![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
vioxx
|
recalled due to cardiovascular complications
|
|
|
benefits of oral contraceptives?
|
decreased risk of endometrial and ovarian cancer
|
|
|
risks of oral contraceptives
|
1) venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism
2) CVD, ischemic stroke (increased w/smoking) 3) hepatic adenomas |
|
|
why are estrogen and progestin used in combination?
|
with unopposed estrogen treatment, there is an increase in endometrial hyperplasia and cancer
|
|
|
risk of hormone replacement therapy in women (estrogen and progestin)
|
1) breast cancer
2) same as oral contraceptives 3) myocardial infarcs 4) gallbaldder disease |
|
|
acetaminophen toxicity causes what symptoms?
|
GI toxin: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatic necrosis with ALT and AST elevations (because serious overdosage affects liver)
|
|
|
aspirin/acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) acute toxicity signs?
|
respiratory alkalosis followed by metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
aspirin/acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) chronic toxicity signs?
|
> 3g/day
ulcers, seizures, coma, GI issues, CNS issues |
|
|
why are there issues with bleeding and aspirin?
|
aspirin is an irreversible inhibitory agent against platelet cyclooxygenase
|
|
|
carbon monoxide is produced by?
|
burning gas, oil, coal, wood, natural gas
|
|
|
danger of carbon monoxide?
|
odorless and colorless
|
|
|
early sign of CO poisoning?
|
cherry red skin
|
|
|
symptoms of CO poisoning?
|
headache, dizziness, impaired motor control, coma -> death
|
|
|
action of CO poisoning?
|
binding hemoglobin with higher affinity than oxygen
|
|
|
source of radon?
|
natural decay product of uranium
|
|
|
radon relative to lung cancer?
|
second biggest cause of lung cancer
|
|
|
aliphatic hydrocarbon source?
|
solvents, dry cleaning agents
|
|
|
what causes lead poisoning?
|
high affinity for sulfhydryl groups so competes with Ca ions
|
|
|
two problematic volatile organic compounds found in industrial settings and are poisonous?
|
aliphatic hydrocarbons - carcinogenic, CNS depression, nausea
aromatic hydrocarbons - leukemia, aplastic anemia |
|
|
how is lead introduced to the body and why is it problematic?
|
inhaltion, ingestion, t1/2 = 30 years, 80 - 85% of absorbed lead is taken up by bones in children
|
|
|
area of effects of lead exposure
|
brain, blood, nerves, kidney, gi, bones
|
|
|
what cancer is caused by arsenic and where is it found?
|
skin cancer - squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma
lung and liver cancer found in herbicides |
|
|
what problems are caused by oranocholines (DDT) and where is it found?
|
easily absorbed through skin, GI, lungs, so causes neurotoxicity, hepatotoxicity
found in herbicides |
|
|
what problems are caused by organophosphates and where is it found?
|
absorbed through skin, GI, lungs, irreversibly inhibits cholinesterase
symptoms: DUMBELS - diaphoresis, diarrhea, urination, miosis, bradycardia, bronchorrhea, bronchospasm, emesis, lacrimation, salivation fluids come out of their body everywhere, highly neurotoxic found in herbicides |
|
|
tx of organophosphate toxicity?
|
atropine, 2-PAM
|
|
|
what are the two types of radiation injury?
|
1) ionization - short wavelength, high frequency - x-rays, gamma rays, cosmic rays
2) nonionizing - long wavelength, low frequency - electricity, microwaves, UV, infrared |
|
|
what causes the carcinogenic properties of ionizing radiation?
|
alters DNA structure, whereas nonionizing does not
|
|
|
Gray (gy)
|
a dosage unit of ionizing radiation.
> 10 Gy -> necrosis > 1-2 Gy -> kills proliferating cells < 1 Gy -> DNA damage |
|
|
how much Gy does radiation therapy push?
|
30 to 70 Gy
|
|
|
abrasion
|
superficial epidermal injury. skin is rubbed away
|
|
|
laceration
|
deeper skin injury from blunt trauma. tissue bridging differentiates from incised wound
|
|
|
contusion
|
bruise, blood vessel damaged after injury, skin is still intact
|
|
|
how do you qualify a thermal burn?
|
1) depth of burn (skin layers involved)
2) %BSA (body surface area) involved 3) internal injuries from inhalation |
|
|
what are the 2 types of thermal burn layers quality?
|
1) full thickness - epidermis and dermis is lost
2) partial thickness - at least deep portions of the dermis is maintained |
|
|
what is the rule of nines?
|
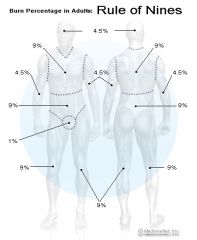
this is a percentage of sections of the body used to determine %BSA in a burn victim.
ex: front chest = 9% front abdomen = 9% groin = 1% |
|
|
what is frostbite
|
long term constriction caused by body keeping core warm rather than preserve apendages that will cause ischemia
|
|
|
how are 1st, 2nd, 3rd degree burns qualified?
|
1st - epidermis
2nd - part of dermis 3rd - all of dermis and epidermis |
|
|
cycad flour
|
phytotoxin containing cycasin that may produce ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) if injested
|
|
|
aflatoxin B1
|
produced by fungus that can cause heptocellular carcinoma
|
|
|
ciguatoxin
|
occurs in tropical fish after they ingest dinoflagellates. humans ingest fish, results in paresthesias, paresis, vomiting, diarrhea
|
|
|
gunshot wounds
|
long range - clean shot
short range - see black discoloration because of smoke, gunpowder, heat |

