![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many visits to the ER have there been in the south per 2006?
|
50.624 M
|
|
|
How many visits to the ER in the US were for uninsured or charity?
|
20.777 M uninsured
2.232 M charity |
|
|
What percent of visits to the ER in 2006 for the US were seen after PCP closed for the day?
|
64%
|
|
|
What % of of the pts in the ER in the US were admitted?
|
13%
|
|
|
What % of pts going to the ER in 2006 were seen again within 3 days resulting in a different Dx?
|
3.6%
|
|
|
What % of pts required immediate tx even though they came to the ER?
|
16%
|
|
|
Why is it economically more reasonably to practice OMM in an ER setting?
|
pts report more face-time with their doc, had fewer re-visits, increased average time by 9 minutes, but pts reported feeling like they had 10 to 15 minutes more with their pts. the extra time was properly reimbursed, which made it justified.
|
|
|
What types of OMM are more helpful in ER?
|
virscero-somatic reflexes, chapman's points, referred pain (somato-somatic), compensatory pain at a remote location indicating somatic dysfunction
|
|
|
What can one do to improve respiratory mechanics?
|
improve alignment, ROM, inhalation/exhalation lesions, diaphragm mechanics with rib raising, BLT or ME to improve kyphosis, counterstrain to release thoracic cage tension
|
|
|
How can one improve upper respiratory infection or congestion?
|
OA release, occipital release, neck soft tissue, cervical HVLA, BLT, ME to improve drainage from head, lymphatic chest pump, pedal pump to move lymph
|
|
|
How does one tx pneumonia per OMM in the ER?
|
enhance movement of fluid and air through lungs: rib raising, ME on ribs, BLT, ME on thoracic, thoracic inlet, lymphatic to enhance immune response
|
|
|
How does one tx cellulitis per OMM in the ER?
|
body need to deliver nutrients and O2 to area of infection: enhance lymphatic flow (BOTH inlet, LE = pelvis, lumbar, UE = thorax, shoulder), remove edema, start appropriate Ab first!
|
|
|
What is the complication of OMM on a cellulitis pt without appropriate antibiotics?
|
septicemia by encouraging infectious agent to be better circulated along with the lymph.
|
|
|
How do you tx migraines in the er with OMM?
|
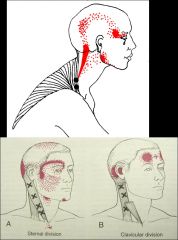
trigger points for migraines and tension HA by suboccipital release, cervical soft tissue, FPR or BLT on trigger points
|
|
|
What is a migraine due to?
|
sudden vascular dilation or contraction
|
|
|
95% of disk herniations occurs at what levels?
|
L4-L5 or L5-S1
|
|
|
What additional symptoms, aside from Lower Back Pain, does an L5-S1 herniation usually present with?
|
mimics shin splints, calf pain mimics thrombophlebitis, peroneal nerve at fibular head or tibial nerve (S1) at tarsal tunnel can be aggravated
|
|
|
When is an xray initially indicated? When is an MRI or CT scan initially indicated?
|
xray - should always be done on an acute injury
MRI/CT - use if neurological impairment accompanies pain |
|
|
What referred pain does psoas, illiacus, and quadratus spasm cause?
|
low back pain, ipsilateral groin pain, contralateral piriformis pain
|
|
|
What referred pain does a piriformis muscle spasm usually cause?
|
ipsilateral buttock and post thigh pain, hip flexor and extensor pain sometimes
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of lower back pain?
|
psoas and quadratus spasm
|
|
|
What level of proof from research has osteopathic FPR and BLT achieved for acute low back pain?
|
level 2 (being second only to level 1 as best evidence)
|
|
|
What level is the following: avoid intramuscular corticosteroid injections, avoid NSAIDS more than 2 days, heat for short term benefit, avoid HVLA?
|
steroid: level 2
NSAIDS: level 2 Heat: level 2 avoid HVLA: level 1 |
|
|
Why should we avoid HVLA in acute low back pain?
|
pts report having more pain and being able to do less 2 days after manipulation. use fpr and counterstrain
|
|
|
Pts most likely to benefit from spinal manipulation must meet 4/5 of what criteria?
|
1. symptom duration < 16 days
2. no symptoms distal to knee 3. score < 19 on fear-avoidance measure 4. at least 1 hypomobile lumbar segment 5. at least 1 hip with > 35 degrees of internal rotation this is known as the prediction rule (level 2) |
|
|
How can we help an ankle inversion injury with OMM in ER?
|
reduce counterstrain, fix talar dysfunction, fix cuboid, fix posterior fibular head. if there is tibial torsion then look for possible strain to deltoid ligament.
|
|
|
How are ankle injuries graded?
|
I - partial tear of a ligament
II - incomplete tear with moderate functional impairment III - complete tear and loss of integrity of ligament |
|
|
What position of the ankle produces a higher risk of damage to the anterior talofibular ligament?
|
plantar flexion
|
|
|
What two tests can be used to check for ankle stability in an acute ankle injury?
|
anterior drawer test
talar tilt test |
|
|
What are the Ottawa ankle rules and how are they used?
|
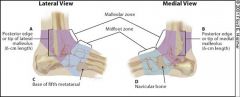
get a radiograph of a painful ankle if:
1. bone tenderness at A, B 2. inability to bear weight radiograph of foot with pain to midfoot if: 1. bone tenderness at C, D 2. inability to bear weight |
|
|
What are the 4 steps of tx for an ankle injury and how is each step leveled?
|
xray if tenderness at bone and unable to walk 4 steps (general/Ottawa-ish)
NSAIDS less than 7 days - level 1 OMT - level 2 RICE for 48 hours - level 2 early mobilization - level 2 |
|
|
What is the Eisenhart study?
|
OMT may improve the range of motion in an acute ankle injury - level 2, p = 0.02
|
|
|
What is the tx for acute ankle injury?
|
1. cuboid inferior, then reduce anteriorly
2. lymphatic drainage 3. proximal fibula displaced posteriorly, then reduce anteriorly 4. torsion to interosseous ligament reduced 5. CTS to fibularis and tendons |
|
|
What tx is most often used for an acute knee injury?
|
million dollar knee technique
|
|
|
What are Ottawa knee rules for xray of acute knee injury?
|
1. age > 55
2. tenderness of fibular head 3. isolated tenderness of the patella 4. inability to flex 90 degrees 5. inability to bear weight for 4 steps (limping is ok) |
|
|
In a patient with lower back and lower extremity presentation, what should you check out regarding the foot?
|
look at the footwear to see what the tread wear is as an indicator of pronation/supination
|
|
|
What is flat feet and indicator of?
|
chronic problem
|
|
|
What is the most common foot complaint dx that you will see in the ER?
|
plantar fasciitis. when a pt presents, you should be sure to check out the ankle, knee, and hip
|

