![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Liberty vs. order
|
Order- govt
Liberty- freedom You can never increase one without decreasing the other Democracy -Mob Rule Rule of Law -In a constitutional system, the people set up and agree on the basic rules and procedures that will govern them. -Rule of law is an ancient British legal principle, that established all are equal before the law, all are subject to the law, and no one is above it. |
|
|
Political spectrum
|
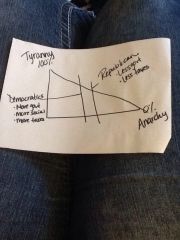
|
|
|
Social contract theory
|
-Social contract is a theory that government has only the authority accorded it by the consent of the governed.
-First proposed by Thomas Hobbes who argued that people set up government to protect natural rights. -Illustrated by the Constitution’s preamble Natural Rights John Locke argued that natural rights (the right to life, liberty, and property) are fundamental and that government cannot take them away. |
|
|
Capitalism
|
Economic system in which businesses and key industries are privately owned and in which individuals, acting on their own or with others, are free to create businesses
|
|
|
Socialism
|
Economic system in which the government owns major industries
|
|
|
Democracy
|
System of government in which the supreme power is vested in the people and exercised by them either directly or indirectly through elected representatives.
-no congress Democracy means: "demos" (people) and Kratia (authority/power, or, rule) Ruled by the people -used majority rule -was associated with mob rule (large, passionate, ignorant, and dangerous) There will be no liberty or safety,; there would be no order |
|
|
Republic
|
Form of government in which power derives from citizens, but public officials make policy and govern according to existing law.
We are a republic -want more order -we are a nation of law, not a nation of men. |
|
|
Representative democracy
|
Form of democracy in which citizens elect public officials to make political decisions and formulate laws on their behalf
|
|
|
Trustee
|
-A trustee is an elected official who does what they think best, even if the public disagrees; elections allow the public to render a judgment on their decisions.
|
|
|
Delegates
|
-A delegate is an elected official who does what the public wants and does not exercise independent judgment.
|
|
|
Sugar Act
|
Happened in 1764
Set forth a long list of items that could be exported only to Great Britian, limiting limiting competition for the colonists goods -imposed tax without representation |
|
|
Stamp act
|
Happened in 1765
Established a tax on virtually all paper used by the colonists |
|
|
Stamp act
|
Happened in 1765
Established a tax on virtually all paper used by the colonists |
|
|
Who quoted "give me liberty, or give me death" and why
|
Patrick Henry
After the stamp act of 1765 he lead groups of rioters at the Virginia House of Burgessess |
|
|
When did the Britain appeal the Stamp Act
|
1766
|
|
|
What was the Stamp Act replaced with
|
Townshend Acts
|
|
|
What was the Stamp Act replaced with
|
Townshend Acts
|
|
|
What was the Townshend Acts
|
Imposed taxes on various imports
|
|
|
What was the Stamp Act replaced with
|
Townshend Acts
|
|
|
What was the Townshend Acts
|
Imposed taxes on various imports
|
|
|
Who declared the Townshend Acts unconstitutional
|
Samuel Adams a Massachusetts legislature.
-no taxation without representation |
|
|
What was the Stamp Act replaced with
|
Townshend Acts
|
|
|
What was the Townshend Acts
|
Imposed taxes on various imports
|
|
|
Who declared the Townshend Acts unconstitutional
|
Samuel Adams a Massachusetts legislature.
-no taxation without representation |
|
|
Boston Massacre
|
1770
Colonists upset with the Townshend Act they resisted. King George III sent troops to quell the resistance, but the presence of soldiers during peacetime aggravated tensions. British soldiers fired on threatening crowd, killing five colonists and wounding six others. |
|
|
What was the Stamp Act replaced with
|
Townshend Acts
|
|
|
What was the Townshend Acts
|
Imposed taxes on various imports
|
|
|
Who declared the Townshend Acts unconstitutional
|
Samuel Adams a Massachusetts legislature.
-no taxation without representation |
|
|
Boston Massacre
|
1770
Colonists upset with the Townshend Act they resisted. King George III sent troops to quell the resistance, but the presence of soldiers during peacetime aggravated tensions. British soldiers fired on threatening crowd, killing five colonists and wounding six others. |
|
|
Boston Tea party
|
1774
Angered by both tax and monopoly, colonists disguised themselves as Indians and dumped a shipload of tea in the Boston Harbor |
|
|
What was the Stamp Act replaced with
|
Townshend Acts
|
|
|
What was the Townshend Acts
|
Imposed taxes on various imports
|
|
|
Who declared the Townshend Acts unconstitutional
|
Samuel Adams a Massachusetts legislature.
