![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
血生理特点
|
1. 血浆胶体渗透压低-血浆白蛋白量低
2. 非蛋白含氮(dan4)物:氨基氮,尿酸氮,尿素氮和肌酸少量 3. 高钾,低钠 4.胆碱酯酶贮(zhu1)量少-对抗胆碱酯酶的药物敏感-容易中毒 5. RBC (有核), WBC and 凝血细胞 6. 缺之凝血因子 IX and XII -靠外源性凝血系统 |
|
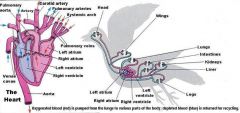
循环系统
|
1. 右心房(atrium dextrum) 大于左心房 (atrium sinistrum)
2. 右心室(ventriculus dexter)却小于左心室(ventriculus sinister) 3. 同时接受交感神经和副交感神经支配 4. 迷走神经和交感神经作用相等(哺乳动物只 ”迷走紧张") 5. 心率始终快 6. 血-脑屏障4周龄后发育健全 |
|
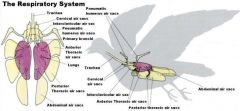
呼吸系统
|
1. 鼻腔(nasal cavity),喉(larynx),气管(trachea),鸣(ming2)管(syrinx),肺(lung)和气囊(air sac).
2. 毛细气管管壁上的膨大结构相当于肺泡 3. 肺位于北侧,四边形,constant volume 4. 9个气囊,only腹气囊与出击支气管延续,rest和secondary bronchii 5. 炎热环境发生热喘呼吸-三级支气管区域的通气量增大-pCO2 偏低-呼吸性碱中毒-死亡 |
|
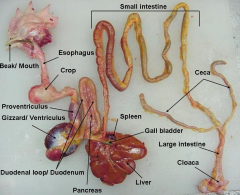
消化系统
|
1. 喙(hui4),口腔,咽(pharynx),食道,嗉囊(crop-鸭和鹅称为食道膨大部分),腺胃(proventriculus),肌胃(gizzard),小肠,盲肠,大肠,直肠,池殖腔,肝,胰.
2. 不属逆呕动物-催吐剂无效果-中毒时,切开嗉囊 3. 腺胃产生胃液,但是胃液的消化作用在肌胃进行 4. 肠道的消化液不含分解纤维素的酶 5. 食物在肠道停留时间短-饲料添加药物吸收不良-要长时间添加药物才达到有效浓度的药物。 |
|
|
泌尿系统
|
1. 无膀胱;肾脏-输尿管-池殖腔-跟粪便排出(尿液偏酸)
2. 用磺胺类药物时,添加碳酸氢钠(碱),减少乙酰化磺胺(酸)结晶对生的损伤 |
|
|
淋巴系统
|
1. 脾脏:圆形小体,腺胃的右侧,不是重要的血液贮存库
2. 胸腺:3-8个淡红色,扁平,形状不规则的叶状物,紧靠颈静脉,排列成一串;成熟时,体积最大,后退化萎(wei3)缩 3. 法氏囊(Bursa Fabricius):体液免疫,池殖腔背侧中央,10weeks体积最大,性成熟后退化萎缩 |
|
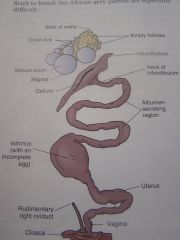
生殖系统(雌)
|
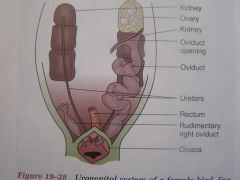
A。卵巢(only左侧卵巢和输卵管发育成熟)
B。输卵管: 1. 漏斗部(infundibulum) 2.蛋白分泌部/膨大部(albumen secreting part/magnum) 3. 峡部(ithmus-其分泌物形成卵内,外壳膜) 4. 子宫或壳腺部(uterus shellgland) 5. 阴道 |
|
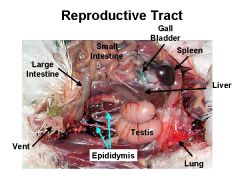
生殖器官(雄)
|
睾丸
睾丸旁导管系统(Juxta testicular duct system) 输精管(ductus deferens) 交媾(gou4)器(copulatory apparatus) |
|
|
病因
|
1. 病原微生物的感染(病毒,细菌,支原体,衣原体,真菌)
2. 寄生虫 3. 营养代谢障碍:e.g. 代谢产生的废氮不能转化成溶解性好的尿素,只能形成溶解性差的尿酸-容易产生以尿酸盐析出和沉积为特征的“通风病(gout)”。 4. 中毒 5. 饲养管理不当和(或)应激 |
|
|
诊断方法
|
1. 禽场基本情况的调查与分析
2. 临床检查:群体和个体 3. 病例解剖学检查(5-10病死鸡,几个不同病程的鸡) 4. 微生物学诊断:病原学,血清学,分子生物学 5. 寄生虫血诊断 6. 饲料营养成分的分析 7. 毒物检验 8. 预防和治疗试验 9. 其他检验:血常规,血生化,etc. |
|
|
综合预防措施
|
1.工作人员要有良好的素质,责任心和自觉性
2.制定必要的操作规章和管理制度(active site security) 3.合理选择和布局养禽场地 4.进行专一的生产(一个禽场只养一种家禽) 5. 实行“全进全出”制度(multiage sites should be avoided) 6. 重视家禽饲养环境的净化(site decontamination) 7. 满足家禽的营养需要 8. 使用健壮无特定病原体的种苗(use poultry stains which have a robust immune system that respond generally to a wide range of diseases) 9. 种苗的合理运送 10. 适时开食和饮水 11. 合理保温 12. 做好通风透气(氨气0.0025%,硫化氢0.0020%,CO2-0.15%) 13. 保持适当的相对湿度(too humid, mold can grow) 14. 适当的光照 15. 避免过分的拥挤 16. 提供充足的垫料(considerable variation in the availability and use of different litter materials for poultry bedding: best would be fresh, dry, white wood shavings) 17. 进行正确,适当的免疫接种 18. 适当预防用药 19. 带禽消毒 20. 断喙:防止喙癖(pi3) 21. 严防工作人员传播疾病 22. 重视病房,淘汰间和解剖室的预防措施(normally, farms are advised against building these; only professionals should handle such cases) 23. 注意孵化房卫生 24. 消除或控制活体媒介物和中间宿主 25. 防止饲养家禽的用具杂物传播疾病 26. 防止中毒 27. 预防热应激 28. 进行抗病育种 29. 建立无特定病原体的种禽群 30. 放牧应注意安全 31. 停产清场 |
