![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Candidiasis ranks where in occurrence of mycoses worldwide?
|
#1
|
|
|
Candida species most common for Candidiasis
|
C. albicans
C. tropicalis C. parapsilosis C. glabrata |
|
|
Candidiasis morphological features
|
Budding yeast, pseudohyphae, hyphae
|
|
|
Candidiasis pathogenicity
|
In immunocompromised patients, infection occurs by inhalation or GI persorption or any other route for candida to infect the blood stream. Commonly spread in hospitals among compromised pts.
|
|
|
Morbidity of mucocutaneous candidiasis
|
Accounts for most severe cases, self-limiting in health individuals. If immunocompromised, then can lead to poor oral intake -> malnutrition -> wasting -> death. Common in AIDs pts.
|
|
|
Morbidity of disseminated candidiasis
|
30 - 40% mortality, not common in AIDs pts.
|
|
|
Candidiasis clinical presentations
|
1) cutaneous and subcutaneous (vagina, oral, dermatits, penis);
2) systemic (esophogus, pulmonary, cardio, hepatospleno, arthritis, meninges, etc) 3) chronic mucocutaenous (genetic, impaired cellular immunity, effects skin and mucous membranes) |
|
|
Candidiasis Dx
|
1) microscopy seen morphology
2) culture - CHROM agar 3) serology - Candida mannan assay |
|
|
Candidiasis Tx
|
1) cutaneous/mucocutaneous - topical antifungal (ketoconazole, miconazole, nystatin)
2) systemic - amphotericin B 3) chronic mucocutaneous - Amphotericin B |
|
|
Cryptococcosis species
|
C. neoformans
US and other temperate climates Found in soil and aged pigeon droppings C. gattii Tropical and subtropical areas Associated with eucalyptus trees |
|
|
Cryptococcosis Pathogenesis
|
Inhaled yeast spores (from bird droppings) deposit into alveoli and are phagocytized by alveolar macrophage. Pathogen capsule causes immunosuppression.
|
|
|
Cryptococcosis Clinical Presentation
|
1) Pulmonary infection: prodrome, bilateral pneumonia, or asymptomatic
2) disseminated: C. gattii shows CNS cryptococcoma, nonspecific shows meningitis, skin lesions |
|
|
Cryptococcosis Dx
|
Microscopy - encapsulated budding yeast
Serology - capsule antigen in CSF and serum by latex agglutination test |
|
|
Cryptococcosis Tx
|
Long term treatment usually necessary Amphotericin B+flucytosine and for AIDs pts fluconazole prophylaxis for life
|
|
|
Aspergillosis Tx
|
1) ABPA - oral steroids
2) Aspergilloma - surgery, smphotericin B intracavity 3) CNPA - antifungal, surgical ressection 4) Invasive aspergillosis - surgical, antifungal (amphotericin B), filter air |
|
|
Aspergillosis Dx
|
Microscopy - septate hyphae and conidia in sputum
Histo - septate hyphae that branches at acute angles Culture - grows in absence of cycloheximide Serology - Rapid dx of invasive (very important), assay for Asperigillus galactomannan Ag in serum |
|
|
Aspergillosis infection types
|
ABPA - Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
CNPA - Chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis Aspergilloma Invasive aspergillosis |
|
|
Invasive aspergillosis clinical presentation
|
Rapidly progressing, can be fatal, prodrome, disseminating even to CNS
|
|
|
Aspergilloma clinical presentation
|
fungus balls (mycetoma) in lung parenchyma
|
|
|
CNPA clinical presentation
|
immunosuppression, progressive cavity pulmonary infiltrate
|
|
|
ABPA presentation
|
hypersensitivity reaction to A. fumigatus in tracheobronchial tree. conjunction with asthma and cystic fibrosis
|
|
|
Aspergillosis species
|
Aspergillus fumigatus
|
|
|
Aspergillosis pathogenicity
|
saprobes that will infect immunosuppressed pts with inherent deficiency, lung disease
|
|
|
Mucormycosis species
|
Mucorales Rhizopus
|
|
|
Mucormycosis pathogenicity
|
air, water, soil inhalation of sporangiospores, but also ingestion and traumatic inoculation can occur. as spores grow, hyphae invade blood vessels -> infarction, necrosis, thrombosis.
|
|
|
Mucormycosis morphology
|
molds in environment, non-septate hyphae form with right angle branch in tissue
|
|
|
Mucormycosis clinical presentation
|
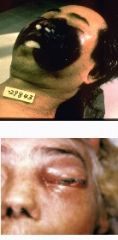
depends on route of infection can be cutaneous, pulmonary, GI, CNS
1) rhino cerebral causing orbital swelling and black pus discharge 2) opthalmoplegias, CN V and VII problems, loss of vision 3) reduced conscious state indicates brain involvement |
|
|
Mucormycosis Dx
|
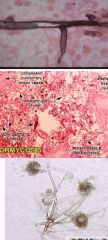
Histo - nonseptate right angle hyphae
Culture - cotton candy appearance (rhizoids) and sporangium |
|
|
Mucormycosis Tx
|
Antifungal (Amphotericin B)
Surgery High mortality rate |
|
|
Fungemia species
|
Malassezia furfur
Trichosporon species |
|
|
Fungemia Trichosporon species
|
Catheter-associated fungemia in neutropenic patients
Individuals with malignancies Anti-fungal therapy usually inefficient 80% fatality rate |
|
|
Fungemia Malassezia furfur
|
Malassezia furfur
Nosocomial infections directly related to the administration of IV lipid supplements through a central venous catheter Infection subsides once lipid infusion stopped and lines removed |