-no taxation without representation |
|
|
Boston Massacre
|
1770
Colonists upset with the Townshend Act they resisted. King George III sent troops to quell the resistance, but the presence of soldiers during peacetime aggravated tensions. British soldiers fired on threatening crowd, killing five colonists and wounding six others. |
|
|
Boston Tea party
|
1774
Angered by both tax and monopoly, colonists disguised themselves as Indians and dumped a shipload of tea in the Boston Harbor |
|
|
Coercive Acts
|
1774
Because of the Boston Tea Party, Britain passed this act which among other things, gave the royal governor the right to select the upper house of Massachusetts the right to try Britain officials charged with capital offenses. -Boston Port Act (forced to feed troops) The aim of the legislation was to restore order to Massachusetts and Punish Bostonians |
|
|
What was the Stamp Act replaced with
|
Townshend Acts
|
|
|
What was the Townshend Acts
|
Imposed taxes on various imports
|
|
|
Who declared the Townshend Acts unconstitutional
|
Samuel Adams a Massachusetts legislature.
-no taxation without representation |
|
|
Boston Massacre
|
1770
Colonists upset with the Townshend Act they resisted. King George III sent troops to quell the resistance, but the presence of soldiers during peacetime aggravated tensions. British soldiers fired on threatening crowd, killing five colonists and wounding six others. |
|
|
Boston Tea party
|
1774
Angered by both tax and monopoly, colonists disguised themselves as Indians and dumped a shipload of tea in the Boston Harbor |
|
|
Coercive Acts
|
1774
Because of the Boston Tea Party, Britain passed this act which among other things, gave the royal governor the right to select the upper house of Massachusetts the right to try Britain officials charged with capital offenses. -Boston Port Act (forced to feed troops) The aim of the legislation was to restore order to Massachusetts and Punish Bostonians |
|
|
First Continental Congress
|
1774
Benjamin Franklin proposed a congress (first continental congress) -rejected a reconciliation plan with England and instead sent King George III a list of grievances One last chance to stop all this before going to war (which they wouldn't stand a chance) Wanted a peaceful reconciliation |
|
|
What was the Stamp Act replaced with
|
Townshend Acts
|
|
|
What was the Townshend Acts
|
Imposed taxes on various imports
|
|
|
Who declared the Townshend Acts unconstitutional
|
Samuel Adams a Massachusetts legislature.
-no taxation without representation |
|
|
Boston Massacre
|
1770
Colonists upset with the Townshend Act they resisted. King George III sent troops to quell the resistance, but the presence of soldiers during peacetime aggravated tensions. British soldiers fired on threatening crowd, killing five colonists and wounding six others. |
|
|
Boston Tea party
|
1774
Angered by both tax and monopoly, colonists disguised themselves as Indians and dumped a shipload of tea in the Boston Harbor |
|
|
Coercive Acts
|
1774
Because of the Boston Tea Party, Britain passed this act which among other things, gave the royal governor the right to select the upper house of Massachusetts the right to try Britain officials charged with capital offenses. -Boston Port Act (forced to feed troops) The aim of the legislation was to restore order to Massachusetts and Punish Bostonians |
|
|
First Continental Congress
|
1774
Benjamin Franklin proposed a congress (first continental congress) -rejected a reconciliation plan with England and instead sent King George III a list of grievances One last chance to stop all this before going to war (which they wouldn't stand a chance) Wanted a peaceful reconciliation |
|
|
When was the revolutionary war
|
April 19th 1775
|
|
|
Second Continental Congress
|
After Revolutionary war
May 1775- 1781 King George III denied reconciliation and goes to war with George Washington leading the war. (Continental Army) -acted as the common government of the states between 1775-1781 |
|
|
Second Continental Congress
|
After Revolutionary war
May 1775- 1781 King George III denied reconciliation and goes to war with George Washington leading the war. (Continental Army) -acted as the common government of the states between 1775-1781 |
|
|
Declaration of Independence
|
1776- the Continental Congress debated on independence resolution
Author: Thomas Jefferson Jul 2- motioned the independence Jul4- wrote it Aug 2- implemented it |
|
|
Articles of Confederation
|
1781-1788
Initial governing authority of the United States --all 13 states was individually ran States retained all powers -congress had full authority over foreign, military, and Indian affairs, coin money, and decide boundary and other disputes between states - Congress did not have the authority regulate commerce (can't tax citizens or products) |
|
|
Articles of Confederation
|
1781-1788
Initial governing authority of the United States --all 13 states was individually ran States retained all powers -congress had full authority over foreign, military, and Indian affairs, coin money, and decide boundary and other disputes between states - Congress did not have the authority regulate commerce (can't tax citizens or products) |
|
|
Problems with the Articles of Confederation
|
Insufficient funds - nations debts were unpaid
-without centralized authority to regulate commerce, states taxed imports from other states, stunting economical growth -lack of military power Allowed Spain to block commercial access to the Mississippi River |
|
|
Articles of Confederation
|
1781-1788
