![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Sigmund freud
|
Psychoanalytic theory Of personality: levels of consciousness, structure of personality, stages of child development.
|
|
|
|
Alfred adler
|
Individual psychology: personality development, importance of birth order, self image, methods of pyschoanalysis
|
|
|
|
John B Watson
|
Behaviorism: developed an objective way of analyzing behavior that emphasized the observable behavior of individuals rather than emotional or mental state. "Little Albert"-fear of white rat then white bunny.
|
|
|
|
Ivan pavlov
|
Classical or respondent conditioning: dog theory about unconditioned and conditioned stimulus and response behaviors.
|
|
|
|
Jean piaget
|
Developed a stage modem if how children's cognitive ability develop over time
|
|
|
|
Leo Vigotsky
|
Child development: focused on children's learning process and use of language in learning.
|
|
|
|
Kurt Lewin
|
Social psychology: organizational management and applied psychology. Leadership climates (authoritarian, democratic, laissez-faire)
|
|
|
|
Anna freud
|
Ego defense mechanisms: identified unconscious defense mechanisms used to protect the ego.
|
|
|
|
Abraham madlow
|
Hierarchy of needs: pyramid of human needs thAt range from basic to higher order needs
|
|
|
|
Rene Spitz
|
Ego development: focused on ego development of child and relationship between mother and child. Identified "hospital ism" or "anaclitic depression"
|
|
|
|
Erik erikson
|
Ego psychology: expanded Freudian theories to adult development. From birth to death.
|
|
|
|
Margret mahler
|
Separation and individuation/ object relations: worked with disturbed children looking at infant mother interaction, and process for infant individuation. Stage based developmental theory from b-4.
|
|
|
|
BF Skinner
|
Operant conditioning: outlined behavioral therapy. Use of consequences to modify the Occurrence and form of behavior.
|
|
|
|
Lawrence Kohlberg
|
Moral development: development of moral reasoning, 6 stage model of moral judgement.
|
|
|
|
John Bowlby
|
Attachment theory: identified characteristics of a child's attachment to his or her caregiver and the phases that child experiences when separated from caregiver
|
|
|
|
Elisabeth Kubler-ross
|
Death and dying: stages individuals go through in the dying process.
|
|
|
|
James Karl and Karen Wandrei
|
Person in environment system (PIE): developed an assessment system that evaluates social, environmental, mental and physical health problems, and client strenghs.
|
|
|
|
Salvador Minuchin
|
Identified the concept of Structural family therapy.
|
|
|
|
Murray Bowen
|
Family theory that focuses on separation from family of origin. Triangulation central to model.
|
|
|
|
Gregory Bateson, Don Jackson, Virginia Satir, Jay Haley
|
Experimental family therapy came out of the mental research institute 1960.
|
|
|
|
Yalom
|
Group work: believes individual work with group therapy is not effective. Members Gould be Heterogeneous based on conflict area.
|
|
|
|
Jay Haley
|
Strategic family therapy: focused on using resistance of family members to create change within families.
|
|
|
|
Piaget
|
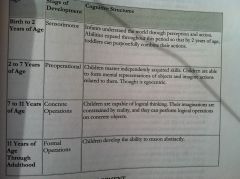
|
|
|
|
Maslow
|
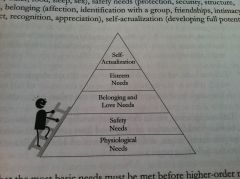
|
|
|
|
Mahler stages
|
1. Normal autism (b-1m) 2. Symbiosis/ normal (1m-4m) 3. Separation-individuation (4-8m, through 36m) - differentiation from mother/hatching (4-8m) - practicing (8-15m) - Rapprochement (15-24m) - achievement of individuality (24-36m to 4yrs)
|
|
|
|
Kholberg
|
L1: pre conventional morality, individual perspective Stage 1: punishment and obedience orientation, punishment and reward motivate. Stage 2: Naive instrumental orientation, satisfies own and others need/ hedonistic reciprocity L2: conventional morality, member if society perspective. Stage3: good boy/nice girl orientation, want to receive approval and intention is important. Stage 4: law and order orientation, correct behavior conforms to social norms. L3: post-conventional morality, autonomous identification with universal moral principles. Stage 5: social contact with societal consent. Stage 6: universal ethical principles/ individual conscience one has selected.
|
L1: pre conventional morality, individual perspective Stage 1: punishment and obedience orientation, punishment and reward motivate. Stage 2: Naive instrumental orientation, satisfies own and others need/ hedonistic reciprocity L2: conventional morality, member if society perspective
|
|
|
David Kolb
|
Model for experimental learning: sound, watching, feeling, thinking.
|
|
|
|
Kubler-ross
|
Stage1- denial, stage 2- anger, stage 3- bargaining, stage 4- depression, stage 5- acceptance.
|
|
|
|
Leon Chestang
|
Asserts that everyone is a part of 2 systems. Nurturing- family, friends, immediate community. Sustaining system- larger society. "Dual perspective" must switch between cultural expectations.
|
|
|
|
Karl Marx/ Max Weber
|
Conflict theory/ social conflict theory: individuals born to conflict, attempt to better one self over others. Results in societal change. Relationships about power and exploration.
|
|
|
|
Karl Marx/ Max Weber
|
Conflict theory/ social conflict theory: individuals born to conflict, attempt to better one self over others. Results in societal change. Relationships about power and exploration.
|
|
|
|
William Glasser
|
Reality therapy: individuals have innate needs, which the brain attempts to act on the world to meet those needs.
|
|
|
|
Aaron beck
|
Cognitive therapy
|
|
|
|
Albert Ellis
|
Rational emotive behavior therapy
|
|
|
|
Donald Meichenbaum
|
Self-management/ self-instruction
|
|
|
|
Marsha M Linehan
|
Dialectical behavioral therapy: mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, distress tolerance, emotional regulation.
|
|
|
|
Marsha M Linehan
|
Dialectical behavioral therapy: mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, distress tolerance, emotional regulation.
|
|
|
|
Steve de Shazer/ Insoo Kim Berg
|
Solution focused therapy, miracle ?, exception finding ?, scaling ?, presupposition all ?
|
|
|
|
Carl rodgers
|
Person centered therapy
|
|
|
|
Carl rodgers
|
Person centered therapy
|
|
|
|
Carl Jung
|
Jungian personality theory: Libido general psychic energy, personal and collective unconscious, personality made up of 2 parts- attitudes and basic functions
|
|
|
|
Fritz Perls
|
Gestalt- humans constantly discovering and reconstructing who they are
|
|
|
|
Eric Berne
|
Transactional analysis
|
|
|
|
Satir
|
Styles of communicating (4 styles serve to protect family members from revealing who they really are, 1 is functional) placater, blamer, super-reasonable, irrelevant, congruent communicator
|
|
|
|
Seven stage crisis intervention model
|

|
|