|
|
Biosecurity management practices
|
1. Vaccination
2. Medication 3. Environmental control 4. Terminal hygiene cleansing and disinfection 5. National/international exclusion/stamping out policies 6. Active site security |
|
|
Components of a biosecurity program
|
1. Procedural biosecurity (HACCP-Hazard Analysis Critical Control point): identify the critical control points, put procedures in place to reduce the hazard posed by these weak points (disease points of entry: personnel, other poultry, vehicles, equipment, vermin)
2. Physical biosecurity: location, avoid putting birds on range, effective waste disposal, well-drained areas, ideal house design and site layout 3. Operational biosecurity: people (employees, servicemen, lorry drivers, vaccination crews), poultry (incoming poultry from high-health-status sources, multiage sites should be avoided, disposal of on farm deaths/culls), vehicles entering the site should be kept to minimum and visibly clean before entering, equipment (egg flats, trolleys and transport cages), feed, litter (fresh, dry, white wood shavings are preferred; straw can get contaminated and microbiological build-up can occur), water (control the risk of water-borne infections by choosing correct disinfectant), vermin, insects and beetles, wild birds, site decontamination. |
|
|
**Operational biosecurity**
|
Spans 2 distinct but overlapping areas of operation:
1. ongoing site security with procedures aimed at countering the effects of the hazard posted by the CCP's (critical control points) identified; this can involve vaccination programmes, medication strategies ,environmental control and management/husbandry activities. 2. relates to site decontamination or so-called terminal cleansing and disinfection; plays a major role in breaking the cycle of infection |
|
|
Disinfection procedures
|
1. selection of a disinfectant (consider: type of surface, water hardness, contact time, efficacy and efficiency, safety)
2. application of disinfectant 3. terminal disinfection of poultry houses (dry clean, sanitize the drinking water system, pre-clean the house or pen and equipment) 4. hatching and hatchery hygiene: success of hatching depends largely on the quality of the egg; egg hygiene starts at the farm-consideration should be give to next boxes and their management (cleaned and litter replaced regularly) |
|
|
免疫接种
|
1. 制定免疫程序时应考虑的主要因素:本地的疫情,母源抗体的影响,疫苗剂型(活苗或灭活苗,etc.)