Initial governing authority of the United States --all 13 states was individually ran States retained all powers -congress had full authority over foreign, military, and Indian affairs, coin money, and decide boundary and other disputes between states - Congress did not have the authority regulate commerce (can't tax citizens or products) |
|
|
Problems with the Articles of Confederation
|
Insufficient funds - nations debts were unpaid
-without centralized authority to regulate commerce, states taxed imports from other states, stunting economical growth -lack of military power Allowed Spain to block commercial access to the Mississippi River |
|
|
Who believed that too much order would cause the United States to sufder
|
James Madison and Thomas Jefferson,
|
|
|
Articles of Confederation
|
1781-1788
Initial governing authority of the United States --all 13 states was individually ran States retained all powers -congress had full authority over foreign, military, and Indian affairs, coin money, and decide boundary and other disputes between states - Congress did not have the authority regulate commerce (can't tax citizens or products) |
|
|
Problems with the Articles of Confederation
|
Insufficient funds - nations debts were unpaid
-without centralized authority to regulate commerce, states taxed imports from other states, stunting economical growth -lack of military power Allowed Spain to block commercial access to the Mississippi River |
|
|
Who believed that too much order would cause the United States to sufder
|
James Madison and Thomas Jefferson,
|
|
|
Constitutional Convention
|
1787
55 delegates REVISE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION CREATE NEW DOCUMENT The convention's rules granted each state one vote, reguard less of their size of state or the number of delegates it sent |
|
|
Virginia plan
|
The Virginia Plan was created by James Madison but presented to the Constitutional Convention by Edmund Randolph, the governor of Virginia, on May 29, 1787. This was a proposal for a new form of government and called for the number of votes each state received in Congress to be based on population, rather than each state receiving one vote.
The purpose of the plan was to protect the large states' interests in the new government, which would be stronger federally than under the Articles of Confederation. The Articles of Confederation was the first form of government and had weak federal control; the states had all of the power. The Virginia Plan would change this by creating an entirely new form of government rather than amending the Articles of Confederation. The Virginia Plan was countered with the New Jersey Plan, -bicameral -matters by population. The bigger the state the more representatives |
|
|
New Jersey Plan
|
The New Jersey Plan was a proposal for the US Constitution by William Patterson. It was focused on insuring that small states got an equal share of representation in the government. In the final compromise, the New Jersey Plan served as the model for the current US Senate, every state has the same representation, regardless of size and population. -unicameral |
|
|
Connecticut Compromise
|
Roger Sherman proposed a compromise on legislative representation whereby the lower chamber is based on population and the upper chamber provides equal representation to the states
-bicameral -blueprint of the Constitution |
|
|
Enumerated powers
|
Article 1 Section 8. (Federal govt) Powers expressly granted to Congress by the constitution
-authority to tax to provide general welfare -to regulate commerce among the states and with foreign nations -borrow money, declare war, raise armies, and maintain a navy *the tax and commerce powers were among those missing in the Articles |
|
|
Electoral College
|
The presidential electors, selected to represent the votes of the respective states, who meet every four years to cast the electoral votes for president and Vice President
|
|
|
17th amendment
|
Gives the people instead of state legislatures, the right to choose U.S. Senators directly
|
|
|
17th amendment
|
Gives the people instead of state legislatures, the right to choose U.S. Senators directly
|
|
|
Marbury v. Madison
|
Election of 1800
In Marbury v. Madison (1803) the Supreme Court announced for the first time the principle that a court may declare an act of Congress void if it is inconsistent with the Constitution. William Marbury had been appointed a justice of the peace for the District of Columbia in the final hours of the Adams administration. When James Madison, Thomas Jefferson’s secretary of state, refused to deliver Marbury’s commission, Marbury, joined by three other similarly situated appointees, petitioned for a writ of mandamus compelling delivery of the commissions. Chief Justice John Marshall, writing for a unanimous Court, denied the petition and refused to issue the writ. Although he found that the petitioners were entitled to their commissions, he held that the Constitution did not give the Supreme Court the power to issue writs of mandamus. Section 13 of the Judiciary Act of 1789 provided that such writs might be issued, but that section of the act was inconsistent with the Constitution and therefore invalid. Although the immediate effect of the decision was to deny power to the Court, its long-run effect has been to increase the Court’s power by establishing the rule that ‘it is emphatically the province and duty of the judicial department to say what the law is.’ Since Marbury v. Madison the Supreme Court has been the final arbiter of the constitutionality of congressional legislation. |
|
|
Concurrent Powers
|
Powers both the National and the state share. -taxing, borrowing, spending, regulating health, regulating education, licensing, setting time place and manner of congressional elections
|
|
|
Article 6
|
The Supremacy Clause (Article 6)
Makes federal laws supreme over state laws |
