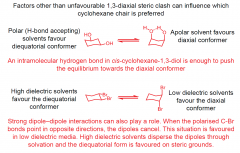
|
|
|
What are spiro compounds?
|
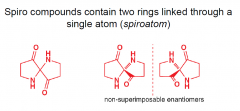
|
|
|
What are decalins?
|
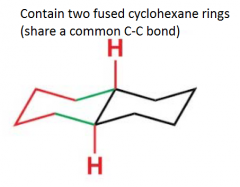
|
|
|
Difference between cis and trans decalins?
|
Trans-decalins are conformationally locked, while cis-decalins are able to undergo ring flipping. |
|
|
what is the base structure of all steroids? |
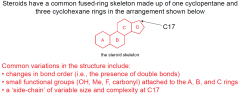
|