2. 疫苗的运输与保管 3.疫苗的使用剂量 4.疫苗的稀释:稀释液应是清凉的 5.疫苗的接种途径(see next slide):操作上的失误,可造成免疫失败 6. 免疫效果的监测 7. 免疫失败原因分析(see slide after next) |
|
|
疫苗的接种途径
|
1.饮水(drinking water):疫苗应是高效的活毒疫苗,饲料中也不应含能灭活疫苗病毒和细菌的药物; 饮水中要加入0.1%的脱脂乳或山梨糖醇
2. 滴眼滴鼻(eye drop/intranasal route) 3. 肌肉或皮下注射(injection) 4. 气雾(spray):加入0.1%脱脂乳or3-5%甘油 5. 翼膜刺种(wing web):用于鸡痘疫苗的接种 6. 滴肛或擦肛:只用于强毒型传染性喉气管炎疫苗 7. In ovo: being used for the administration of MD and other live vaccines. Fertile chicken eggs are inoculated at 18 days on transfer to the hatchers. |
|
|
免疫失败原因
|
1. 疫苗质量不佳
2. 疫苗选择不当 3. 免疫程序不当 4. 疫苗稀释失误 5. 接种途径选择不当 6. 免疫接种时的错漏 7. 多种疫苗之间的干扰作用:传染性支气管炎疫苗and ND疫苗 8. 抗菌药物对弱毒活菌苗的作用 9. 免疫缺陷 10. 免疫麻痹:抗原量过多,超过一定的限度,抗体的形成反而受到抑制;叫“免疫麻痹” 11. 免疫抑制 12. 幼禽免疫器官未成熟 13. 机体的非特异性免疫功能的失常 14. 抗原的变异,超强毒株或新血清型的出现 |
|
|
新城疫(ND):亚洲鸡瘟
病原学 While lentogenic strains cause only a mild respiratory disease, mesogenic strains produce disease with moderate mortality. Velogenic strains cause severe respiratory disease, in combination with visceral haemorrhages, or neurological signs, and mortality up to 100% in chickens. |
1. NDV
2. 单股负链病毒目 3. 副黏病毒科(Paramyxoviridae) 4.病毒表面有纤突:血凝素神经氨酸酶 (Haemagglutinating and neuraminidase activity- HN) 和融合蛋白(Fusion protein-F) 5. 病毒分型:NVD属I型禽副黏病毒 6. NDV is also designtad APMV-I (Avian Paramyxovirus type I) 7.脑,肺,脾含病毒颗粒量最大 *Only 3 diseases have 血凝特性:AI, ND, EDSV (egg drop syndrome virus)* |
|
|
ND-流行病学
|
1.各种鸡均易感;鸡,火鸡,一些水禽
2.发病急,传播快 3.死亡率极高 4.人类感染后:眼结膜炎 5.冬季最为严重 6.传播方式(水平):消化道,呼吸道,结膜;无垂直传播 |
|
|
ND-临床症状:
1.最急性,急性,慢性型 2.美国的分型 3.典型和非典型新城疫 |
1.精神高度沉郁
2.呼吸困难 3.嗉囊积液,有波动感 4.倒提病鸡有大量酸臭液体从口中流出 5.下痢,粪便稀薄,黄绿色/黄白色 6.神经临诊症状明显 |
|
|
ND-特征性病理变化
|
1.食道和腺胃,腺胃和肌胃交界处可见出血带或出血斑
2.腺胃乳头出血 3.肠黏膜枣核样溃疡 4.盲肠,扁桃体出血,坏死 |
|
|
ND-(实验室)诊断和防止
|
1.临床调查:尤其免疫情况(是否失败)
2.临床症状,病变 3.病理分离鉴定 (virus isolation) 4.血清学试验(serological tests:ELISA,HI) 防制: 1. 抗体监测 2.选择合理免疫疫苗 |
|
|
禽流感-Avian Influenza AI
病原学 Only viruses of the Influenzavirus A genus are known to infect poultry |
A. 正黏病毒科(Orthomyxoviridae)流感病毒属(Influenzavirus)的A型流感病毒(Influenzavirus A)
B. 3 types of proteins: 1. 血凝素(Hemagglutinin HA):16 types;功能:吸附于靶细胞(target)上 2. 神经氨酸酶(neuraminidase NA):9types;功能:parts associated with liquefying mucus and helping to spread the influenza virus within the host 3.核蛋白和基质蛋白:功能:病毒颗粒复制 C. 单股负链RNA病毒,分8个节段 |
|
|
AIV 的核酸为什么易发生变异?
