![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
describe how Water is absorbed
|
- most absorption of water is through the root hair cells, whcih provide a large surface area
- water is absorbed by osmosis from a higher water potential in the soil water to a lower potential in the xylem |
|
|
how are ions absorbed?
|
diffusion and active transport
|
|
|
how does water move through the apoplast pathway?
|
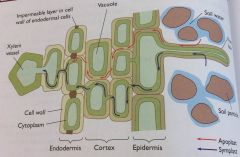
through the cell walls and the spaces between cells
|
|
|
how does water move through the symplast pathway?
|
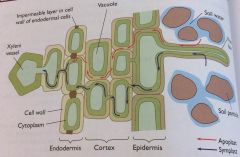
through the cytoplasm via plasmodesmata
|
|
|
how does water move through the vacuolar pathway?
|
from vacuole to vacuole in adjacent cells through the cytoplasm
|
|
|
How is the endodermis involved in the uptake and movement of water and mineral ions
|
- suberin is deposited in the cell walls and forms bands called Casparian strips in the endodermal cells, which block the apoplast pathway.
- mineral ions are actively transported into the cytoplasm of the cells through the symplast pathway - this lowers the water potential of the cells, causing water to move into the symplast pathway by osmosis. - The endodermal cells actively pump ions into the xylem - this helps to generate a water potential gradient across the root, drawing water in from the soil. - the endodermis allows the plant to selectively uptake ions from the soil. |