|
|
article 1 section 8
|
The Commerce Clause—Article 1, Section 8 - Established Congress’s exclusive authority to regulate commerce among the states
-States may not regulate interstate commerce and cannot establish trade barriers against goods from other states. -States may tax goods from other states equal to the amount that they tax goods produced in their own states, but they cannot charge extra taxes to goods that are made out of state. |
|
|
Article 4 section 1
|
Full Faith and Credit Clause—Article 4, Section 1- Requires states to accept court decisions and most contracts made in other states
|
|
|
Article 4, section 2
|
Privileges and Immunities Clause—Article 4, Section 2 - Requires that a state treat people from other states equally to its own residents
|
|
|
Unitary System
|
The national government has virtually every power
|
|
|
Confederal System
|
State grant limited powers to the national government
|
|
|
Federal system
|
National and State governments derive their authority from the people
|
|
|
Article 1 section 9
|
Habeas Corpus
-a guarantee that incarcerated people can go before a judge to have the legality of their confinement determined-except in cases of invasion or rebellion Ex Post Facto -Latin for "after the fact," which refers to laws adopted after an act is committed making it illegal although it was legal when done, or increases the penalty for a crime after it is committed. Bills of Attainer -cannot deprives the person or persons singled out for punishment of the safeguards of a trial by jury. |
|
|
State- Centered Federalism
|
View that the states created the Constitution and the federal government Jefferson opposed Hamilton and the federalists, and he was a strong supporter of states’ rights. -conservatives (state power centered. Believes in limited government) |
|
|
Nation-Centered Federalism
|
View that the Constitution and the federal government derive from the people, not from the states
Hamilton sought expansive federal power and, in 1790, proposed that Congress establish a national Bank of the United States. -liberals (national-centered government. Believes in a big government) |
|
|
Three Eras of Federalism
|
-dual
-cooperative -new federalism |
|
|
Dual Federalism
|
-two powers and nothing shared
Doctrine holding that, although the national government is supreme in some spheres, state governments remain supreme in others, with layers of authority separate from one another. -powers were limited -power mostly in states -govt had no interaction with citizens -govt got money through tariffs |
|
|
Cooperative Federalism
|
1930s-1960s (marble cake)
A view that state and national governments work together to solving problems -Congress passed a series of laws designed to lift the ailing economy Recovering from Great Depression -provide general welfare -housing -civil rights act (prohibit job discrimination and segregation in public accommodation) -new deal (The programs were in response to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call the "3 Rs": Relief, Recovery, and Reform. That is Relief for the unemployed and poor; Recovery of the economy to normal levels; and Reform of the financial system to prevent a repeat depression.) -categorical grants (money given to states for a specific purpose.....with strings attached) |
|
|
New Federalism
|
Shifting of power back to the states beginning with Nixon (1969)
Designed to reduce the size and responsibility of the federal government and place more responsibilities and programs on the state. State governments in turn will place more responsibilities on local government General Revenue Sharing -Money from Congress to the states that could be spent however the states wanted -Moved away from categorical grants that were controlled by the national government. Block Grants- (Money from Congress to the states that could be spent in broad rather than specific categories) Contract with America- Campaign proposal containing ten legislative initiatives used by Republicans running for the House of Representatives in 1994 designed to reduce the power of the national government The Contract With America was a statement drafted in 1994 by a number of leading House Republicans, and signed by almost all House Republicans at the time. It was a comprehensive list of promises the Republicans made to the American people, should they be granted a majority in the House of Representatives during the 1994 election. |
|
|
Recall elections
|
Direct Democracy in federalism
Allow citizens, if they gather enough petition signatures, an opportunity to hold a special vote to remove state or local elected officials before their terms expire |
|
|
Initivatives
|
Direct Democracy in Federalism
A process that allows citizens who collect the required number of petition signatures to place proposed laws directly on the ballot |
|
|
Referendum
|
Direct Democracy in Federalism
A process that allows legislatures to put certain issues on the ballot for citizen approval or requires legislatures to seek citizen approval for certain actions by the legislature |
|
|
Who defended the British soldiers after boston Massacre
|
John Adams
|
|
|
Who defended the British soldiers after boston Massacre
|
John Adams
|
|
|
The framers believed democracy could lead to
|
Mob rule
|
|
|
Who defended the British soldiers after boston Massacre
|
John Adams
|
|
|
The framers believed democracy could lead to
|
Mob rule
|
|
|
Who was the person who came up with name natural rights
|
John Locke
|
|
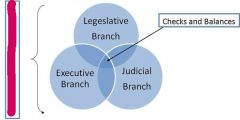
What is the name of the 3 branches of Government
|
Madisonian Model
|
|
|
Life, liberty, and .....
|
Property
|
|
|
How much of the constitution did Thomas Jefferson write
|
None he was in France
|