Viruses are differentiated based on how they reproduce within a cell. There are several types including single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses (ssRNA), single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses, double-stranded RNA viruses, retroviruses, and double-stranded DNA viruses. The animation shows reproduction of ssRNA viruses within a cell. This virion brings its own RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) into the cell; RdRp uses RNA as a template to make more RNA. In step 1, the viral RdRp uses the negative-sense RNA strand to make positive-sense single strands of RNA. These positive-sense strands of RNA are used as mRNA which act as the guide to make the structural proteins of the virion. That is shown in step 2. More viral RdRp, as well as structural proteins, are made (step 3). This RdRp helps to make a replicative complex and more positive-sense RNA. As shown in step 4, the positive-sense RNA acts as more mRNA or is used as a template to make more negative-sense RNA. The negative-sense RNA, viral RdRp, and structural proteins join together to form the final virions, shown in step 5. The virions exit the cell via budding or lysis (explosion of the cell). |
1.RNA viruses generally have very high mutation rates compared to DNA viruses, because viral RNA polymerases lack the proof-reading ability of DNA polymerases
2. The segmentation allows reassortment of genes to occur of 2 viruses infect and replicate within the same cell. |
|
|
AIV 的命名
A/equine/Prague/1/56 (H7N7) |
型别(type)
host 分离地点(the geographic origin) 毒株序号(the isolate/strain number) 分离年代(the year) HA和NA亚型(subtype) |
|
|
How to define AI strains based on degree of pathogenicity?
|
AI in its notifiable form (NAI) is defined as an infection of poultry caused by any influenza A virus of the H5 or H7 subtypes or by any AI virus with an intravenous pathogenicity index (IVPI) greater than 1.2 (or as an alternative at least 75% mortality) as described below. NAI viruses can be divided into HPNAI and LPNAI.
1-5只试验鸡死亡,在无被胰酶处理条件下可在细胞上生长,则需要测定amino acid sequence. |
|
|
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) 高致病力禽流感毒株
H5N1 most notorious strain |
HPNAI viruses have a IVPI in 6-week-old chickens greater than 1.2 or, as an alternative, cause at least 75% mortality in 4- to 8-week-old chickens infected intravenously. H5 and H7 viruses which do not have an IVPI of greater than 1.2 or cause less than 75% mortality in an intravenous lethality test should be sequenced to further determine whether the multiple basic amino acids are present at the cleavage site of the precursor HA molecule (HA0); if the amino acid motif is similar to that observed for other HPNAI isolates, the isolate being tested should be considered as HPNAI.
