![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When is the best time to measure preload?
|
end of diastole
|
|
|
During what part of the cardiac cycle is the characteristic pressure and volume found?
|
end of diastole
EDP EDV |
|
|
What are four phases of the cardiac cycle?
|
1. filling
2. isovolumic contraction 3. ejection 4. isovolumic relaxation |
|
|
When is the tricuspid valve open?
|
when pressure of RA > pressure of RV
|
|
|
When is the pulmonic valve open?
|
when pressure of RV > PA
|
|
|
When is the mitral valve open?
|
when pressure of LA > LV
|
|
|
When is the aortic valve open?
|
when pressure of LV > aorta
|
|
|
When is the aortic pressure less than the ventricular pressure?
|
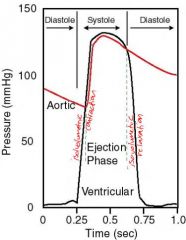
the only time the aortic pressure is less is during systole after the isovolumic contraction and before the isovlumic relaxation... so.... that's ejection.
|
|
|
Tell me about the filling phase............. yo.
|
there is a rapid, slow, and diastasis portion of filling.
speed depends on the pressure gradient. the end of the slow diastasis filling marks the end of diastole and at this point the ventricular pressure = EDP. |
|
|
What are these heart sounds that I keep hearing?
|
S1 = mitral vale closing
S2 = aortic (mainly) and pulmonary valves closing S3 = rapid ventricular filling (normal in kids) S4 = atrial contraction (rarely normal) |
|
|
Where does the P, QRS complex, and T waves hit in regard to heart sounds?
|
QRS complex is electrical stimulation for the physical ventricular contraction which occurs right before the mitral valve closes so right before S1
T occurs 0.2 s after QRS and 0.1 s before S2 (recall T is ventricular repolarization) P occurs 0.1 s before S1 |
|
|
Why does the QRS not hit on S1?
|
electrical precedes mechanical... duh.
|
|
|
What will /\ EDV and \/ ESV do for preload and contractility, respectively?
|
1. /\ EDV implies /\ preload
2. \/ ESV implies /\ contractility |
|
|
What are all the parts of a normal PV loop? Tell me now!
|
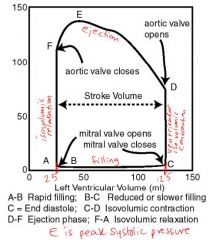
normal ESV = ~ 25 ml
normal EDV = ~ 135 ml normal peak force = ~ 140 normal EDP = ~ 75 mmHg |
|
|
What does a change in contractility do to the PV loop?
|
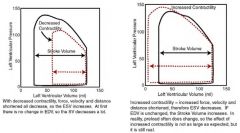
|
|
|
Um.... how do you measure contractility?
|
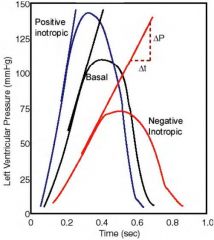
check this out: if you consider, on a pressure vs time graph of the L ventricle, the max dP/dt, then you can correlate that with the contractility.
/\ dP/dt => /\ contractility sweet. P.S. normal dP/dt ~ 3000 mmHg/sec |

