![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the significance of the 3 carbon unit (like pyruvic acid) and 2 carbon units (acetyl groups)?
|
With combinations of odd number and even numbers of carbons you can build any number of carbons except one. 2s and 3s are magic numbers. You can also break them down well.
|
|
|
Where does decarboxylation occur?
|
Mitochondria. The first decarboxylation occurs in the intermembrane space, but the cycle itself happens inside the matrix. CoA is waiting in the inner membrane, it is membrane bound, to accept the Acetyl Groups (actually there are many CoAs in the membrane) waiting to accept many 2C Acetyl Groups.
|
|
|
How many ATP are produced by the Citric Acid Cycle?
|
2 more ATP (per glucose molecule) are produced by the TCA, Krebs, Citric Acid Cycle. That's a gross of 6, and a net of 4 so far for each Glucose molecule that's gone through glycolysis and the TCA. There will be at least 32 more later after ETS.
|
|
|
What are coenzymes?
|
"Co" means With. These are NOT enzymes, they work in conjunction with enzymes. Enzymes are proteins. These are not proteins, they come from vitamins. i.e. CoA
|
|
|
What types of reactions are like a game of hot potato?
|
Redox reactions, which characterize the ETS. Once something becomes Reduced (gains energy/electron), it tries to get rid of the extra negative energy by throwing it to another molecule and thereby becoming reduced.
|
|
|
What are cofactors?
|
Metalloproteins made from miners and proteins that help or work with ("co" means "with") enzymes. They are sometimes called respiratory enzymes, but they are really not enzymes. They are also called cytochromes.
|
|
|
Metalloproteins
|
A protein with a little metal added to it. i.e. hemoglobin protein with iron, colored red.
|
|
|
What metals produce what colors when added to proteins?
|
nickel - green
iron - red cobalt - blue |
|
|
What does cytochrome mean?
|
"Cell Color" 5 enzymes (metalloproteins) with iron cofactors, brightly colored in pure form. In order of participation in the Electron Transport Chain (System) they are B, C1, C, A, A3.
|
|
|
What are the nicknames of the coenzymes?
|
NAD
FAD FMN CoQ (ubiquinone) |
|
|
What do the coenzymes want to do and what do they sometimes do as well?
|
They want to pick up electrons, but sometimes they pick up protons.
|
|
|
What is the oxidized form of hydrogen?
|
A single proton (p+)
|
|
|
What is the reduced form of hydrogen
|
A proton with an electron on it. (P+ with e-)
|
|
|
Technically, is the coenzyme pert of oxidative phosphorylation part of the ETS?
|
No, it happens in the mitochondria and they are electron donors to the ETS in terms of "handing off" but ETS doesn't start until 2 electrons are handed off to the metalloproteins.
|
|
|
What is the order of the handing off electrons to CoQ?
|
2 e- handed to NAD, then handed to FMN, then handed to CoQ
Also FAD hands to CoQ? |
|
|
After CoQ, where are the 2 electrons handed off to?
|
To the ETS where they are handed off to oxidized metalloproteins (respiratory "enzymes", cytochromes, cofactors) that then become reduced. Cytochrome B gets them first, then C1, then C, then A, the A3. Simple order is B,C,A,A3.
|
|
|
When a molecule has the electrons is it reduced or oxidized?
|
Reduced. Remember GER. Gain Electron Reduced. Things start out oxidized then get reduced.
|
|
|
What is the point of the handing off of the electrons?
|
It creates a "battery". Metals are conductive and good for transporting electrons. Winds up creating an electrical charge. In mitochondria, H+ ions(protons) in intermembrane space (very acidic, positive atmosphere) go through H+ ion channel in Inner mitochondrial membrane. Called "chemiosmosis" -- spark that turns ADPs and phosphates into ATP (30-34).
|
|
|
Where are the coenzymes and cytochromes located?
|
They are membrane bound, in the innner mitochondrial membrane.
|
|
|
How do hydrogen ions relate to pH?
|
The more Hydrogen Ions, the pH number on the scale goes down (more acidic).
|
|
|
During oxidative phosphorylation, is the intermembrane space acidic or basic?
|
It's very acidic, but it's mostly lipid so it doesn't destroy the cell membrane. It's a positively charged atmosphere (as opposed to the negative atmosphere inside).
|
|
|
Why is the mitochondria like a battery in oxidative phosphorylation?
|
Because the positive (acidic) atmosphere outside and the negative atmosphere inside are kept apart. However, they are connected by the H+ ion channel. Chemiosmosis occurs because the + gets together with the - there, and ATP is created via this "battery".
|
|
|
How do hydrogen ions relate to rocket fuel in the aerobic respiration?
|
Splitting H+ ions (into protons and electrons) and reuniting them makes water (H2O + ATP), just like when the shuttle takes off and leaves steam trail in its wake.
|
|
|
Where does the most ATP production occur? Is it Aerobic or Anaerobic?
|
It happens in the matrix of the mitochondria and is aerobic (needs oxygen).
|
|
|
What is the purpose of ETS? Does it produce ATP?
|
To create the conditions necessary for Oxidative Phosphorylation. It does NOT produce ATP but it creates the conditions necessary. The actual aerobic part doesn't occur until oxygen arrives (like battery doesn't RUN the car..it creates conditions necessary to start it up and make it go.
|
|
|
What drives Oxidative Phosphorylation?
|
Chemiosmosis drives Oxidative Phosphorylation.