|
|
|
Low pathogenic avian influenza (LPAI) 低致病力病毒
H9N2 one of the other LPAI strains |
All influenza viruses of H5 and H7 subtype that are not HPNAI viruses.
|
|
|
AI-Epidemiology:hosts
|
水禽,natural host:鸭子(带菌,不表现症状)
易感动物:鸡,火鸡 其他:鸡-猪-人类 |
|
|
AI-Epidemiology-发病特点
|
养禽密度越高,传染率越高
水禽作为传播媒介 火禽交易也造成本病的传播 一年四季可流行,但以冬季为严重 传播方式:高度接触性的传染病:the feacal-oral route may be the main source of spread. |
|
|
AI-临床症状
|
H9N2:肺支气管有纤维素性渗透物,动物有时可堵死。
H5N1: 冠和肉髯发黑,羽毛蓬松无光泽,粪便黄绿色并带多量的黏液或血液,呼吸症状,可见的地方出血,多灶性坏死灶,在发病后的5-7天内死亡率几乎达到100%,少数病程较长或耐过未死的病鸡出现神经症状,鸡脚鳞片下呈紫红色或紫黑色。 |
|
|
AI-病理变化
|
大量出血:
腺胃与肌胃交界处,腺胃与食道交界处,肌胃角质膜下,喉气管黏膜充血 胰腺有坏死灶,心肌炎 |
|
|
AI-实验室诊断
|
分离病毒
琼扩试验 血凝抑制试验 |
|
|
Infectious Bronchitis-IB-传染性支气管炎
|
感染呼吸道 ,泌尿生殖
特征:咳嗽,喷嚏,气管啰音,呼吸道黏膜呈浆液性卡他性炎症 产蛋鸡:产蛋量减少,蛋白品质下降 |
|
|
IB-病原学
|
1.IBV
2.冠状病毒科(Coronoviridae),冠状病毒属 3.不分段的正链单股RNA(linear,single-stranded RNA virus of positive sense)-RNA病毒中最长的一种RNA病毒 |
|
|
IB-3种病毒特异性结构蛋白
|
纤突糖蛋白(S)
膜蛋白/基质糖蛋白(M) 核衣壳蛋白(N) 交叉保护较弱,血清型众多。 |
|
|
IB-病原学
|
1.IBV不能直接凝集鸡的RBC;需要经过1%胰酶/磷脂酶C在37度处理3h后,可具有血凝活性;这一活性能被特异性的抗血清所抑制
2. IBV能在10-11日日龄的发育鸡胚中生长 3. 将IBV野毒材料首次接种于鸡胚后,90%的胚仍能存活,少数出现生长退缓或矮小化 |
|
|
IB-流行病学
|
1.鸡:雏(chu2)鸡和产蛋鸡,《40日龄发病严重
2.传播方式:病鸡从呼吸道排毒 3.一年四季,冬,春寒冷季节严重 4.混合感染和饲料管理不当可诱发 |
|
|
IB-临床症状
5种类型 |
1.呼吸型
2.肾型 3.肌肉型 4.嗜肠型 5.腺胃型 |
|
|
IB-.呼吸型
|
发病突然
4周龄以下的幼鸡:伸颈,张口呼吸,咳嗽 2周龄以内的鸡:还有鼻窦肿胀,流鼻夜,流泪,频频甩头 气管和支气管有黏条状或干酪样渗出物 鼻腔及上部气管也可看到浆液或黏性渗出物 气囊混浊 支气管周围可见局灶型炎症 |
|
|
IB-肾型
|
发生于2-4周龄的鸡
典型病程有3个阶段: 1.轻微呼吸症状 2.病鸡表现康复 3.鸡群会突然发病:排出水样白色稀粪,内含大量尿酸盐 肾脏苍白,肿大,小叶突出,花斑肾 |
|
|
IB-肌肉型
|
精神沉郁
闭眼嗜睡 腹泻 鸡冠发绀 眼脸和下额肿胀 |
|
|
IB-实验室诊断为了确诊
|
病毒分离:接种于9-11日龄SPF鸡胚或非免疫健康鸡胚的尿囊腔内,收获尿囊液进行血清学或分子生物学检测。胚体矮小“侏儒胚”
