![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 2 types of light sensitive cells?
|
Cones
Rods |
|
|
Describe Cones
|
Concentrated over fovea
High resolution and color sensitive perception |
|
|
Describe Rods
|
Concentrated more broadly
Low resolution perception/peripheral vision More sensitive to temporal change |
|
|
Describe Adaptation
What visual parameter is influenced? (resolution or contrast)? |
changes in pupil diameter in response to ambient light levels
Contrast |
|
|
Describe Accommodation
What is the mean latency? |
Change in the shape of the lens to focus light from an object on the retina
400 msec |
|
|
Describe vergence
What is the mean latency? |
Process of directing the eye towards a target
200 msec |
|
|
Is (higher/lower) contrast needed to perceive differences in dark regions of an image?
|
higher
Lower contrast is needed in lighter areas of an image |
|
|
This condition where the eyes are fully and optimally adapted to a relatively uniform but changeable luminance.
how does contrast change with light levels |
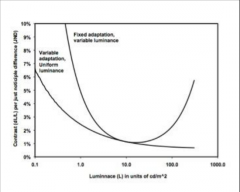
Variable adaptation
More contrast needed in darker areas |
|
|
This condition where the eyes are adapted to a highly non-uniform image (Medical images) and the eyes get adapted to an average luminance.
How does contrast change with light levels? |
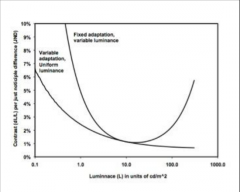
Foxed adaptation
More contrast is needed in very bright and very dark areas of the image. The contrast sensitivity is optimized for the average light level |
|
|
What types of cells are responsible for high-fidelity fovial vision?
What is the angular range/area on image when viewed from 2 ft |
Cones
1-2 degrees 1-2 cm |
|
|
What types of cells are responsible for peripheral vision?
What is the angular range? |
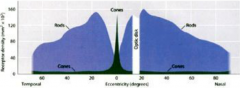
rods
170 degrees |
|
|
Order the following:
Recognition Local Attention Making a decision Global Attention |
Global Attention (fastest)
Local Attention Recognition Making a decision |
|
|
How long must fovial fixation occur to indicate some level of visual processing
|
0.3 seconds
|
|
|
Fixation time is (longer/shorter) for true positives
Fixation time is (shorter/longer) for true negatives How about false negatives |
shorter
shorter some time in between true positives and true negatives The longer you stare at something the more likely it's a false positive |
|
|
What is the relationship between accuracy of interpretation and number of cases read
|
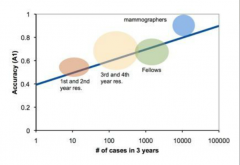
linearly with the logarithm of number of cases read
|
|
|
What percentage of interpretation errors are attributed to failure of recognition.
You just didn't see it. (visual error) |
55%
|
|
|
What percentage of interpretation errors are attributed to decision errors
You saw it but didn't call it (cognitive error) |
45%
|
|
|
Error in which a second abnormality is overlooked after the first is found
|
Satisfaction of search
|
|
|
What are three components of image quality
|
Inherent attributes: Sharpness, blur, noise, motion
Presentation attributes: Different filters applied, contrast ratios Anatomical Attributes: "anatomic noise" anatomic variability |
|
|
What are ergonomic factors
They may affect accuracy (directly/indirectly) |
Proper posture
Display quality Workstation functionality (CAD) Ambient lighting Environmental factors (audio-noise) indirectly by distraction and fatigue |
|
|
What is CAD
what is CADe What is CADx What is CAC What is CADr |
CAD-Computer assisted decision support
CADe-Computer aided detection- looks for "abnormality" (widely available) CADx-Computer aided diagnostic- sees abnormality and gives a diagnosis (not yet mainstream) CAC- Computer aided characterization CADr- computer aided risk assessment |
|
|
What are the two basic components of a typical CAD system?
|
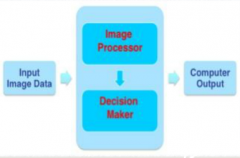
Image analysis module (image processor)
inference engine (decision maker) |
|
|
CAD systems use (fixed/learning Algorithms)
|
Learning algorithm
(neural network etc.) |
|
|
CADe systems output a (binary/continuous) value?
CADx ? |
Both are technically based on continuous values
CADe: binary- is a lesion there or not (based on whether a threshold value is met) CADx: continuous- likelihood score CADe: probable location CADx: probable diagnosis |
|
|
Performance Metrics:
Sensitivity Specificity Positive predictive value Negative predictive value |
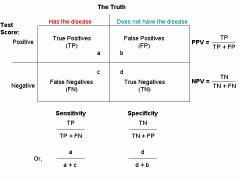
AKA True positive fraction
|
|
|
Performance Metrics:
Accuracy |
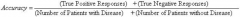
Sum formula of sensitivity and specificity
|
|
|
Performance Metrics:
ROC- Receiver operator characteristics (used for binary system) |
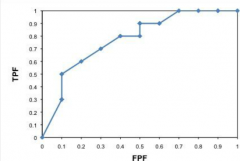
Plot of sensitivity vs. False positive fraction (1-specificity)
|
|
|
Performance Metrics
FROC- free response operating characteristics (used for binary system where multiple findings per study) |
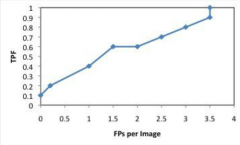
Plot of Sensitivity vs False positives/image
|
|
|
What's the difference between standalone and clinical performancy evaluation schemes
|
Whether or not the radiologist is "in-the-loop"
|
|
|
CAD- mammography
Always-never rule |
Approved for use as "second reader"
Always read mammogram first without CAD, then compare Never ignore finding if not picked up by CAD |
|
|
CAD-mammography
CAD is best are detecting which of the following: Architectural distortion amorphous calcs masses focal calcs usually helpful for less experienced radiologists |
focal calcs and masses
|
|
|
Other CAD in radiology
Lung nodules virtual colonoscopy Pulmonary emboli Atherosclerotic plaque |
BS
|