|
|
|
What does anaerobic metabolism create the conditions for?
|
It creates conditions for aerobic metabolism.
|
|
|
How many ATP are used to make one muscle contraction?
|
3.75 billion ATP. The production of ATP happens rapidly.
|
|
|
What does building aerobic endurance do for the body?
|
It makes the metabolism work better for the body.
|
|
|
What does glyconeogenesis do?
|
It turns pyruvic acid back into glucose.
|
|
|
What does the name oxidative phosphorylation indicate?
|
The name indicates that oxidation is occurring somewhere...the redox reactions drive the phosphorylation. Ox Phos. Not to be confused with the garden variety phosphorylation that occurs in glycolysis or dephosphorylation that occurs in krebs. It's Oxidative.
|
|
|
What drives Ox Phos Oxidative Phosphorylation?
|
Chemiosmosis (the movement of H+ ions drives oxidative Phosphorylation.
|
|
|
What is glycogen?
|
It's the storage form of carbohydrate, and the only polysaccharide (a polysaccharide of glucose) in the human body. Analagous to starch in plants. It is stored in liver and muscles.
|
|
|
How many days worth of glycogen is stored in the body?
|
2 days worth of carbs is stored in the body in this form.
|
|
|
How does the body use glycogen?
|
It breaks it down (catabolizes) it into glucose. That's called glycogenolysis. (glycogen + lysis or "breaking up").
|
|
|
How does the body break down glucose?
|
It's catabolized through glycolysis, which breaks it down into 2 pyruvic acids.
|
|
|
How does the body break down pyruvic acid?
|
It gets decarboxylated and becomes acetyl groups (one 2C Acetyl Group for each Pyruvic Acid)
|
|
|
What's gluconeogenesis?
|
If you have an excess of pyruvic acid (2 3Cs) you can anabolize it or make new glucose out of it.
|
|
|
What's glycogenesis?
|
If you take glucose and put it into storage, you are anabolizing it, or turninig it into glycogen.
|
|
|
What's proteolysis?
|
Dissolution (catabolism, hydrolysis) of proteins into amino acids.
|
|
|
What's protein synthesis?
|
Dehydration synthesis of amino acids to form proteins.
|
|
|
What's the storage form of Amino Acids?
|
Protein
|
|
|
What's the storage form of lipids?
|
Triglycerides.
|
|
|
What is lipolysis?
|
The dissolution (catabolism, hydrolysis) of lipids into 3 fatty acid and 1 glycerol (3C).
|
|
|
How do you make a triglyceride and what is it called?
|
Lipogenesis. You are adding 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol.
|
|
|
Do lipids have even or odd numbers of carbons?
|
Even numbers. They are broken down through beta oxidation.
|
|
|
Can some amino acids be broken down into Pyruvic acids (units of 3)?
|
Yes, some can be broken down into pyruvic acids. They can also be broken down into units of 2 (Acetyl Groups).
Every amino acid will fall into either 2 or 3 carbon groups. |
|
|
Are fatty acids broken down into even or odd numbers of carbons?
|
They are broken down to even numbers of carbons, so they always make acetyl groups (2C).
|
|
|
What does 3C glycerol become?
|
Glycerol becomes 3C Pyruvic acid, because it is a 3C unit.
|
|
|
What does a glycerol molecule look like? How does it become a triglyceride?
|
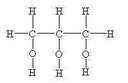
Dehydration synthesis attaches the fatty acids to it (they replace the -OH side)
|
|
|
How do you hook up a fatty acid to glycerol?
|
Dehydration Synthesis. This forms triglycerides if you have 3 FAs and a glycerol. When you take the water out, it gets sticky.
|
|
|
How many carbons is a typical fatty acid chain?
|
Usually 20-30 carbon carbon skeleton, always even numbers.
|
|
|
What is the C-O-O-H group called that's at the end of a fatty acid chain?
|
A Carboxyl Group (Carboxylic Acid). There's a Carbon/Oxygen Double Bond, and another Oxygen coming off, and a Hydrogen coming off that. It is acidic and a fat, so it's called a fatty acid.
|
|
|
How are the carbons on a FA chain named?
|
The first one, the one that's part of the carboxyl group is called the alpha carbon. The one directly next to that is the beta. Then, go all the way to the other end and start naming them omega 1, omega 2, omega 3 etc.
|
|
|
How is a fatty acid chain burned for fuel?
|
Through beta oxidation, cutting off two carbons at a time and feeding them into the mitochondria.
|
|
|
What elements have the ability for 1, 2, 3, 4 bonds?
|
H (1), O (2), N (3), C (4)
|
|
|
What do the alpha and beta carbons of a FA become in beta oxidation?
|
They become an acetyl group to be handed off to oxoacetalic acid. The next ones in the chain become the new alpha (becomes carboxyl group when it picks up oxygen and hydrogen) and the new beta.
|
|
|
What cofactors must be present for Beta Oxidation?
|
FAD, NAD, CoA.
These enzymes act like clippers to cut the fatty acid chains into acetyl groups. |
|
|
What is an omega 3 fatty acid?
|
When the hydrogen double bonds at the omega 3 position. The omega number indicates where the double bond is.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of beta oxidation?
|
To produce acetyl groups (2C).
|
|
|
What happens if you have more acetyl groups than you need?
|
They can be stored as fatty acids, in triglyceride forms.
|
|
|
What increases metabolism?
|
Exercise, some stimulants such as caffiene, etc.
|