病毒鉴定:干扰试验 IBV在鸡胚中能够干扰NDV-B1株产生血凝素。具体做法:取9-11日龄SPF或无母源抗体的鸡胚(embryonated chicken eggs)10-20只,分成两组。其中一组先通过尿囊腔内(allantoic cavity)接种经无菌处理的病料,没只鸡胚0.1ml,另一组作为对照,不接种。孵化10h后,两个组同时经尿囊腔接种含NDV-B1株的鸡胚尿囊液,每只鸡胚0.1ml。继续孵化36-48h后,把两组所有鸡胚置4度冰箱内4h以上,然后逐只收获并测定尿囊液的血凝效价。若病料中确实存在IBV,则该组鸡胚有50%以上的血凝效价在1:20以下,而对照组的鸡胚则有90%以上的血凝效价在1:40或以上。 |
|
|
IB-防制
|
1. Attention to management factors (temp and ventilation) are essential in controlling the effects of secondary bacterial infection
2. Vaccination: Live attenuated and inactivated (oil-adjuvanted) vaccines are highly effective and widely used; to achieve optimal benefit from the inactivated vaccine, at least 4-6 weeks should elapse between the last application of live vaccines and administration of the inactivated vaccine. |
|
|
Infectious Laryngotracheitis-ILT-传染性喉气管炎
|
ILTV:疱疹病毒科(Herpesviridae),alpha-型疱疹病毒亚科(Alphaherpesvirinae),ILTV属禽疱疹病毒I型(Gallid herpesvirus 1)
双链DNA病毒:基因组长度约为155kb 只有一个血清型,但不同毒株的毒力不同 |
|
|
ILT-病原学
|
1.适宜在鸡胚中增殖,接种10日龄鸡胚绒毛尿囊膜(chorioallantoic membrane),鸡胚2-9d后死亡。
2.胚体变小,鸡胚绒毛尿囊膜增生和坏死,形成不透明的边缘隆起,灰白色,中心凹陷的痘斑样坏死灶。 |
|
|
ILT-流行病学
|
鸡,育成鸡和成年产蛋鸡
麻雀等不易感 传播方式:呼吸道及眼感染,消化道 Virus enters the bird in infective droplets or mucus via the upper respiratory tract and conjunctiva and remains confined to the respiratory tract. It is shed mainly in exudates from the nares, oropharynx, trachea and conjunctiva and is transmitted in aerosol or expectorant form (blood and mucus). Among recovered birds and even birds given attenuated live vaccines, the virus can become latent and the birds become carriers. 鸡群发病后可获得较坚强的保护力,但康复鸡的带毒和排毒可称为易感鸡群发生本病的主要传染源 |
|
|
ILT-临床症状:
1.急性型(喉气管型) 2.温和型 |
1. 伸颈张口吸气,低头缩颈呼气 dyspnoea, increasing obstruction of the trachea with exudate causes the bird to breathe with long-drwan-out gasps, with a wide-open beak and often a high-pitched squawk, and invariably moist rales can be heard.
