![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Requirements for Impression materials
|
1 •Sufficient working time
2 •Sufficient resilience (elastic materials) 3 •Sufficient resistance (Non-elastic materials) 4 •High dimension stability (low shrinkage or bulking during setting) 5 •High detail reproduction 6 •Compatibility with cast materials 7 •biocompatibility 8 •Appropriate texture 9 •Convenient taste and odour 10 Uncomplex processing 11 •Easy to sanitize after setting 12 •Suitable for storage |
|
|
Draw Classification of Impression materials
|
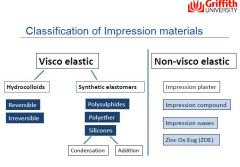
|
|
|
Examples of Hydrocolloids in each category?
|
Reversible: agar
Irreversible: alginate |
|
|
Pros and cons of Agar
|
Pro
10 •Inexpensive 11 •Popular for less critical applications 12 •Reasonable surface detail and dimension accuracy (preparation margin) 13 •Relatively hydrophilic Cons 14 •Need for expensive conditioning baths and water cooled trays 15 •Very poor dimension stability 16 •Need to be cast up immediately 17 •Low tear resistance |
|
|
Pros and cons of Alginate
|
Pro
10 •Easy to use and inexpensive 11 •Popular for less critical applications 12 •Reasonable surface detail and dimension accuracy 13 •Relatively hydrophilic Cons 14 !!!!!!!! Not suitable for crown and bridge preparations 15 •Very poor dimension stability 16 •Need to be cast up immediately 17 •Low tear resistance |
|
|
Synthetic elastomers' main advantage is?
|
Better dimension stability and adequate tear resistance
|
|
|
Pros and cons of Polysulphides?
|
Pro
20 •Available in a range of viscosities (light, medium or heavy bodied) 21 •Excellent tear resistance 22 •Long working time (setting time approx 10min) Cons 23 •Recommended max. storage time of the set impression is about 48h 24 •Objectionable odour 25 •Messy to handle 26 •Casts are generally wider and shorter then the tooth preparation |
|
|
What is a popular Polyether impression material?
|
Impregum
|
|
|
Pros and cons of Polyether?
|
Pro
30 •Fast setting time(<5min) 31 •Very good dimension stability 32 •Adequate tear resistance 33 •Very good elastic properties Cons 34 •Must be stored dry 35 •Should be poured within 48h 36 •Relatively rigid (may preclude their use in cases where severe undercuts are present) |
|
|
What are two types of Silicones?
|
Condensation and Addition
|
|
|
Silicones are also known as?
|
Vinylpolysiloxane
|
|
|
Differences between C and A silicones?
|
Condensation - Setting reaction produce by-product (ethyl-alcohol)
Addition - Set by an addition cured polymerisation reaction |
|
|
Pros and cons of A-Silicone
|
Pro
40 •Excellent, most dimensionally stable impression material! 41 •No by-product 42 •Remain unchanged over a substantial period of time. (Can be stored) Cons 43 •relatively hydrophobic (‘blowholes’ if teeth not properly dried) 44 •Setting goes on for at least 3h 45 •Costs |
|
|
Pros and cons of C-Silicones
|
Pros
46 •very good elastic properties 47 •Absolutely neutral in colour and taste 48 •Suitable for sub-and supragingivalpreparation 49 •Widely used. Cost effective. Cons 50 •Shrinkage on storage 51 •Should be cast within 6h 52 •Setting goes on for at least 3h |
|
|
Pros and cons of Impression plaster
|
Pro
50 •Easy to mix 51 •Low viscosity 52 •Good dimension stability and accuracy 53 •cheap Cons 54 •Problematic in undercut areas. 55 •Rough surface finish 56 •Poor abrasion-resistance 57 •Rigid once set. May needs to be fractured to remove from oral cavity 58 •Dry sensation in mouth |
|
|
What are constituents of Impression Compound?
|
Resin
Filler Lubricants |
|
|
Pros and cons of Impression compound?
|
Pro
60 •Non irritant and non toxic 61 •Good dimension stability and accuracy if not exposed to heat. 62 •Reusable. Can be reheated and readapted 63 •Can support other materials for wash impressions Cons 64 •Poor dimension stability in warm environment 65 •Complicated procedure for single tooth. 66 •High Expansion coefficient 67 •Will distort if removed from undercuts 68 •If inserted too hot, pulp may gets irritated |
|
|
Indications for Alginate Impressions
|
1 •Study model (Pros and Ortho)
2 •Models for splints, mouthguards 3 •Models for functional diagnostics 4 •Models for immediate dentures 5 •Models of edentulous jaws, full dentures 6 •Models for individual impression trays |
|
|
Indications for Silicone Impressions
|
10 •Models for inlays and onlays,
11 •Models for crowns, short bridges 12 •Putty phase for keys 13 •Light body phase for denture relining 14 •A-silicones, when absolute precision is mandatory: e.g veneers, double crown dentures, implantology, long bridges, multiple abutments. |
|
|
Indications for Polyether Impressions
|
20 •veneers
21 •adhesive bridges 22 •crowns, bridges (esp, long bridges with multiple abutments) 23 •implantology(supraconstructions) 24 •removable partial dentures 25 •edentulous jaws with individual trays |
|
|
What are the functions of Dorsal dam?
|
30 •To achieve an even thickness of impression material
31 •Provides stability during setting time (espwhen providing support on palate) 32 •Prevents impression material flowing towards the throat (gag reflex) 33 •Saving of impression material |
|
|
What are the requirements of a tray?
|
40 •Have sufficient extension to support an impression of all structures to be recorded
41 •Be rigid in use 42 •Incorporate occlusal stops 43 features appropriate to aid retention of impression material 44 •Have a robust handle 45 •Be capable of withstanding autoclave sterilisation, if not designed for single use |
|
|
What are features appropriate to aid retention of impression material in a tray?
|
adhesive
perforation retention |