产蛋量下降,幅度可达35%或停产 病理变化: 初期-喉头气管黏膜肿胀,充血,出血,甚至坏死,喉头气管可见带血样分泌物或条状血凝块。The mucosa of the respiratory tract shows an inflammatory response and necrosis, with or without hemorrhage. Mucus and other exudates frequently cause an (partially) obstructive plug in the laryngeal and syrinx regions. |
|
|
ILT-诊断
|
病毒分离与鉴定:
1.鸡胚接种 2.包涵体的检查:在发病早期(1-5d),取发病鸡气管,喉头,眼结膜上皮细胞,经Giemsa stain-核内嗜酸性包涵体。后期上皮细胞脱落,查不到包涵体。 3.细胞培养:inoculation on preformed monolayers of chick embryo kidney cell cultures causes syncytium formation (multinucleated cells) after several days. 4.病毒中和试验 动物接种 血清学诊断 分子生物学方法 鉴别诊断:黏膜型鸡痘(隆起的单个或融合在一起的灰白色痘斑),VitA def(白色小结或覆盖有一层白色的豆腐渣样的薄膜,剥离后黏膜完整) |
|
|
ILT-防制
|
1. Improve management practices and increase biosecurity
2. In areas where the disease has not yet occurred and there is no imminent threat, vaccination is discouraged. In other circumstances, vaccination would be of value using live vaccines. 首免:30-60riling 二免:首免后6周 种鸡,蛋鸡在开产前20-30d再接种1次。 |
|
|
Infectious Bursal Disease IBD-传染性法氏囊病
Gumboro Disease-甘保罗病 bursa of Fabricius enlarges at first and later bursa becomes smaller |
发病率高
腹泻 腿肌和胸肌出血 导致免疫抑制,使鸡对多种疫苗的免疫应答下降,造成免疫失败,使鸡群对其他病原体的易感性增加 |
|
|
IBD-病原学
|
1. IBDV属于双RNA病毒科(Birnaviridae),禽双RNA病毒属(Avibirnavirus genus)
2. 分节段的RNA,分A,B两个节段 3. 5种主要蛋白VP1-VP5;VP2是IBDV最重要的结构蛋白(抗原,变异主要发生在VP2上) 4. 两种血清型:I 和 II 5. 在外界环境下极为稳定 |
|
|
IBD-流行病学
|
3-6周龄的鸡对本病最易感
病鸡和带毒鸡是重要传染源 直接接触传播:饲料,饮水 |
|
|
IBD-临床症状
1.典型感染(new endemic areas) 2.非典型感染(old endemic areas) target cells of IBDV are B-lymphocytes in the bursa |
潜伏期:2-3d
初期:有些鸡啄自己的池殖腔 羽毛蓬松 ruffled feathers 白色黏稠或水样稀粪 |
|
|
IBD-病理变化
|
1.脱水明显
2.胸肌,腿肌有出血点 3.特征:法氏囊肿大,出血和水肿,体积增大,重量增加,是正常的2-3倍,囊壁增厚3-4倍,质地变硬,外形变圆,黏膜皱褶上有出血点或出血斑,渗出液呈淡粉红色。 |
|
|
IBD-诊断
|
In most cases, the history, clinical signs and gross lesions are adequate for recognition of acute disease.
血清学试验:琼脂扩散试验,ELISA |
|
|
IBD-防制
MDA:Maternally derived antibody |
活苗,灭活苗
Young chicks with maternally derived antibody are immune to infection while antibodies are high (passive immunity) but become susceptible when titres drop. vvIBDVs appear to be capable of breaking through MDA at an earlier age. A satisfactory level of protection of protection can be induced either passively by immunizing parent flocks with inactivated vaccines or actively by immunizing the chick with live vaccines given in the drinking water. Ideal vaccine: not cause disease/bursal lesions, not be immunosuppressive, must confer long-lasting immunity even in birds with a high level of maternal immunity. Inactivated vaccines produce high, uniform and long-lasting antibody titres prior to lay in hens that have been vaccinated with a live virus; are administered 16-20 weeks in order to transmit high levels of MDA to progeny; but progeny could no longer be passively protected during entire fattening process (vvIBDV) and live vaccination became necessary. Therefore, interference of MDA with vaccination has become the key issue and serological monitoring us necessary to determine optimal timing for vaccination. Live IBD vaccines: mild, intermediate and hot strains. The hot strains induce, in SPF chickens, histological lesions comparable to those caused by pathogenic strains, the only difference being that they do not cause mortality. Mild vaccine strains that cause no bursal lesions cannot be used effectively in chicks with MDA until about 4 weeks of age as they are neutralized. |

